Abstract
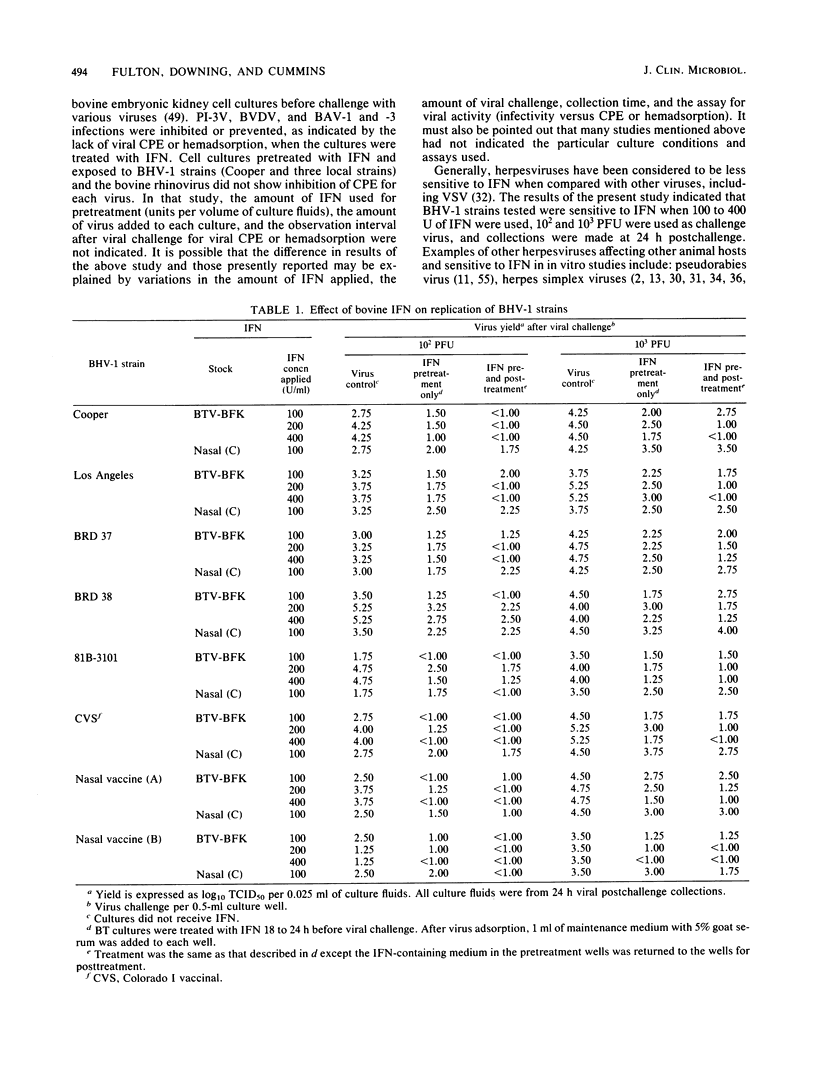
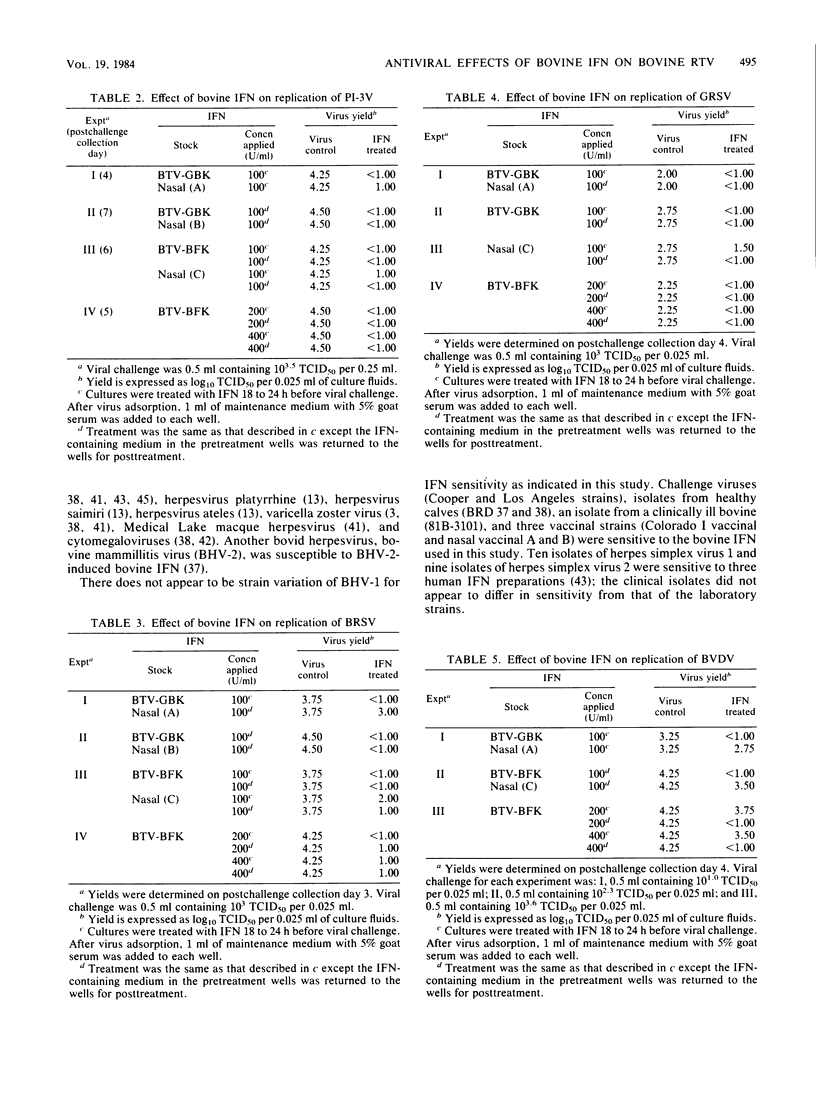
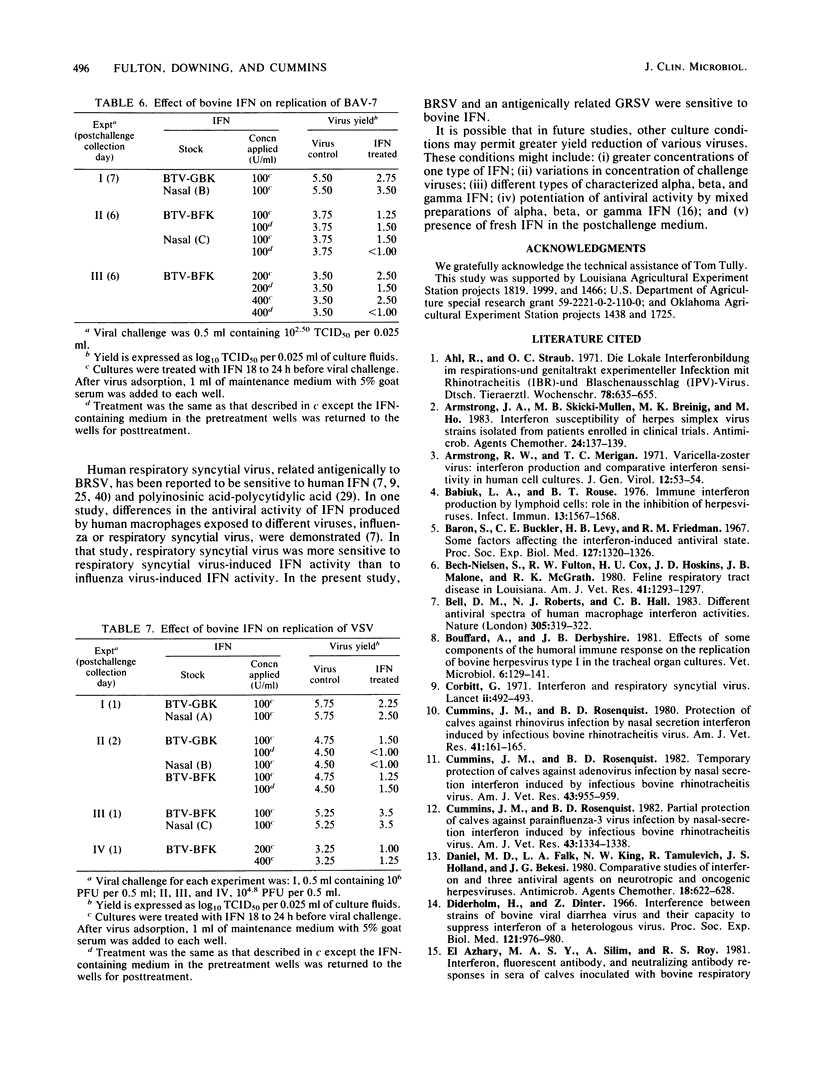
The antiviral effects of bovine interferons on the replication of bovine respiratory tract viruses were studied. Bovine turbinate monolayer cultures were treated with bovine interferons and challenged with several bovine herpesvirus 1 strains, bovine viral diarrhea virus, parainfluenza type 3 virus, goat respiratory syncytial virus, bovine respiratory syncytial virus, bovine adenovirus type 7, or vesicular stomatitis virus. Treatment with bovine interferons reduced viral yield for each of these viruses as compared with that of control cultures.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahl R., Straub O. C. Die lokale Interferonbildung im Respirations- und Genitaltrakt nach experimenteller Infektion mit Rhinotracheitis (IBR)- und Bläschenausschlag (IPV)-Virus. Dtsch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1971 Dec 15;78(24):653–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. A., Skicki-Mullen M. B., Breinig M. K., Ho M. Interferon susceptibility of herpes simplex virus strains isolated from patients enrolled in clinical trials. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jul;24(1):137–139. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong R. W., Merigan T. C. Varicella zoster virus: interferon production and comparative interferon sensitivity in human cell cultures. J Gen Virol. 1971 Jul;12(1):53–54. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-12-1-53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babiuk L. A., Rouse B. T. Immune interferon production by lymphoid cells: role in the inhibition of herpesviruses. Infect Immun. 1976 Jun;13(6):1567–1578. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.6.1567-1578.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron S., Buckler C. E., Levy H. B., Friedman R. M. Some factors affecting the interferon-induced antiviral state. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Aug-Sep;125(4):1320–1326. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bech-Nielsen S., Fulton R. W., Cox H. U., Hoskins J. D., Malone J. B., Jr, McGrath R. K. Feline respiratory tract disease in Louisiana. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Aug;41(8):1293–1298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell D. M., Roberts N. J., Jr, Hall C. B. Different antiviral spectra of human macrophage interferon activities. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):319–321. doi: 10.1038/305319a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbitt G. Interferon and respiratory syncytial virus. Lancet. 1971 Aug 28;2(7722):492–493. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92660-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummins J. M., Rosenquist B. D. Partial protection of calves against parainfluenza-3 virus infection by nasal-secretion interferon induced by infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Aug;43(8):1334–1338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummins J. M., Rosenquist B. D. Protection of calves against rhinovirus infection by nasal secretion interferon induced by infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Feb;41(2):161–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummins J. M., Rosenquist B. D. Temporary protection of calves against adenovirus infection by nasal secretion interferon induced by infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Jun;43(6):955–959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel M. D., Falk L. A., King N. W., Tamulevich R., Holland J. S., Bekesi J. G. Comparative studies of interferon and three antiviral agents on neurotropic and oncogenic herpesviruses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Oct;18(4):622–628. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.4.622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diderholm H., Dinter Z. Interference between strains of bovine virus diarrhea virus and their capacity to suppress interferon of a heterologous virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Mar;121(3):976–980. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmann W. R., Jr, Georgiades J. A., Osborne L. C., Johnson H. M. Potentiation of interferon activity by mixed preparations of fibroblast and immune interferon. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):248–253. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.248-253.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman A. J., Babiuk L. A., Misra V., Baldwin F. Susceptibility of bovine macrophages to infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus infection. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1048–1057. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1048-1057.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton R. W., Downing M. M., Hagstad H. V. Prevalence of bovine herpesvirus-1, bovine oral diarrhea, parainfluenza-3, bovine adenoviruses-3 and -7, and goat respiratory syncytial viral antibodies in goats. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Aug;43(8):1454–1457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton R. W., Pearson N. J. Interferon induction in bovine and feline monolayer cultures by four bluetongue virus serotypes. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Jan;46(1):100–102. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton R. W., Pearson N. J. Interferon production by bovine tracheal organ cultures infected with bovid herpesvirus 1 strains. Can J Comp Med. 1980 Oct;44(4):447–452. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton R. W., Root S. K. Antiviral activity in interferon-treated bovine tracheal organ cultures. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):672–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.672-673.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton R. W., Rosenquist B. D. In vitro interferon production by bovine tissues: induction with infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus. Am J Vet Res. 1976 Dec;37(12):1497–1502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher J. G., Khoobyarian N. Adenovirus susceptibility to human interferon during one-step replication. Infect Immun. 1972 Jun;5(6):905–908. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.6.905-908.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner P. S., McGuckin R., Beale A., Fernandes R. Interferon and respiratory syncytial virus. Lancet. 1970 Mar 14;1(7646):574–575. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90821-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber J. D., Marron A. E., Kucera C. J. Local and systemic cellular and antibody immune responses of cattle to infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus vaccines administered intranassally or intramuscularly. Am J Vet Res. 1978 May;39(5):753–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallum J. V., Thacore H. R., Youngner J. S. Factors affecting the sensitivity of different viruses to interferon. J Virol. 1970 Aug;6(2):156–162. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.2.156-162.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon M. W., Greenberg S. B., Johnson P. E. Rapid onset of the interferon-induced antiviral state in human nasal epithelial and foreskin fibroblast cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1980 Jun;164(2):146–152. doi: 10.3181/00379727-164-40838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. A., Baron S., Chanock R. M. Sensitivity of common respiratory viruses to an interferon inducer in human cells. Lancet. 1969 Jul 26;2(7613):187–188. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91425-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imanishi J., Matsubara M., Kishida T., Ozaki Y., Kurimura T. Comparative studies on the inhibitory effects of interferon on various strains of herpes simplex viruses in vitro. Biken J. 1980 Sep;23(3):107–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janz C., Wigand R. Combined interaction of antiherpes substances and interferon beta on the multiplication of herpes simplex virus. Arch Virol. 1982;73(2):135–143. doi: 10.1007/BF01314722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern E. R., Glasgow L. A. Effect of interferon on systemic herpesvirus infections. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1977;35:472–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lab M., Koehren F. Maintenance and recovery of the interferon-induced antiviral state. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Oct;153(1):112–115. doi: 10.3181/00379727-153-39491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar R., Breinig M. K., Armstrong J. A., Ho M. Response of cloned progeny of clinical isolates of herpes simplex virus to human leukocyte interferon. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):708–712. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.708-712.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmkuhl H. D., Gough P. M., Reed D. E. Characterization and identification of a bovine respiratory syncytial virus isolated from young calves. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Jan;40(1):124–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner A. M., Bailey E. J. Differential sensitivity of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 to human interferon: antiviral effects of interferon plus 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine. J Infect Dis. 1976 Oct;134(4):400–404. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.4.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letchworth G. J., 3rd, Carmichael L. E. Production of interferon by bovine peripheral blood monocytes infected with bovid herpesvirus 2. Vet Microbiol. 1983 Feb;8(1):69–80. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(83)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin M. J., Leary P. L. Inhibition of human herpesviruses by combination of acyclovir and human leukocyte interferon. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):995–999. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.995-999.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLachlan N. J., Rosenquist B. D. Duration of protection of calves against rhinovirus challenge exposure by infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus-induced interferon in nasal secretions. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Feb;43(2):289–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring J. M., Forsyth B. R. The role of the interferon system in respiratory syncytial virus infections. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Dec;138(3):1009–1014. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-36039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann-Haefelin D., Sundmacher R., Sauter B., Karges H. E., Manthey K. F. Effect of human leukocyte interferon on vaccinia-and herpes virus-infected cell cultures and monkey corneas. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):148–155. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.148-155.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oie H. K., Easton J. M., Ablashi D. V., Baron S. Murine cytomegalovirus: induction of and sensitivity to interferon in vitro. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1012–1017. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1012-1017.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overall J. C., Jr, Yeh T. J., Kern E. R. Sensitivity of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 to three preparations of human interferon. J Infect Dis. 1980 Dec;142(6):943–943. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.6.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen L., Farley L. B. Inhibition of Herpesvirus hominis replication by human interferon. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):104–108. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.104-108.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenquist B. D., Loan R. W. Interferon induction in the bovine species by infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus. Am J Vet Res. 1969 Aug;30(8):1305–1312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenquist B. D., Loan R. W. Interferon production with strain SF-4 of parainfluenza-3 virus. Am J Vet Res. 1967 May;28(124):619–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenquist B. D., Loan R. W. Production of circulating interferon in the bovine species. Am J Vet Res. 1969 Aug;30(8):1293–1303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savan M., Angulo A. B., Derbyshire J. B. Interferon, antibody responses and protection induced by an intranasal infectious bovine rhinotracheitis vaccine. Can Vet J. 1979 Aug;20(8):207–210. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smorodintsev A. A. The production and effect of interferon in organ cultures of calf trachea. Br J Exp Pathol. 1968 Oct;49(5):511–515. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. E., 2nd, Lockart R. Z., Jr Relative antiviral resistance induced in homologous and heterologous cells by cross-reacting interferons. J Virol. 1970 Dec;6(6):795–799. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.6.795-799.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straub C., Ahl R. Lokale Interferonbildung beim Rind nach intranasaler Infektion mit avirulentem IBR/IPV-Virus und deren Wirkung auf eine anschlie Bende Infektion mit Maul-und Klauenseuche-virus. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1976 Jun;23(5-6):470–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. D., Volenec F. J., Paton I. M. Interferon in nasal secretions and sera of calves after intranasal administration of avirulent infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus: association of interferon in nasal secretions with early resistance to challenge with virulent virus. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):699–706. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.699-706.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trueblood M. S., Manjara J. Response of bovine viruses to interferon. Cornell Vet. 1972 Jan;62(1):3–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vengris V. E., Maré C. J. Swine interferon. I. Induction in porcine cell cultures with viral and synthetic inducers. Can J Comp Med. 1972 Jul;36(3):282–287. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Thacore H. R., Kelly M. E. Sensitivity of ribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleic acid viruses to different species of interferon in cell cultures. J Virol. 1972 Aug;10(2):171–178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.2.171-178.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zygraich N., Lobmann M., Vascoboinic E., Berge E., Huygelen C. In vivo and in vitro properties of a temperature sensitive mutant of infectious bovine Rhinotracheitis virus. Res Vet Sci. 1974 May;16(3):328–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



