Abstract
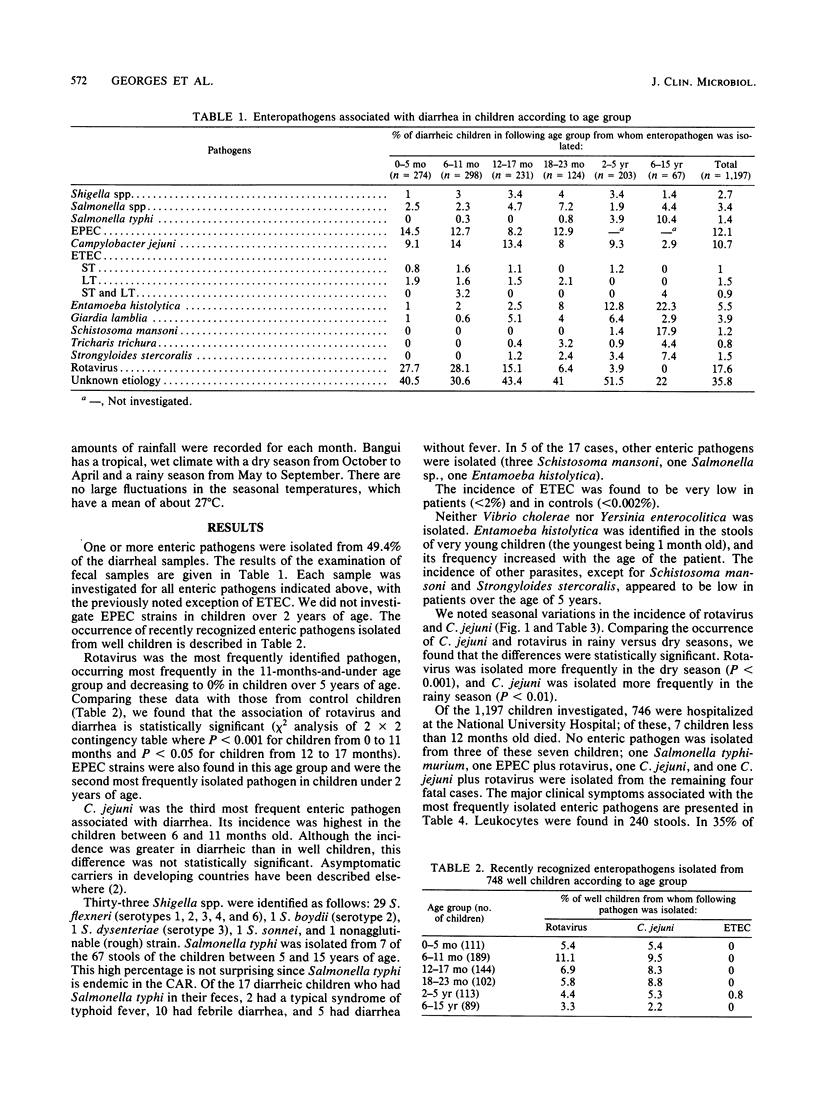
A total of 1,197 diarrheic children less than 15 years old were investigated for parasitic, bacterial, and viral enteropathogens from March 1981 through February 1982 in the Central African Republic. One or more pathogens were identified from 49.4% of the patients. Rotavirus was the most frequently identified pathogen among children less than 18 months old. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli was the second most frequently isolated pathogen (12.1%) in children less than 2 years of age. Campylobacter jejuni was also isolated frequently from diarrheic children less than 5 years of age (10.9%). Entamoeba histolytica was identified in very young children and was found to be the most frequent enteropathogen associated with diarrhea in children over the age of 2 years. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli was rarely isolated (ca. 2%). There was a peak in the incidence of rotavirus during the dry season and in the incidence of Campylobacter jejuni during the rainy season.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Black R. E., Merson M. H., Rahman A. S., Yunus M., Alim A. R., Huq I., Yolken R. H., Curlin G. T. A two-year study of bacterial, viral, and parasitic agents associated with diarrhea in rural Bangladesh. J Infect Dis. 1980 Nov;142(5):660–664. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.5.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Glass R. I., Huq M. I., Stoll B., Kibriya G. M., Alim A. R. Isolation of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni from Bangladeshi children. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):744–747. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.744-747.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis. Clin Gastroenterol. 1979 Sep;8(3):737–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruickshank J. G., Zilberg G. Winter diarrhoea and rotaviruses in Rhodesia. S Afr Med J. 1976 Nov 6;50(47):1895–1896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson G. P., Bishop R. F., Townley R. R., Holmes I. H. Importance of a new virus in acute sporadic enteritis in children. Lancet. 1975 Feb 1;1(7901):242–246. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dossetor J. F., Chrystie I. L., Totterdell B. M. Rotavirus gastro-enteritis in northern Nigeria. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1979;73(1):115–116. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(79)90144-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Blacklow N. R., Vollet J. L., 3rd, Ulyangco C. V., Cukor G., Soriano V. B., DuPont H. L., Cross J. H., Orskov F., Orskov I. Reovirus-like agent and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infections in pediatric diarrhea in the Philippines. J Infect Dis. 1978 Sep;138(3):326–332. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.3.326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georges M. C., Wachsmuth I. K., Birkness K. A., Moseley S. L., Georges A. J. Genetic probes for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from childhood diarrhea in the Central African Republic. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):199–202. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.199-202.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Kim H. W., Wyatt R. G., Cline W. L., Arrobio J. O., Brandt C. D., Rodriguez W. J., Sack D. A., Chanock R. M., Parrott R. H. Human reovirus-like agent as the major pathogen associated with "winter" gastroenteritis in hospitalized infants and young children. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 29;294(18):965–972. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604292941801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koornhof H. J., Robins-Browne R. M., Richardson N. J., Cassel R. Etiology of infantile enteritis in South Africa. Isr J Med Sci. 1979 Apr;15(4):341–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merson M. H., Sack R. B., Kibriya A. K., Al-Mahmood A., Adamed Q. S., Huq I. Use of colony pools for diagnosis of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Apr;9(4):493–497. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.4.493-497.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Huq I., Alim A. R., So M., Samadpour-Motalebi M., Falkow S. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by DNA colony hybridization. J Infect Dis. 1980 Dec;142(6):892–898. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.6.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutanda L. N. Epidemiology of acute gastroenteritis in early childhood in Kenya. VI. Some clinical and laboratory characteristics relative to the aetiological agents. East Afr Med J. 1980 Sep;57(9):599–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paniker C. K., Mathew S., Mathan M. Rotavirus and acute diarrhoeal disease in children in a southern Indian coastal town. Bull World Health Organ. 1982;60(1):123–127. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul M. O., Erinle E. A. Influence of humidity on rotavirus prevalence among Nigerian infants and young children with gastroenteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):212–215. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.212-215.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland M. G., McCollum J. P. Malnutrition and gastroenteritis in The Gambia. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1977;71(3):199–203. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(77)90006-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder R. W., Sack D. A., Kapikian A. Z., McLaughlin J. C., Chakraborty J., Mizanur Rahman A. S., Merson M. H., Wells J. G. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and Reovirus-like agent in rural Bangladesh. Lancet. 1976 Mar 27;1(7961):659–663. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92776-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis: a "new" disease. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 2;2(6078):9–11. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6078.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stintzing G., Bäck E., Tufvesson B., Johnsson T., Wadström T., Habte D. Seasonal fluctuations in the occurrence of enterotoxigenic bacteria and rotavirus in paediatric diarrhoea in Addis Ababa. Bull World Health Organ. 1981;59(1):67–73. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teesdale C. H., Amin M. A. Comparison of the Bell technique, a modified Kato thick smear technique, and a digestion method for the field diagnosis of schistosomiasis mansoni. J Helminthol. 1976 Mar;50(1):17–20. doi: 10.1017/s0022149x00028777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toledo M. R., Alvariza M. do C., Murahovschi J., Ramos S. R., Trabulsi L. R. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli serotypes and endemic diarrhea in infants. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):586–589. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.586-589.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. A., Warren K. S. Selective primary health care: an interim strategy for disease control in developing countries. N Engl J Med. 1979 Nov 1;301(18):967–974. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197911013011804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Kim H. W., Clem T., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for detection of human reovirus-like agent of infantile gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1977 Aug 6;2(8032):263–267. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90951-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


