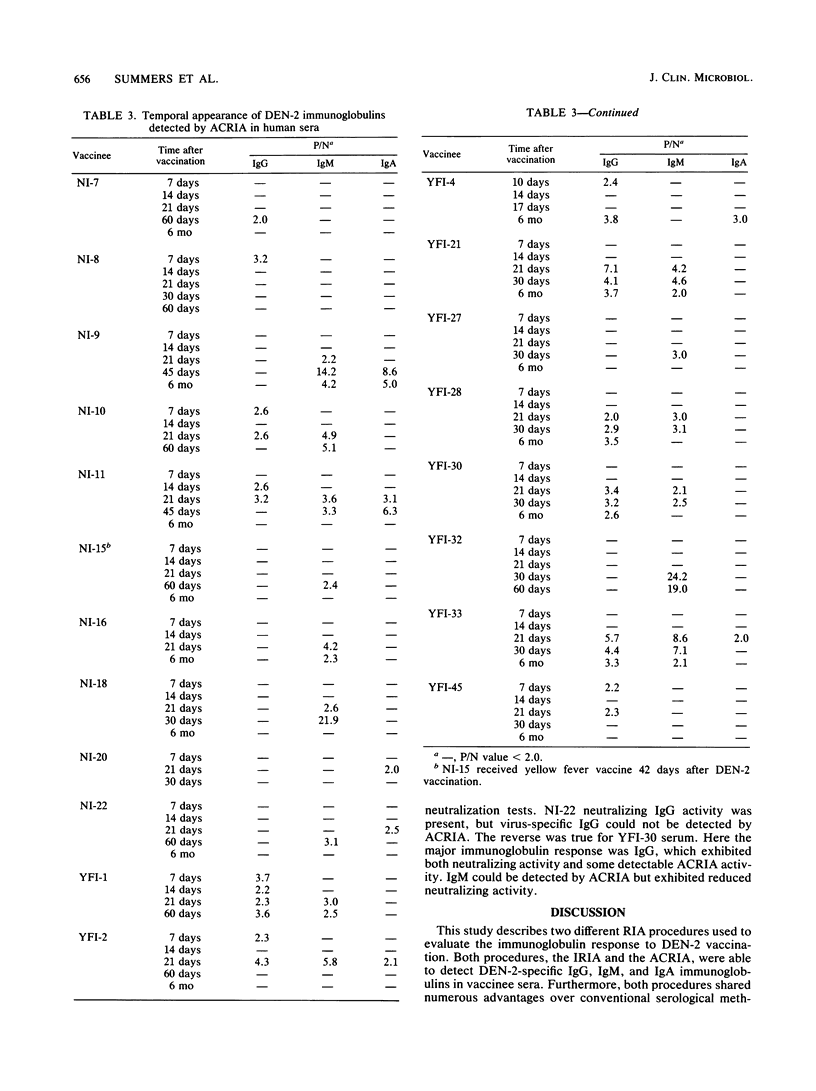
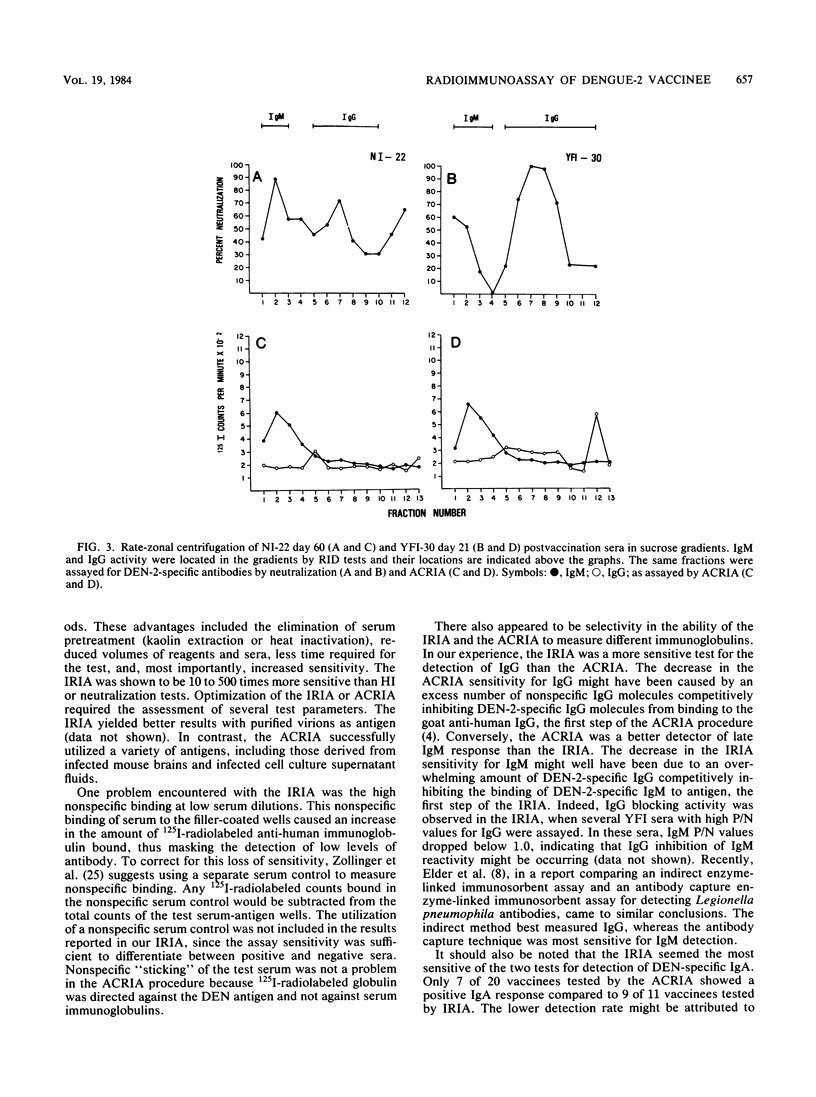
Abstract
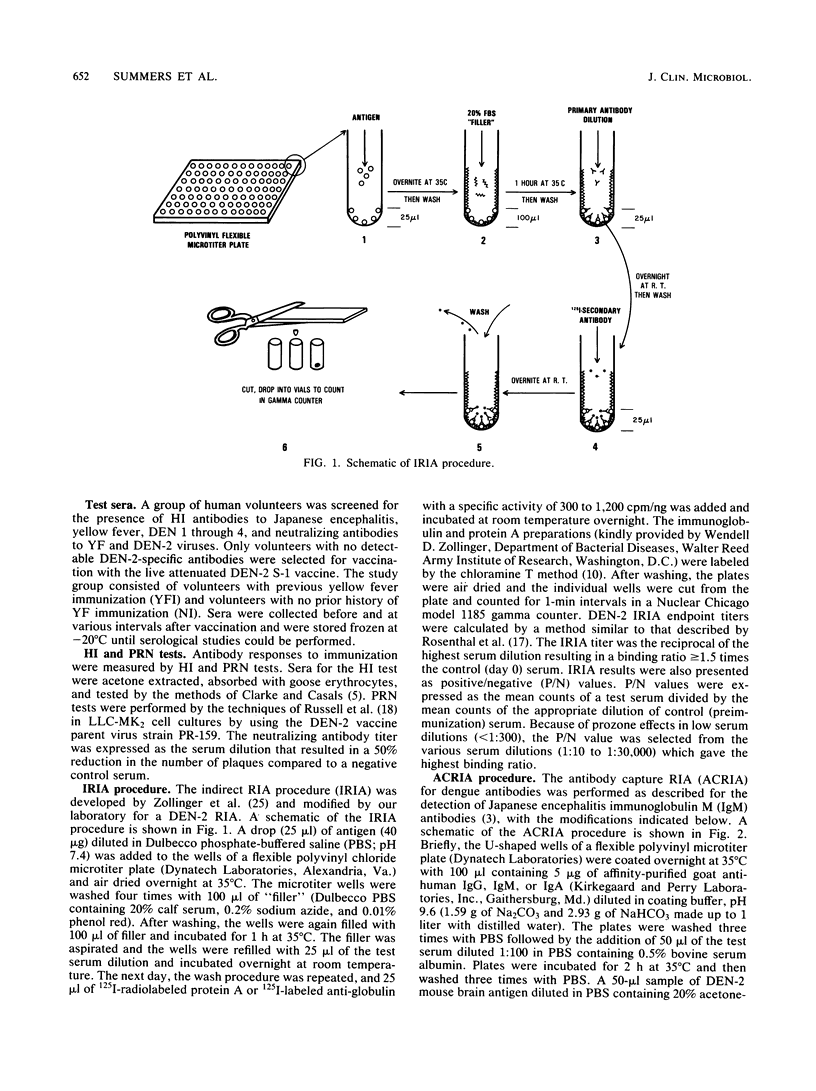
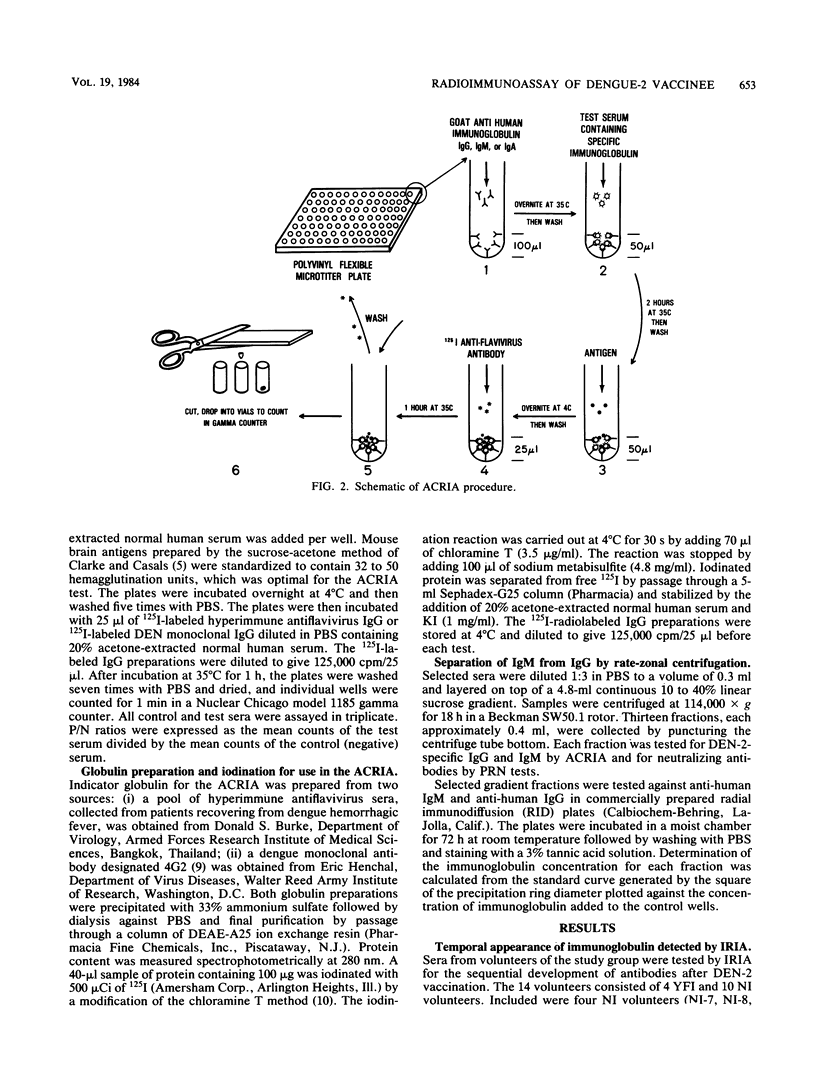
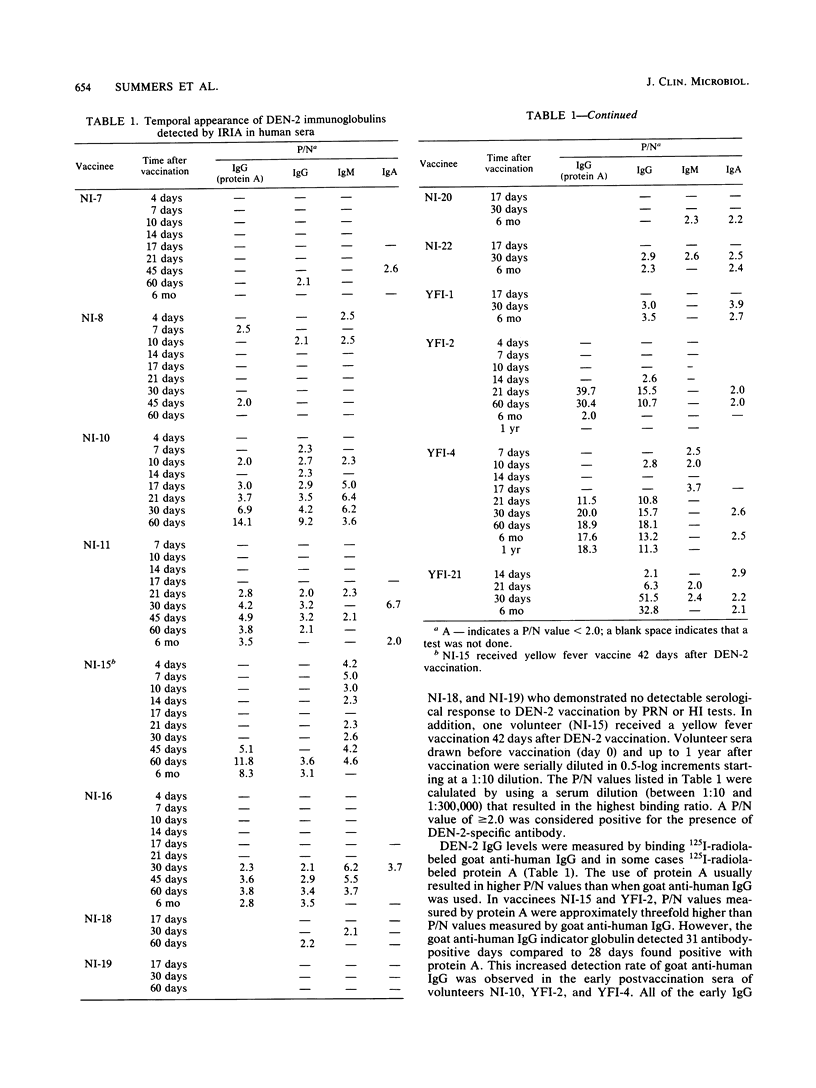
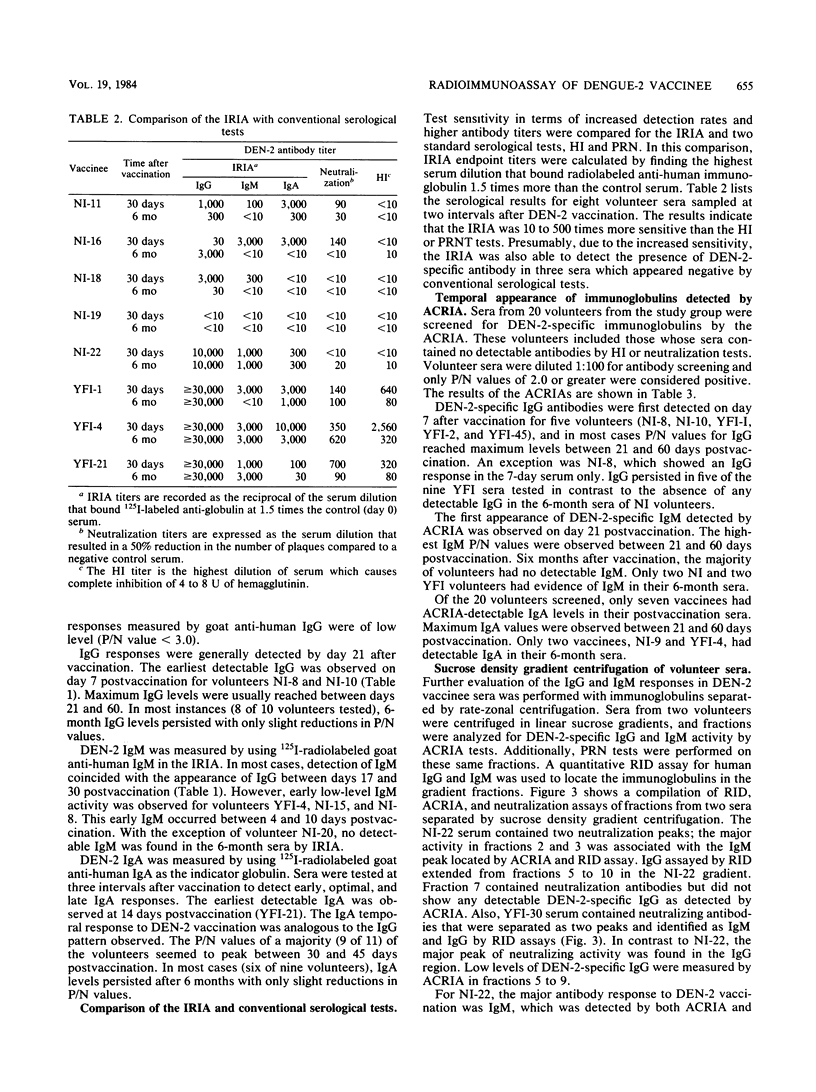
Two different radioimmunoassays were used to detect virus-specific antibodies in sera from human volunteers inoculated with an attenuated dengue type 2 (DEN-2) vaccine (PR-159/S-1). An indirect radioimmunoassay required purified DEN-2 virions for optimal reactivity but was 10 to 500 times more sensitive than neutralization or hemagglutination inhibition tests. An antibody capture radioimmunoassay was able to utilize crude antigens from either DEN-infected mouse brains or Aedes albopictus cell culture supernatants. When the two radioimmunoassay techniques were compared, the indirect method appeared to be the best assay for immunoglobulin G (IgG), whereas the antibody capture method was more sensitive for IgM detection. Selected human sera were examined for IgG, IgM, and IgA responses by using both techniques at various intervals after immunization. Although there were differences in magnitude, yellow fever immune as well as flavivirus nonimmune volunteers responded to DEN-2 vaccination by demonstrating IgG, IgM, and IgA antibody responses. In the nonimmune group, the most prevalent immunoglobulin detected was IgM, whereas in the yellow fever immune group, the predominant post-DEN-2 vaccine immunoglobulin was IgG. The preponderance of DEN-2-specific neutralizing antibodies were associated with either IgM or IgG according to the immune status of the volunteer. All classes of immunoglobulins attained maximum levels between 21 and 60 days postvaccination. In the majority of volunteers, IgM responses were relatively transient and could not be detected 6 months after immunization, whereas IgG and IgA antibodies were still detectable after this period.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bancroft W. H., Top F. H., Jr, Eckels K. H., Anderson J. H., Jr, McCown J. M., Russell P. K. Dengue-2 vaccine: virological, immunological, and clinical responses of six yellow fever-immune recipients. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):698–703. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.698-703.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt W. E., Buescher E. L., Hetrick F. M. Production and characterization of arbovirus antibody in mouse ascitic fluid. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1967 May;16(3):339–347. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1967.16.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. S., Nisalak A. Detection of Japanese encephalitis virus immunoglobulin M antibodies in serum by antibody capture radioimmunoassay. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Mar;15(3):353–361. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.3.353-361.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. S., Nisalak A., Ussery M. A. Antibody capture immunoassay detection of japanese encephalitis virus immunoglobulin m and g antibodies in cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Dec;16(6):1034–1042. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.6.1034-1042.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE D. H., CASALS J. Techniques for hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition with arthropod-borne viruses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Sep;7(5):561–573. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DORRANCE W. R., FRANKEL J. W., GORDON I., PATTERSON P. R., SCHLESINGER R. W., WINTER J. W. Clinical and serologic response of man to immunization with attenuated dengue and yellow fever viruses. J Immunol. 1956 Nov;77(5):352–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckels K. H., Harrison V. R., Summers P. L., Russell P. K. Dengue-2 vaccine: preparation from a small-plaque virus clone. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):175–180. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.175-180.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman R., Nisalak A., Pariyanonda A., Udomsakdi S., Johnsen D. O. Immunoglobulin response and viremia in dengue-vaccinated gibbons repeatedly challenged with Japanese encephalitis virus. Am J Epidemiol. 1973 Mar;97(3):208–218. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder E. M., Brown A., Remington J. S., Shonnard J., Naot Y. Microenzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin M antibodies to Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):112–121. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.112-121.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry M. K., Henchal E. A., McCown J. M., Brandt W. E., Dalrymple J. M. Identification of distinct antigenic determinants on dengue-2 virus using monoclonal antibodies. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1982 May;31(3 Pt 1):548–555. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1982.31.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMMON W. M., RUDNICK A., SATHER G. E. Viruses associated with epidemic hemorrhagic fevers of the Philippines and Thailand. Science. 1960 Apr 15;131(3407):1102–1103. doi: 10.1126/science.131.3407.1102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOTTA S. Experiments of active immunization against dengue with mouse-passaged unmodified virus. Acta Trop. 1954;11(2):97–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornsleth A., Leerhoy J., Grauballe P., Spanggaard H. Persistence of rubellavirus-specific immunoglobulin M and immunoglobulin A antibodies: investigation of successive serum samples with lowered immunoglobulin G concentration. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):804–808. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.804-808.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Matsuno S., Kono R., Sangkawibha N., Thongcharoen P. Hemagglutination-inhibiting immunoglobulin A antibody in the serum of patients with dengue hemorrhagic fever. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1980 Jun;33(3):181–184. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.33.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii K., Matsunaga Y., Kono R. Immunoglobulins produced in response to Japanese encephalitis virus infections of man. J Immunol. 1968 Oct;101(4):770–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monath T. P. Neutralizing antibody responses in the major immunoglobulin classes to yellow fever 17D vaccination of humans. Am J Epidemiol. 1971 Feb;93(2):122–129. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal J. D., Hayashi K., Notkins A. L. Rapid micro-radioimmunoassay for the measurement of antiviral antibody. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):171–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P. K., Nisalak A., Sukhavachana P., Vivona S. A plaque reduction test for dengue virus neutralizing antibodies. J Immunol. 1967 Aug;99(2):285–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin A. B., Schlesinger R. W. PRODUCTION OF IMMUNITY TO DENGUE WITH VIRUS MODIFIED BY PROPAGATION IN MICE. Science. 1945 Jun 22;101(2634):640–642. doi: 10.1126/science.101.2634.640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. M., Eckels K. H., Bancroft W. H., Summers P. L., McCown J. M., Anderson J. H., Russell P. K. Dengue 2 vaccine: dose response in volunteers in relation to yellow fever immune status. J Infect Dis. 1983 Dec;148(6):1055–1060. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.6.1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway E. G., Della-Porta A. J., Reedman B. M. Specificity of IgM and IgG antibodies after challenge with antigenically related togaviruses. J Immunol. 1974 Feb;112(2):656–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway E. G. Greater specificity of 19S than 7S antibodies on haemagglutination-inhibition tests with closely related group B arboviruses. Nature. 1968 Jul 6;219(5149):78–79. doi: 10.1038/219078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Dalrymple J. M., Artenstein M. S. Analysis of parameters affecting the solid phase radioimmunoassay quantitation of antibody to meningococcal antigens. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):1788–1798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


