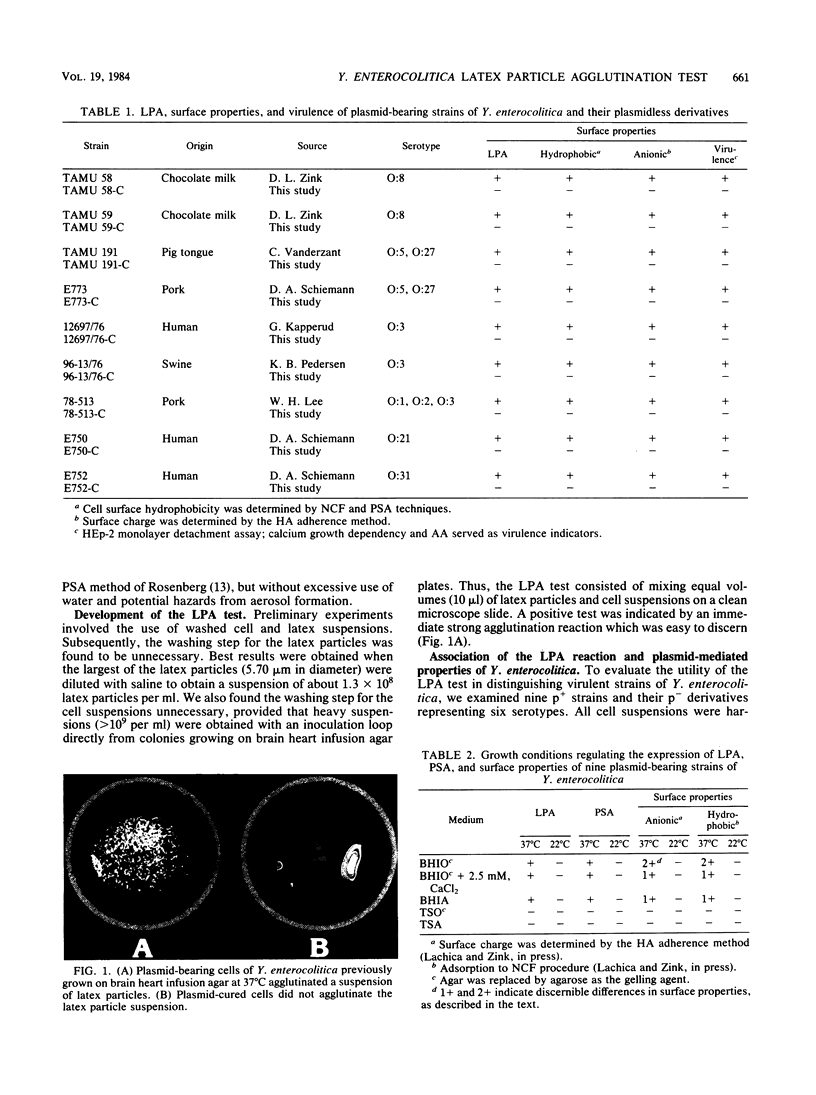
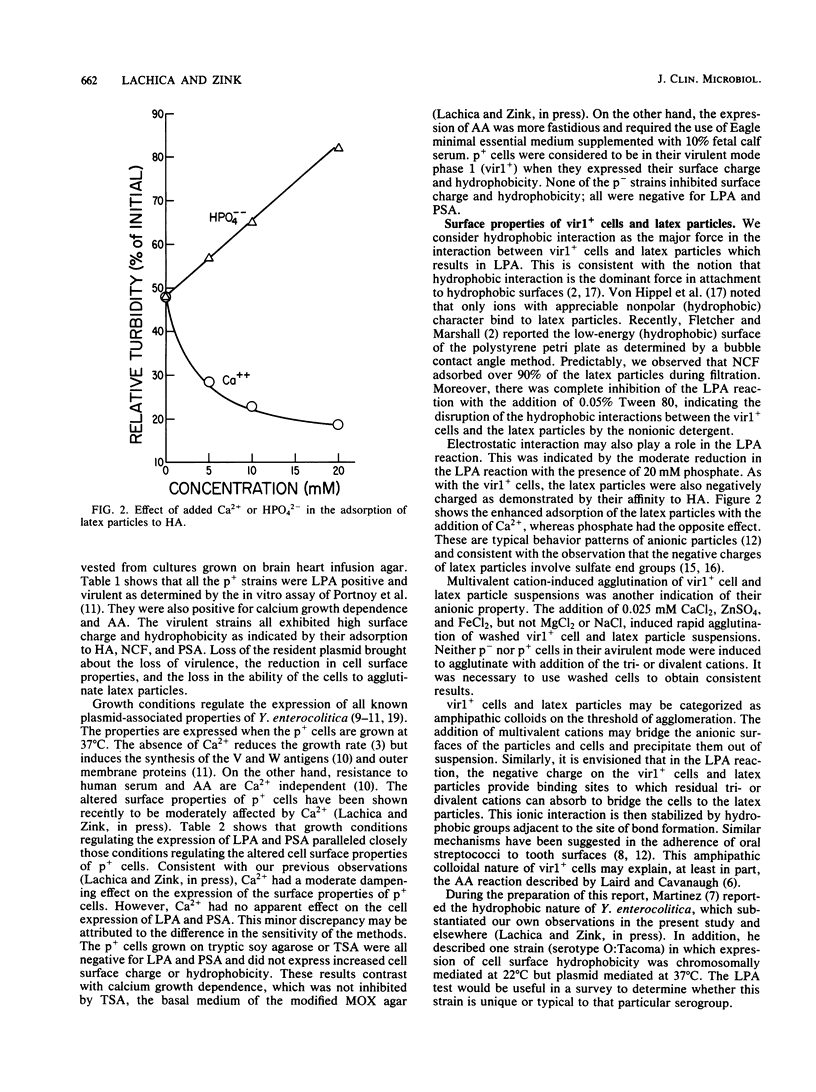
Abstract
A quick and simple method was developed to distinguish hydrophobic from hydrophilic cells. The latex particle agglutination test is based on the hydrophobic interactions between cells and latex particles which result in the agglutination of the suspension mixture. There was a direct correlation between the expression of plasmid-associated cell surface properties and latex particle agglutination by Yersinia enterocolitica. Multivalent cation-induced agglutination of suspensions of washed cells of virulent Y. enterocolitica and latex particles is indicative of their amphipathic character. Electrostatic interaction may also play a role in the latex particle agglutination reaction.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bottone E. J. Yersinia enterocolitica: a panoramic view of a charismatic microorganism. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1977;5(2):211–241. doi: 10.3109/10408417709102312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher M., Marshall K. C. Bubble contact angle method for evaluating substratum interfacial characteristics and its relevance to bacterial attachment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jul;44(1):184–192. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.1.184-192.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T. Plasmid associated with pathogenicity and calcium dependency of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):682–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.682-685.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesemann J., Laufs R. Construction of a mobilizable Yersinia enterocolitica virulence plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):761–767. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.761-767.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird W. J., Cavanaugh D. C. Correlation of autoagglutination and virulence of yersiniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):430–432. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.430-432.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R. J. Plasmid-mediated and temperature-regulated surface properties of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):921–930. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.921-930.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt W. E., Doyle R. J., Taylor K. G. Hydrophobic interactions and the adherence of Streptococcus sanguis to hydroxylapatite. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):637–644. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.637-644.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., DeStephano L. Serum resistance associated with virulence in Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):605–611. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.605-611.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. D., Brubaker R. R. Vwa+ phenotype of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):166–171. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.166-171.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M. Bacterial adherence to polystyrene: a replica method of screening for bacterial hydrophobicity. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Aug;42(2):375–377. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.2.375-377.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rölla G., Iversen O. J., Bonesvoll P. Lipoteichoic acid - the key to the adhesiveness of sucrose grown Streptococcus mutans. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;107:607–617. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3369-2_69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Tavassoli M. A minibead method to study cell surface receptors for various proteins coupled to latex particles. J Ultrastruct Res. 1981 May;75(2):205–217. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(81)80136-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Hippel P. H., Peticolas V., Schack L., Karlson L. Model studies on the effects of neutral salts on the conformational stability of biological macromolecules. I. Ion binding to polyacrylamide and polystyrene columns. Biochemistry. 1973 Mar 27;12(7):1256–1264. doi: 10.1021/bi00731a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink D. L., Feeley J. C., Wells J. G., Vanderzant C., Vickery J. C., Roof W. D., O'Donovan G. A. Plasmid-mediated tissue invasiveness in Yersinia enterocolitica. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):224–226. doi: 10.1038/283224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]