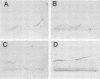
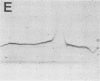
Abstract
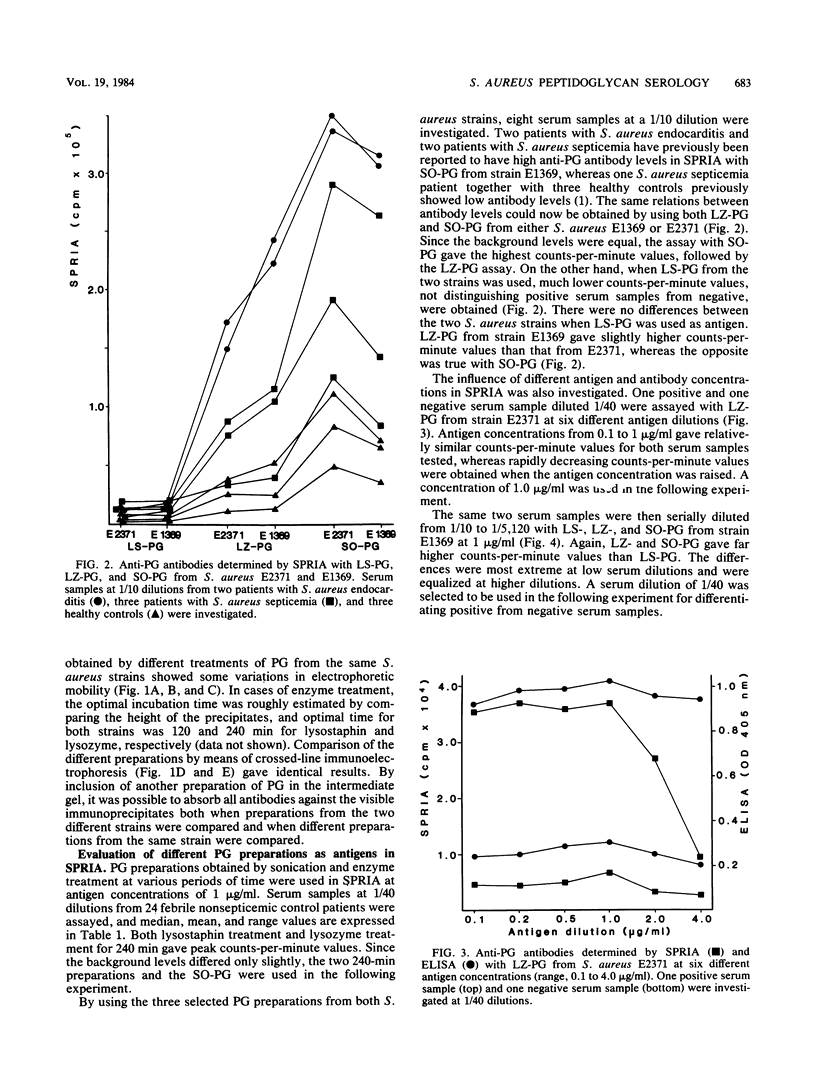
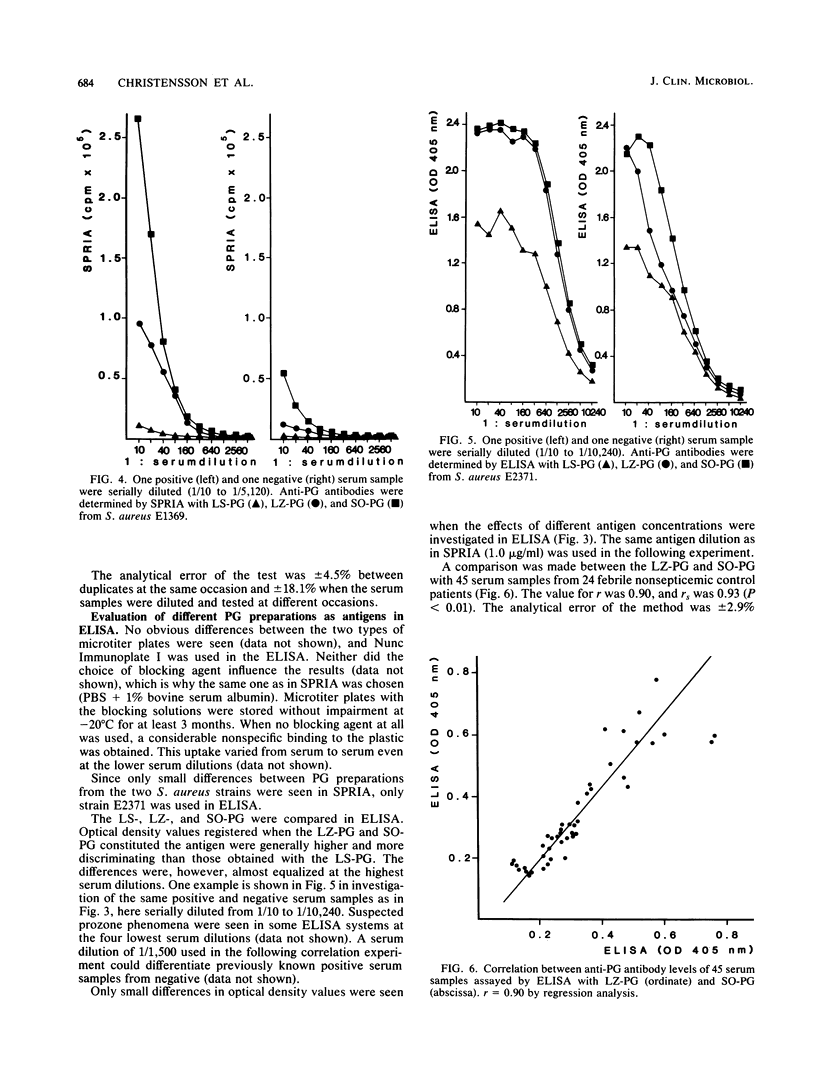
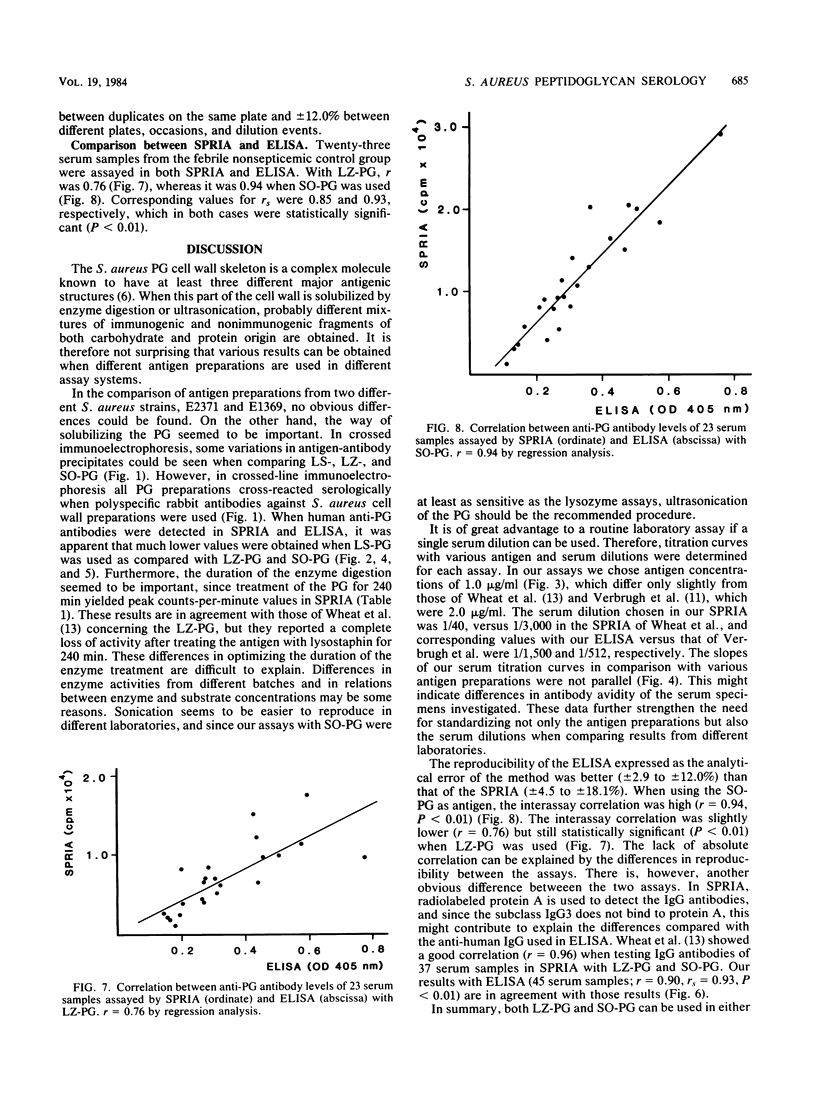
In the present studies we compared the ability of two commonly used assays, solid-phase radioimmunoassay and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), to detect human antibodies to Staphylococcus aureus peptidoglycan. ELISA was superior, with a reproducibility of 12.0%, as compared with 18.1% in solid-phase radioimmunoassay. Much lower serum dilutions could be used in ELISA. We also studied the effects of solubilizing the antigen by lysostaphin, lysozyme, or ultrasonication. Lysostaphin-treated peptidoglycan cannot be recommended since solid-phase radioimmunoassay could not distinguish positive from negative serum samples with this preparation. On the other hand, the sensitivity in both assays was high when peptidoglycan treated with lysozyme for 240 min or with ultrasonication for 30 min was used as antigen. The interassay correlation between solid-phase radioimmunoassay and ELISA was slightly better with sonicated peptidoglycan (correlation coefficient = 0.94, P less than 0.01), as compared with lysozyme-treated peptidoglycan (correlation coefficient = 0.76, P less than 0.01). We recommend the ELISA with sonicated peptidoglycan as antigen for use in routine serology.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Christensson B., Espersen F., Hedström S. A., Kronvall G. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay of immunoglobulin G antibodies to Staphylococcus aureus peptidoglycan in patients with staphylococcal infections. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1983 Dec;91(6):401–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1983.tb00067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espersen F., Clemmensen I. Isolation of a fibronectin-binding protein from Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):526–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.526-531.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espersen F., Hertz J. B., Høiby N., Mogensen H. H. Quantitative immunoelectrophoretic analysis of Salmonella typhi antigens and of corresponding antibodies in human sera. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1980 Aug;88(4):237–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb02634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harboe N., Ingild A. Immunization, isolation of immunoglobulins, estimation of antibody titre. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:161–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helgeland S., Grov A., Schleifer K. H. The immunochemistry of Staphylococcus aureus mucopeptide. I. Antigenic specificity of the peptide subunits. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Aug;81(4):413–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02224.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heymer B., Bernstein D., Schleifer K. H., Krause R. M. Measurement of peptidoglycan antibodies by a radioimmunoassay. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1975 Jul;149(2-4):168–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T., HANCOCK R. A fractionation procedure for studies of the synthesis of cell-wall mucopeptide and of other polymers in cells of Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Feb;22:249–258. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-1-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiøtz P. O., Høiby N., Hertz J. B. Cross-reactions between Staphylococcus aureus and fifteen other bacterial species. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Dec;87(6):329–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1979.tb02447.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., Peters R., Rozenberg-Arska M., Peterson P. K., Verhoef J. Antibodies to cell wall peptidoglycan of Staphylococcus aureus in patients with serious staphylococcal infections. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jul;144(1):1–9. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeke B. Crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:47–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03778.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheat L. J., Wilkinson B. J., Kohler R. B., White A. C. Antibody response to peptidoglycan during staphylococcal infections. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):16–22. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]