Abstract
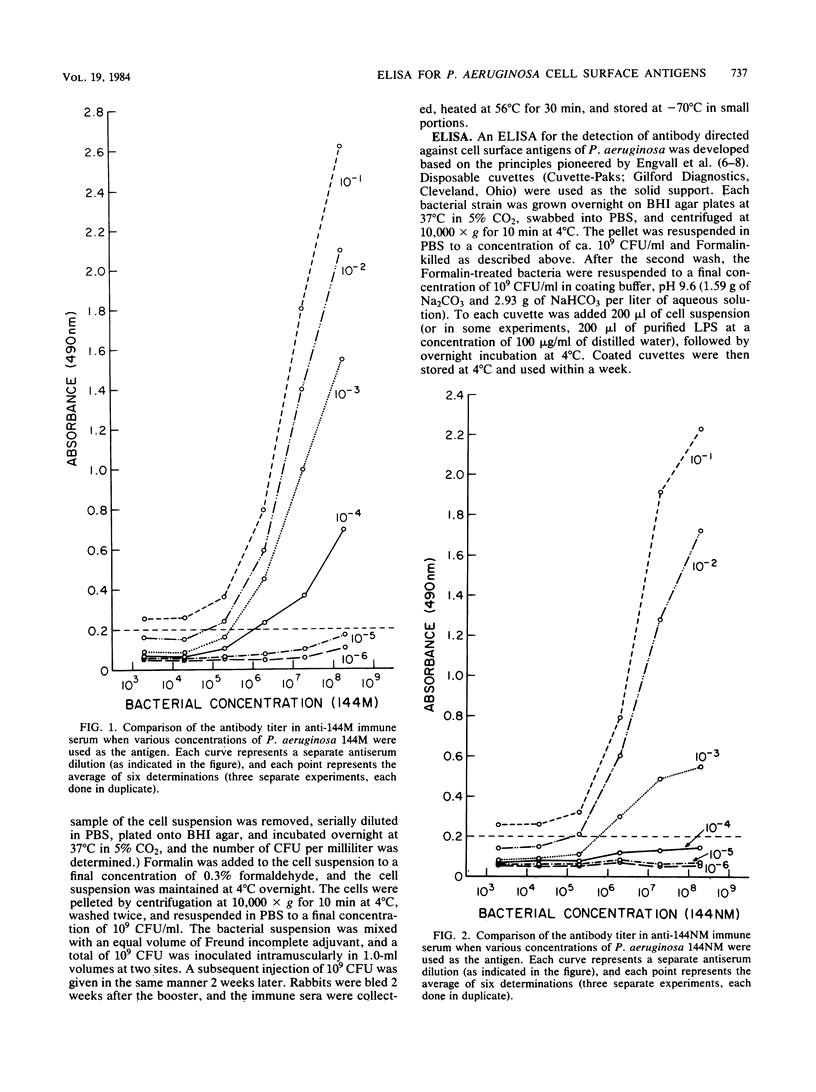
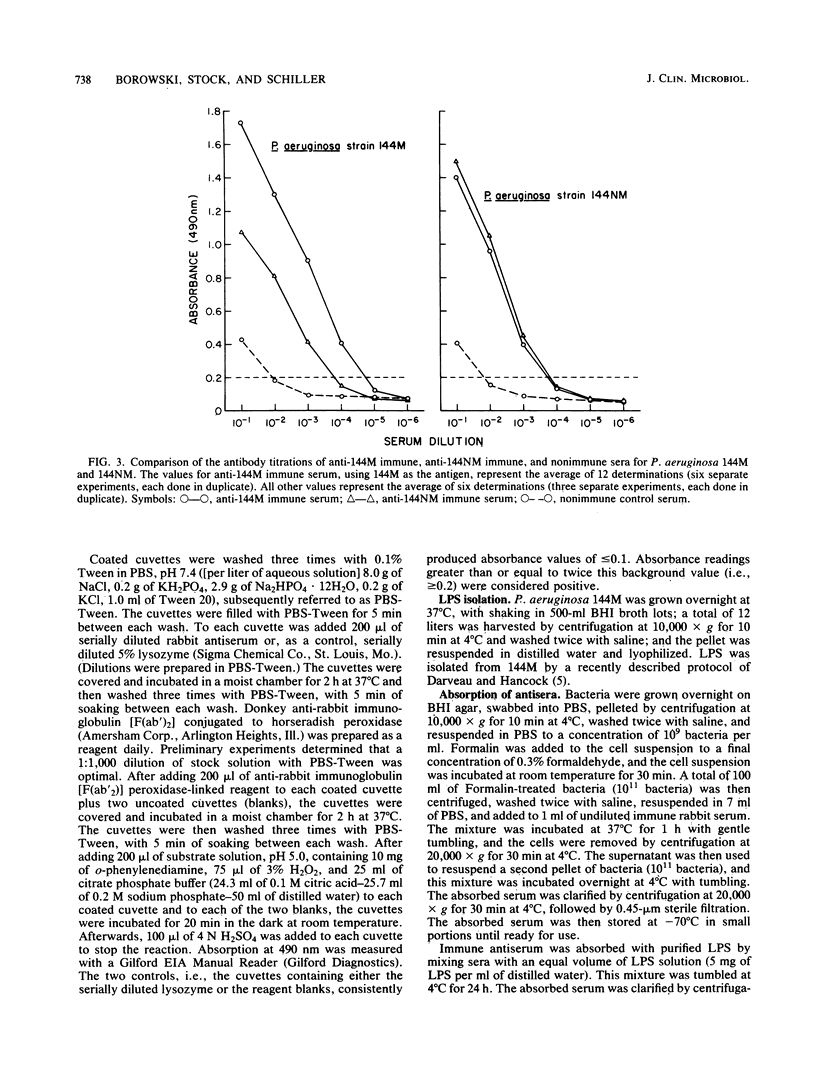
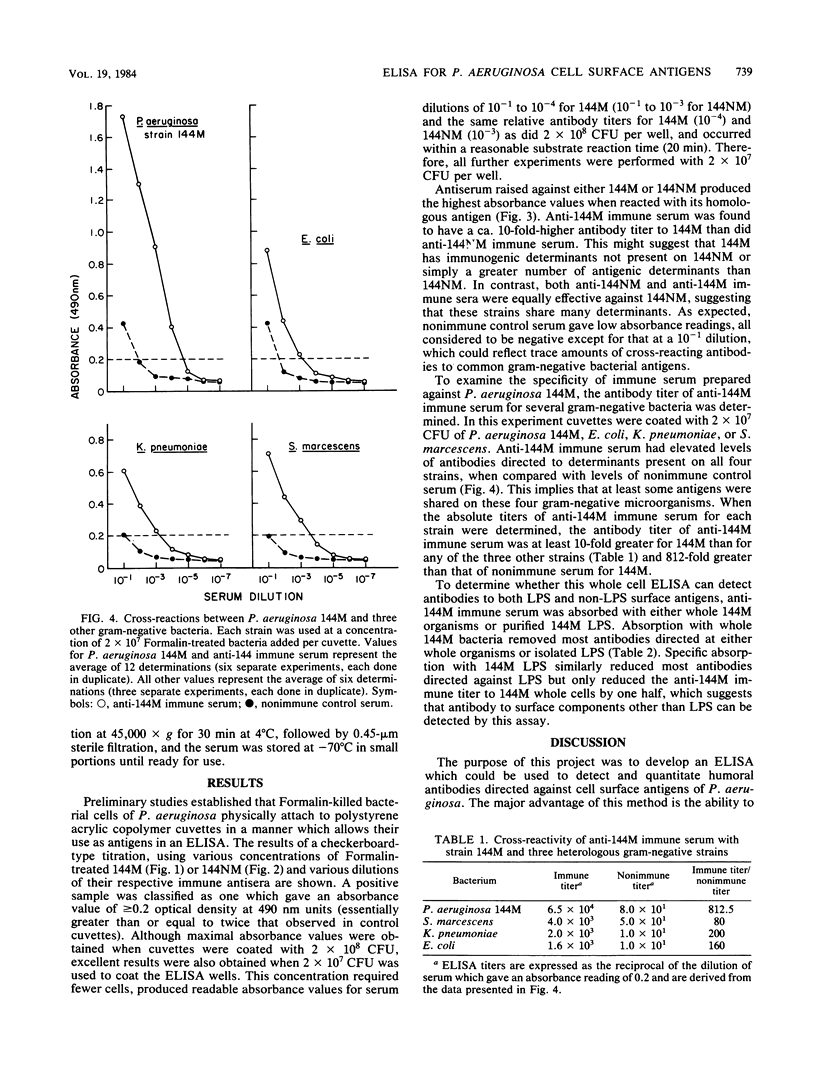
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the measurement of antibodies directed against Pseudomonas aeruginosa cell surface antigens was developed. Formalin-killed whole cells of P. aeruginosa, adsorbed to polystyrene acrylic copolymer cuvettes, were used as immobilized antigens. Antisera to P. aeruginosa mucoid strain 144M and to its spontaneous nonmucoid derivative, 144NM, were raised in rabbits by immunization with Formalin-killed bacteria. By using this enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, anti-144M serum was found to have a ca. 10-fold-higher antibody titer to 144M than did anti-144NM serum, suggesting that 144M may have either immunogenic determinants not present on 144NM or perhaps simply more antigenic determinants. In contrast, anti-144M and anti-144NM immune sera were found to have nearly identical antibody titers to 144NM, suggesting that these strains share many determinants. Anti-P. aeruginosa immune serum was found to contain Pseudomonas-specific antibodies as well as antibodies which cross-reacted with other gram-negative bacteria. Finally, absorption studies demonstrated that this assay can detect both LPS and non-LPS surface-exposed antigenic determinants. Thus, this whole bacterial cell enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay should prove useful in monitoring patient sera and secretions for potentially protective immunoglobulins directed at P. aeruginosa cell surface antigens.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodey G. P., Bolivar R., Fainstein V., Jadeja L. Infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr;5(2):279–313. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.2.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Fürer E., Germanier R. Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for studying Vibrio cholerae cell surface antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):41–45. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.41-45.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cukor G., Blacklow N. R., Nowak N. A., Rich C. M., Braverman L. E., Fischer R. A. Comparative analysis of serum antibody responses to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A by cystic fibrosis and intensive care unit patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):457–462. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.457-462.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darveau R. P., Hancock R. E. Procedure for isolation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides from both smooth and rough Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Salmonella typhimurium strains. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):831–838. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.831-838.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Jonsson K., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. II. Quantitative assay of protein antigen, immunoglobulin G, by means of enzyme-labelled antigen and antibody-coated tubes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 28;251(3):427–434. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90132-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granfors K., Viljanen M. K., Toivanen A. Measurement of immunoglobulin M, immunoglobulin G, and immunoglobulin A antibodies against Yersinia enterocolitica by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: comparison of lipopolysaccharide and whole bacterium as antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jul;14(1):6–14. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.1.6-14.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Mutharia L. M., Chan L., Darveau R. P., Speert D. P., Pier G. B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis: a class of serum-sensitive, nontypable strains deficient in lipopolysaccharide O side chains. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):170–177. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.170-177.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiby N., Axelsen N. H. Identification and quantitation of precipitins against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis by means of crossed immunoelectrophoresis with intermediate gel. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Jun;81(3):298–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høiby N., Hertz J. B., Sompolinsky D. Antibody response in patients with Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection to a 'common antigen' from P. aeruginosa analysed by means of quantitative immunoelectrophoretic methods. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1980 Jun;88(3):149–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb00088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ison C. A., Hadfield S. G., Glynn A. A. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to detect antibodies in gonorrhea using whole cells. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Sep;34(9):1040–1043. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.9.1040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagger K. S., Robinson D. L., Franz M. N., Warren R. L. Detection by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays of antibody specific for Pseudomonas proteases and exotoxin A in sera from cystic fibrosis patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1054–1058. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1054-1058.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinger J. D., Straus D. C., Hilton C. B., Bass J. A. Antibodies to proteases and exotoxin A of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis: Demonstration by radioimmunoassay. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jul;138(1):49–48. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam J. S., Mutharia L. M., Hancock R. E., Høiby N., Lam K., Baek L., Costerton J. W. Immunogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane antigens examined by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):88–98. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.88-98.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompolinsky D., Hertz J. B., Høiby N., Jensen K., Mansa B., Pedersen V. B., Samra Z. An antigen common to a wide range of bacteria. 2. A biochemical study of a "common antigen" from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1980 Oct;88(5):253–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb02637.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompolinsky D., Hertz J. B., Høiby N., Jensen K., Mansa B., Samra Z. An antigen common to a wide range of bacteria. I. The isolation of a 'common antigen' from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1980 Jun;88(3):143–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb02620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


