Abstract
The objective of this study was to evaluate the prevalence and significance of antibody titers to organisms in the family Legionellaceae in 128 serum samples collected from cystic fibrosis patients at routine examinations. Antibody titers were determined for 10 antigenic types of Legionellaceae; Legionella pneumophila serogroups 1 to 6, Fluoribacter (Legionella) bozemanae, Fluoribacter (Legionella) dumoffii, Fluoribacter (Legionella) gormanii, and Tatlockia (Legionella) micdadei. The method of antibody titer determination was the microagglutination test. Elevated titers (greater than or equal to 1:64) to one or more antigens were found in 41.3% of cystic fibrosis patients but in only 9.7% of 103 normal control subjects (P less than 0.01). Titers to 8 of the 10 antigens were directly correlated with the number of Pseudomonas aeruginosa precipitating antibodies in patient sera, as determined by crossed immunoelectrophoresis (correlation coefficients, greater than or equal to 0.74). Cross-reactions between P. aeruginosa and L. pneumophila were substantiated by crossed immunoelectrophoresis of hyperimmune rabbit serum as well as patient sera against P. aeruginosa and Legionellaceae antigens. Monospecific antibody to the "common antigen" of P. aeruginosa was used to demonstrate the presence of this antigen in L. pneumophila. The presence of cross-reacting antibodies in cystic fibrosis patients chronically infected with P. aeruginosa emphasizes the need for cautious interpretation of antibody titers to members of the family Legionellaceae.
Full text
PDF
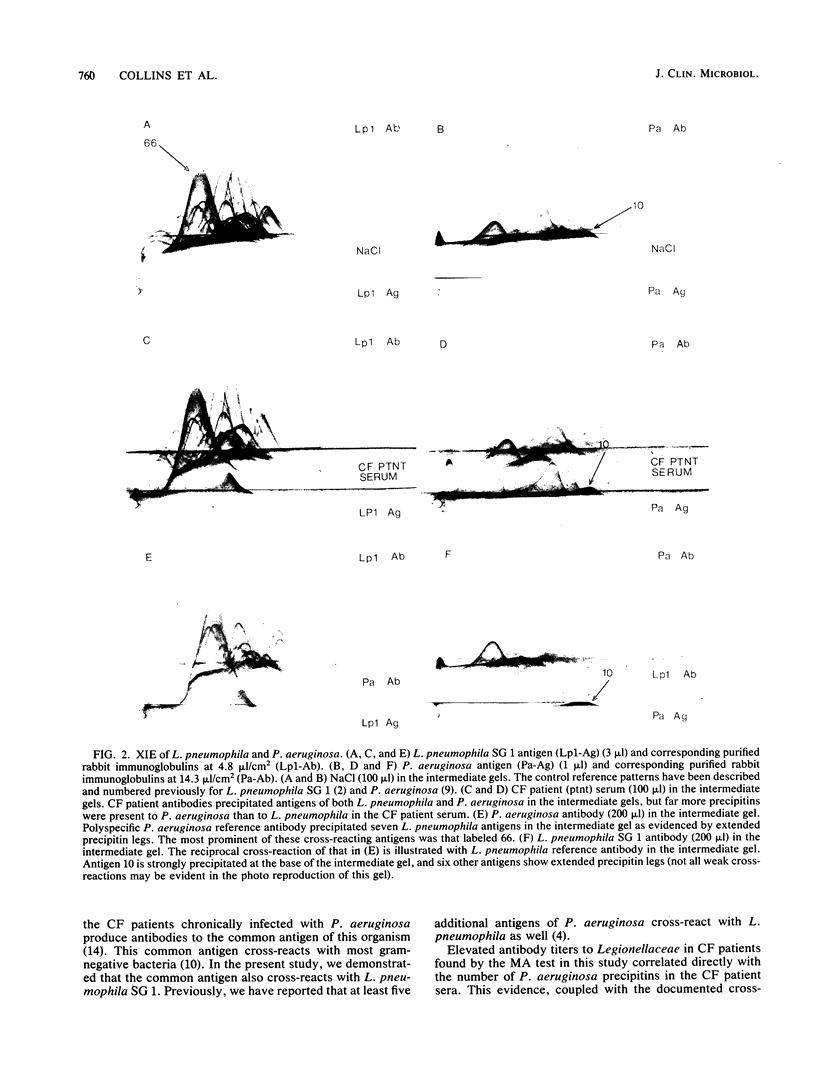


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Collins M. T., Cho S. N., Høiby N., Espersen F., Baek L., Reif J. S. Crossed immunoelectrophoretic analysis of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 antigens. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1428–1440. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1428-1440.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. T., Cho S. N., Reif J. S. Prevalence of antibodies to Legionella pneumophila in animal populations. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):130–136. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.130-136.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
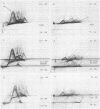
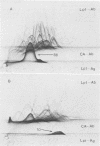
- Collins M. T., Espersen F., Høiby N., Cho S. N., Friis-Møller A., Reif J. S. Cross-reactions between Legionella pneumophila (serogroup 1) and twenty-eight other bacterial species, including other members of the family Legionellaceae. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1441–1456. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1441-1456.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., McKinney R. M., Meyer R. D., Edelstein M. A., Krause C. J., Finegold S. M. Immunologic diagnosis of Legionnaires' disease: cross-reactions with anaerobic and microaerophilic organisms and infections caused by them. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):652–655. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efthimiou J., Hodson M. E., Taylor P., Taylor A. G., Batten J. C. Importance of viruses and Legionella pneumophila in respiratory exacerbations of young adults with cystic fibrosis. Thorax. 1984 Feb;39(2):150–154. doi: 10.1136/thx.39.2.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farshy C. E., Klein G. C., Feeley J. C. Detection of antibodies to legionnaires disease organism by microagglutination and micro-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay tests. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Apr;7(4):327–331. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.4.327-331.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiby N., Axelsen N. H. Identification and quantitation of precipitins against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis by means of crossed immunoelectrophoresis with intermediate gel. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Jun;81(3):298–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiby N. The serology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa analysed by means of quantitative immunoelectrophoretic methods. III. Reproducibility of a polyvalent P. aeruginosa reference standard-antigen. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Oct;83(5):433–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høiby N., Hertz J. B., Sompolinsky D. Antibody response in patients with Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection to a 'common antigen' from P. aeruginosa analysed by means of quantitative immunoelectrophoretic methods. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1980 Jun;88(3):149–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb00088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høiby N., Wiik A. Antibacterial precipitins and autoantibodies in serum of patients with cystic fibrosis. Scand J Respir Dis. 1975 May;56(1):38–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. M., Holsclaw D. S., Jr Serum antibodies to Legionella pneumophila in patients with cystic fibrosis. JAMA. 1982 Nov 12;248(18):2284–2288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. C. Cross-reaction to Legionella pneumophila antigen in sera with elevated titers to Pseudomonas pseudomallei. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jan;11(1):27–29. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.1.27-29.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. C., Jones W. L., Feeley J. C. Upper limit of normal titer for detection of antibodies to Legionella pneumophila by the microagglutination test. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):754–755. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.754-755.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormsbee R. A., Peacock M. G., Lattimer G. L., Page L. A., Fiset P. Legionnaires' disease: antigenic peculiarities, strain differences, and antibiotic sensitivities of the agent. J Infect Dis. 1978 Aug;138(2):260–264. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.2.260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasculle A. W., Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Cordes L. G., Myerowitz R. L., Patton C. M., Gorman G. W., Carmack C. L., Ezzell J. W., Dowling J. N. Pittsburgh pneumonia agent: direct isolation from human lung tissue. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jun;141(6):727–732. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.6.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen N. T., Høiby N., Mordhorst C. H., Lind K., Flensborg E. W., Bruun B. Respiratory infections in cystic fibrosis patients caused by virus, chlamydia and mycoplasma--possible synergism with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1981 Sep;70(5):623–628. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1981.tb05757.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smalley D. L., Ourth D. D. Comparison of the microagglutination test with bactericidal response to Legionella pneumophila (Legionnaires disease bacterium). J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Feb;11(2):200–201. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.2.200-201.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smalley D. L., Ourth D. D. Seroepidemiology of Legionella pneumophila. A study of adults from Memphis, Tennessee, U. S. A. Am J Clin Pathol. 1981 Feb;75(2):201–203. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/75.2.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompolinsky D., Hertz J. B., Høiby N., Jensen K., Mansa B., Samra Z. An antigen common to a wide range of bacteria. I. The isolation of a 'common antigen' from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1980 Jun;88(3):143–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb02620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thunberg A. L., Kindt T. J. Sequence variability of rabbit antibody light chains. Familial occurrence of n-terminal sequence differences between b4 and b9 light chains. Scand J Immunol. 1975;4(2):197–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb02617.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeke B. Crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:47–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03778.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Farshy C. E., Fikes B. J., Cruce D. D., Yealy L. P. Measure of immunoglobulin G-, M-, and A-specific titers against Legionella pneumophila and inhibition of titers against nonspecific, gram-negative bacterial antigens in the indirect immunofluorescence test for legionellosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):685–689. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.685-689.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn W. C., Jr, Cherry W. B., Frank R. O., Casey C. A., Broome C. V. Direct immunofluorescent detection of Legionella pneumophila in respiratory specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jan;11(1):59–64. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.1.59-64.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]