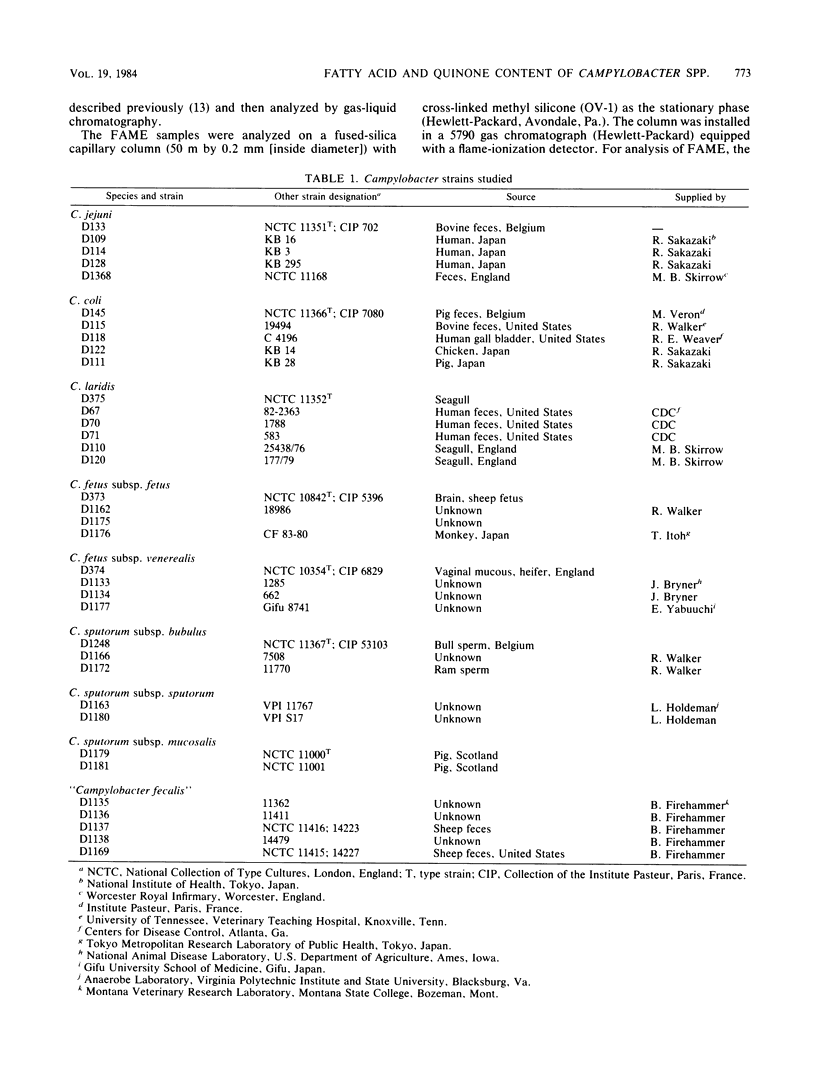
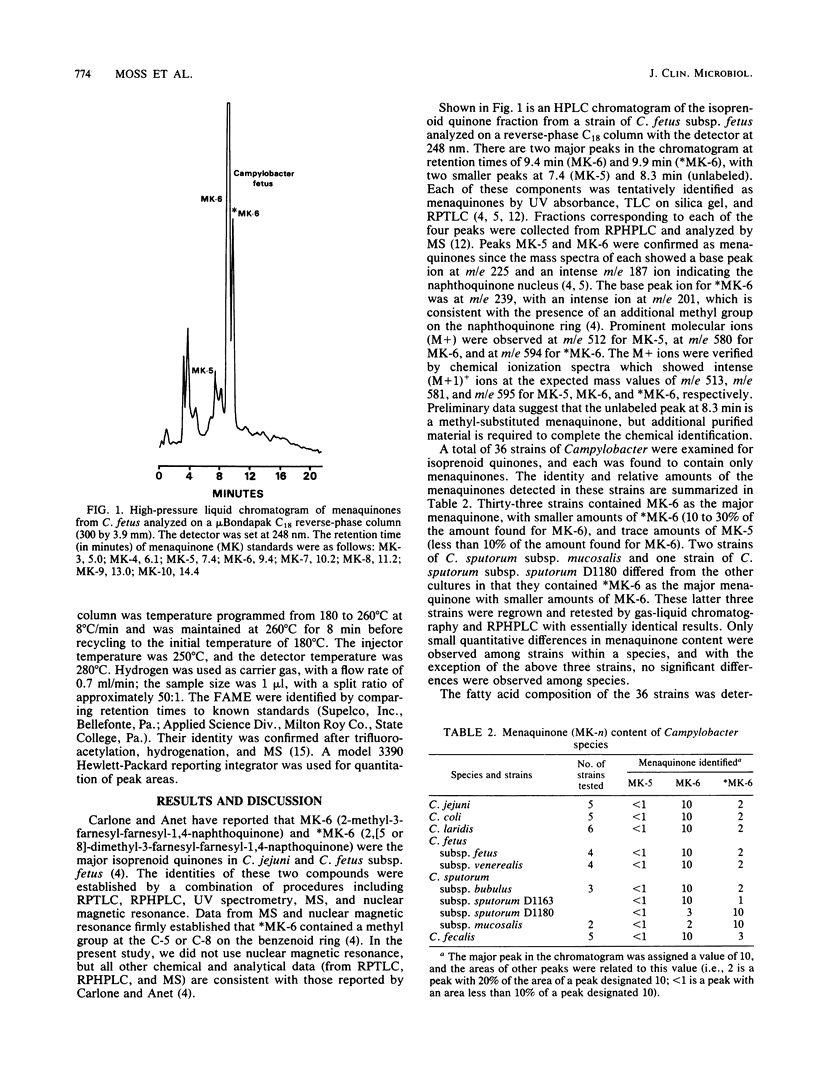
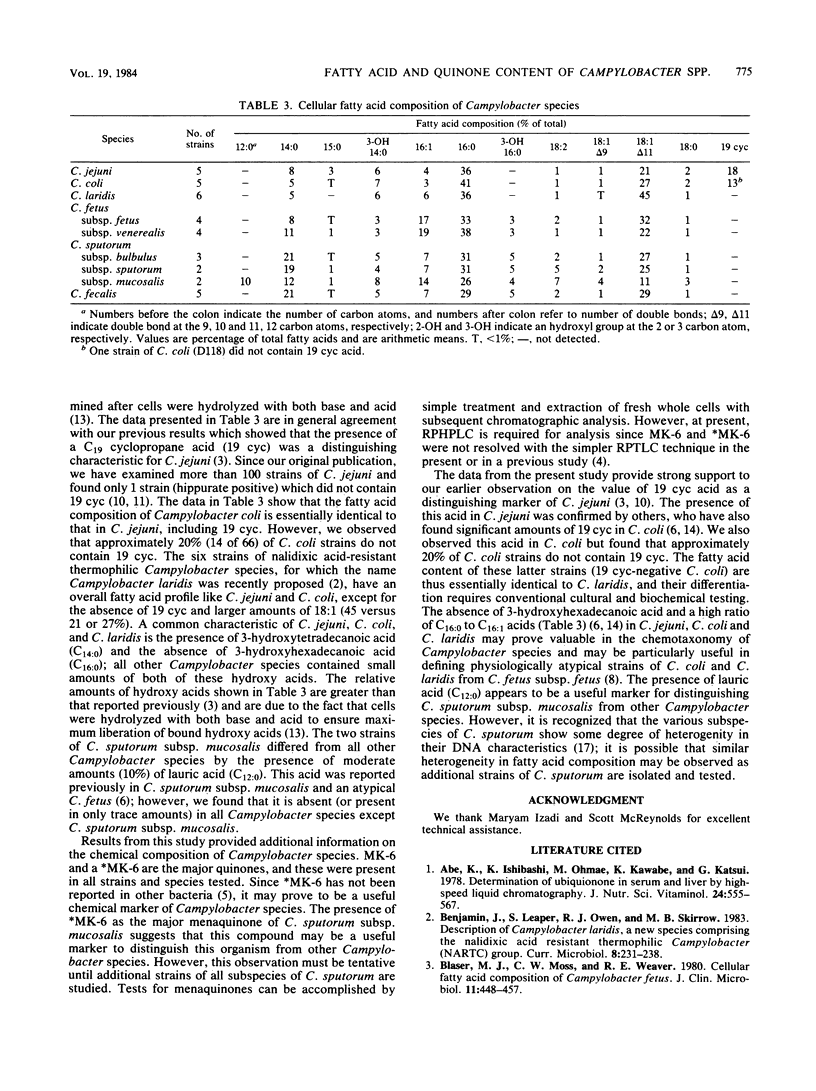
Abstract
A total of 36 strains of Campylobacter species were examined for isoprenoid quinones and cellular fatty acids. The isoprenoid quinone content was determined by reverse-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography, and the fatty acids were determined by capillary gas-liquid chromatography. All Campylobacter species contained menaquinone-6 (2-methyl-3-farnesyl-farnesyl-1,4-naphthoquinone) and a methyl-substituted menaquinone-6 (2,[5 or 8]-dimethyl-3-farnesyl-farnesyl-1,4-napthoquinone) as the major isoprenoid quinones. The latter menaquinone has not been reported in other bacteria and may prove to be a useful chemical marker of Campylobacter species. Campylobacter jejuni and most Campylobacter coli were distinguished from other campylobacteria by the presence of a C19 cyclopropane acid, and Campylobacter sputorum subsp. mucosalis differed from other species by the presence of lauric acid.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe K., Ishibashi K., Ohmae M., Kawabe K., Katsui G. Determination of ubiquinone in serum and liver by high-speed liquid chromatography. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) 1978;24(6):555–567. doi: 10.3177/jnsv.24.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Moss C. W., Weaver R. E. Cellular fatty acid composition of Campylobacter fetus. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 May;11(5):448–451. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.5.448-451.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlone G. M., Anet F. A. Detection of menaquinone-6 and a novel methyl-substituted menaquinone-6 in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter fetus subsp. fetus. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Nov;129(11):3385–3393. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-11-3385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. D., Jones D. Distribution of isoprenoid quinone structural types in bacteria and their taxonomic implication. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Jun;45(2):316–354. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.2.316-354.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis M. A. Cellular fatty acid profiles of campylobacters. Med Lab Sci. 1983 Oct;40(4):333–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey S. M., Greenwood J. R. Probable Campylobacter fetus subsp. fetus gastroenteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1278–1279. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1278-1279.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey S. M. Hippurate hydrolysis by Campylobacter fetus. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):435–437. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.435-437.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert G. A., Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E., Lambert M. A., Blaser M. J., Moss C. W. 30 years of campylobacters: biochemical characteristics and a biotyping proposal for Campylobacter jejuni. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1065–1073. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1065-1073.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert G. A., Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E., Steigerwalt A. G., McKinney R. M., Brenner D. J. Serogroups of Campylobacter jejuni, Campylobacter coli, and Campylobacter fetus defined by direct immunofluorescence. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Mar;17(3):529–538. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.3.529-538.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karr D. E., Bibb W. F., Moss C. W. Isoprenoid quinones of the genus Legionella. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1044–1048. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1044-1048.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert M. A., Moss C. W. Comparison of the effects of acid and base hydrolyses on hydroxy and cyclopropane fatty acids in bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Dec;18(6):1370–1377. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.6.1370-1377.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W. Gas-liquid chromatography as an analytical tool in microbiology. J Chromatogr. 1981 Jan 9;203:337–347. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)80305-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Guerrant G. O. Separation of bacterial ubiquinones by reverse-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):15–17. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.15-17.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. J. Nucleic acids in the classification of Campylobacters. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;2(4):367–377. doi: 10.1007/BF02019473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


