Abstract
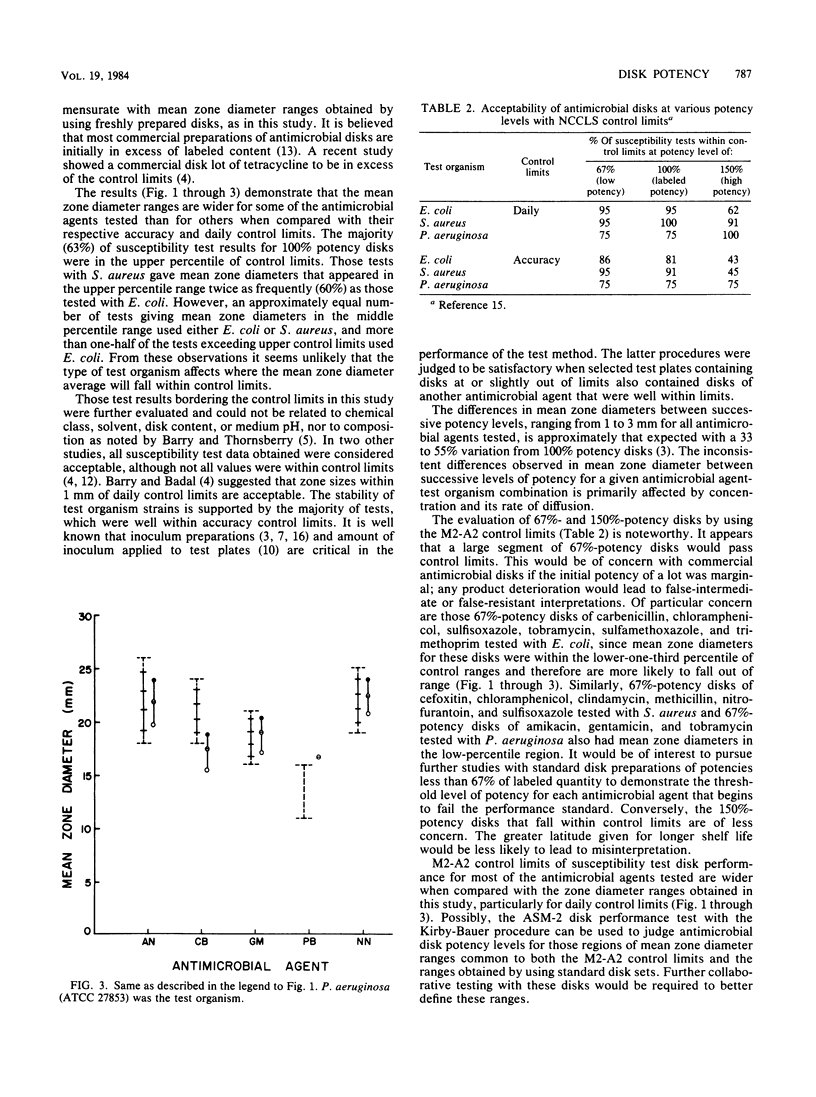
Standard disks of 25 antimicrobial agents were prepared and tested at three levels of potency (67, 100, and 150% of labeled quantity). The method used was a modification of the approved standard M2-A2 of the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Forty-seven susceptibility tests were performed at each potency level by using one to three test organisms. Labeled-potency (100%) disks were within accuracy limits for 85% of the tests and were within daily control limits for 94% of the tests. All susceptibility test data for labeled disks, however, were considered acceptable. The majority (63%) of mean zone diameter data for labeled-content disks were in the upper-one-third percentile of accuracy control limits. A significant proportion (91%) of low-potency disks and considerably fewer (34%) of the high-potency disks were found acceptable when daily control limits were applied. Of most concern are those antimicrobial agents whose low-potency disks approach the lower region of control limits. Zone diameter data from standard disks in the range of potency levels tested suggest that control ranges are excessive for some antimicrobial agent-test organism combinations.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry A. L., Badal R. E. Quality control limits for the agar overlay disk diffusion antimicrobial susceptibility test. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Dec;16(6):1145–1147. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.6.1145-1147.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER K. E. Theory of antibiotic inhibition zones in agar media. Nature. 1955 Sep 10;176(4480):510–511. doi: 10.1038/176510b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrod L. P., Waterworth P. M. A study of antibiotic sensitivity testing with proposals for simple uniform methods. J Clin Pathol. 1971 Dec;24(9):779–789. doi: 10.1136/jcp.24.9.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRSHBAUM A., KRAMER J., ARRET B. The assay and control of antibiotic discs. Antibiot Chemother (Northfield) 1960 Apr;10:249–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. C., Gilmore B. F. Quality control of agar diffusion susceptibility tests. Data from the Quality Assurance Service Microbiology Program of the College of American Pathologists. Am J Clin Pathol. 1981 Oct;76(4 Suppl):590–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


