Abstract
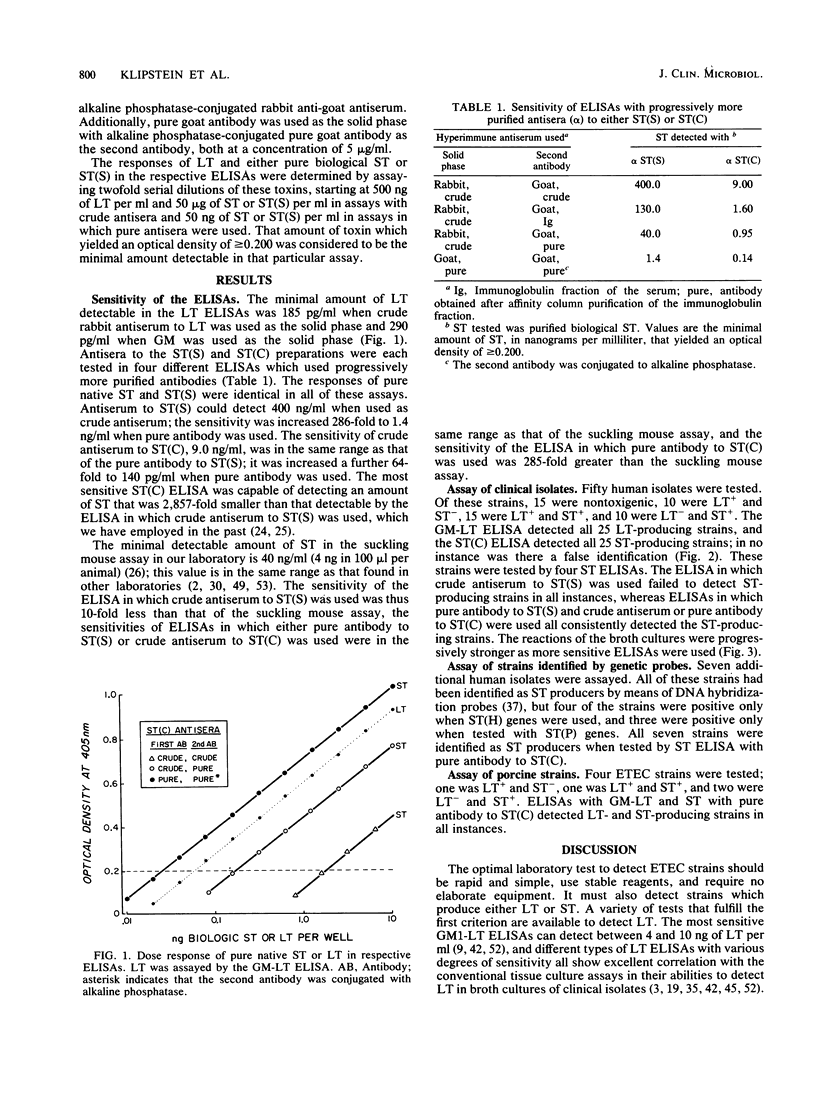
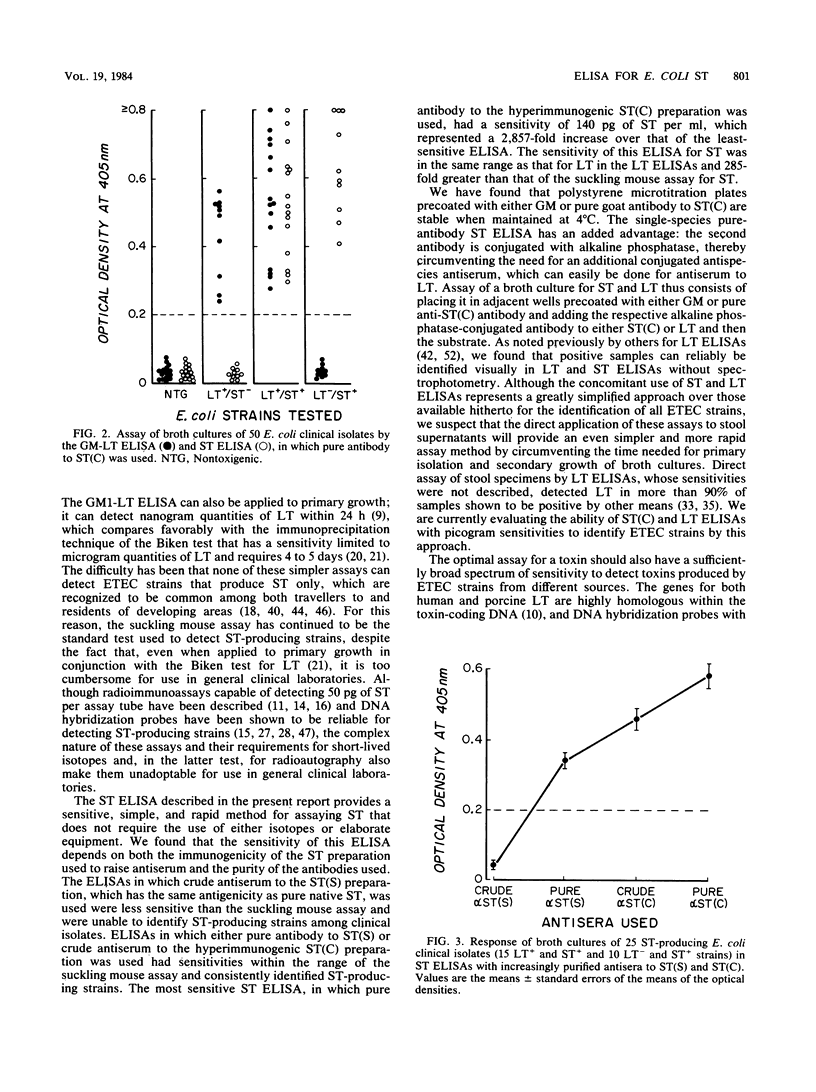
The sensitivity of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to detect pure native Escherichia coli heat-stable toxin (ST) and to identify ST-producing strains among clinical isolates was determined. Two synthetically produced ST preparations were used to raise hyperimmune antisera in rabbits and goats: ST(S), which has the same antigenicity as native ST; and ST(C), which is 15-fold more immunogenic. These antisera were used in the double-sandwich technique as either crude double-species antisera or pure single-species antibody. The sensitivity of the assay was increased by using either a purer antibody preparation or the antiserum to the more potent immunogen; the assay in which pure antibody to ST(C) was used was 2,857-fold more sensitive in detecting ST than the assay in which crude antiserum to ST(S) was used. The minimum amount of ST detectable by the ST(C) ELISA was 140 pg/ml, which was an amount 285-fold smaller than that detectable by the suckling mouse assay. Among 50 human E. coli isolates examined by both the ST(C) ELISA and an ELISA for heat-labile toxin (LT), which had a sensitivity of 290 pg/ml for LT, the respective toxins were consistently identified in broth cultures of 10 LT+ and ST-, 15 LT+ and ST+, and 10 LT- and ST+ strains, and there were no false-positive responses. The ST(C) ELISA also detected ST in all of seven ST - producing E. coli strains tested of human origin, which had been shown elsewhere by DNA hybridization probes to have ST-coding genes of either human or porcine origin, and in all of three ST-producing E. coi strains tested of porcine origin. These results indicate that the sensitivity of the ST(C) ELISA is the same as that of previously described LT ELISAs. The concomitant use of both ST and LT ELISAs provides a rapid, simple, and sensitive method for identifying among clinical isolates enterotoxigenic strains of E. coli which produce either toxin.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aimoto S., Takao T., Shimonishi Y., Hara S., Takeda T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Amino-acid sequence of a heat-stable enterotoxin produced by human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec 15;129(2):257–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Robertson D. C. Purification and chemical characterization of the heat-stable enterotoxin produced by porcine strains of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1021–1030. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1021-1030.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess M. N., Bywater R. J., Cowley C. M., Mullan N. A., Newsome P. M. Biological evaluation of a methanol-soluble, heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin in infant mice, pigs, rabbits, and calves. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):526–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.526-531.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bäck E., Svennerholm A. M., Holmgren J., Möllby R. Evaluation of a ganglioside immunosorbent assay for detection of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Dec;10(6):791–795. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.6.791-795.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceska M., Grossmüller F., Effenberger F. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay method for determination of Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):347–352. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.347-352.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. K., Giannella R. A. Amino acid sequence of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by Escherichia coli pathogenic for man. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7744–7746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Isolation and characterization of homogeneous heat-labile enterotoxins with high specific activity from Escherichia coli cultures. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):760–769. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.760-769.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Flint D. C., Klipstein F. A. Immunological and physicochemical characterization of heat-labile enterotoxins isolated from two strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):806–809. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.806-809.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerkinsky C. C., Svennerholm A. M. Ganglioside GM1 enzyme-linked immunospot assay for simple identification of heat-labile enterotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;17(6):965–969. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.6.965-969.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S. Conformity between heat-labile toxin genes from human and porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):647–652. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.647-652.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus L. A., Frantz J. C., Robertson D. C. Chemical properties of heat-stable enterotoxins produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli of different host origins. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):539–548. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.539-548.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G. Direct serological assay for the heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli, using passive immune hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):604–609. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.604-609.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Yang Z. Rapid test for identification of heat-labile enterotoxin-producing Escherichia coli colonies. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):23–28. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.23-28.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz J. C., Robertson D. C. Immunological properties of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxins: development of a radioimmunoassay specific for heat-stable enterotoxins with suckling mouse activity. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):193–198. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.193-198.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georges M. C., Wachsmuth I. K., Birkness K. A., Moseley S. L., Georges A. J. Genetic probes for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from childhood diarrhea in the Central African Republic. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):199–202. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.199-202.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Drake K. W., Luttrell M. Development of a radioimmunoassay for Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin: comparison with the suckling mouse bioassay. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):186–192. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.186-192.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Sack D. A., Rodriguez W., Sack R. B., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Horswood R. L., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Microtiter solid-phase radioimmunoassay for detection of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):541–545. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.541-545.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Rouse J. D., Hughes J. M., Rowe B. Turista among members of the Yale Glee Club in Latin America. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1980 Sep;29(5):895–900. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1980.29.895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Möllby R. GM1 ganglioside enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of heat-labile enterotoxin produced by human and porcine Escherichia coli strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):298–301. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.298-301.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Akhtar Q., Glass R. I., Kibriya A. K. A simple assay to detect Escherichia coli producing heat labile enterotoxin: results of a field study of the Biken tests in Bangladesh. Lancet. 1981 Sep 19;2(8247):609–610. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92745-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Arita M., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Further evaluation of the Biken test (modified Elek test) for detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli producing heat-labile enterotoxin and application of the test to sampling of heat-stable enterotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):60–62. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.60-62.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Samakoses R., Sornchai C., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Detection by a staphylococcal coagglutination test of heat-labile enterotoxin-producing enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;17(4):592–595. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.4.592-595.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F., Clements J. D. Development of a vaccine of cross-linked heat-stable and heat-labile enterotoxins that protects against Escherichia coli producing either enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):550–557. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.550-557.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F., Clements J. D., Houghten R. A. Protection against human and porcine enterotoxigenic strains of Escherichia coli in rats immunized with a cross-linked toxoid vaccine. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):924–929. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.924-929.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F., Clements J. D., Houghten R. A. Vaccine for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli based on synthetic heat-stable toxin crossed-linked to the B subunit of heat-labile toxin. J Infect Dis. 1983 Feb;147(2):318–326. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.2.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F., Houghten R. A. Properties of cross-linked toxoid vaccines made with hyperantigenic forms of synthetic Escherichia coli heat-stable toxin. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):268–273. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.268-273.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F., Houghten R. A. Properties of synthetically produced Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):117–121. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.117-121.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler E. M. Neonatal enteric colibacillosis of pigs and current research on immunization. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Sep 1;173(5 Pt 2):588–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lallier R., Bernard F., Gendreau M., Lazure C., Seidah N. G., Chrétien M., St-Pierre S. A. Isolation and purification of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin of porcine origin. Anal Biochem. 1982 Dec;127(2):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90171-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lallier R., Lariviere S., St-Pierre S. Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin: rapid method of purification and some characteristics of the toxin. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):469–474. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.469-474.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. H., Moseley S. L., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Gyles C. L., So M. Characterization of the gene encoding heat-stable toxin II and preliminary molecular epidemiological studies of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli heat-stable toxin II producers. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):264–268. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.264-268.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merson M. H., Yolken R. H., Sack R. B., Froehlich J. L., Greenberg H. B., Huq I., Black R. W. Detection of Escherichia coli enterotoxins in stools. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):108–113. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.108-113.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Kohler E. M., Schneider R. A., Whipp S. C. Prevalence of pilus antigens, enterotoxin types, and enteropathogenicity among K88-negative enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli from neonatal pigs. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):222–230. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.222-230.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. R., DuPont H. L., Wood L. V., Ericsson C. D. Comparison of methods to detect Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin in stool and cell-free culture supernatants. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Oct;18(4):798–802. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.4.798-802.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. K., Merson M. H., Sack D. A., Wells J. G., Martin W. T., Dewitt W. E., Feeley J. C., Sack R. B., Bessudo D. M. Laboratory investigation of diarrhea in travelers to Mexico: evaluation of methods for detecting enterotoxigenic Echerichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 May;3(5):486–495. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.5.486-495.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Echeverria P., Seriwatana J., Tirapat C., Chaicumpa W., Sakuldaipeara T., Falkow S. Identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by colony hybridization using three enterotoxin gene probes. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jun;145(6):863–869. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.6.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Hardy J. W., Hug M. I., Echeverria P., Falkow S. Isolation and nucleotide sequence determination of a gene encoding a heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1167–1174. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1167-1174.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Huq I., Alim A. R., So M., Samadpour-Motalebi M., Falkow S. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by DNA colony hybridization. J Infect Dis. 1980 Dec;142(6):892–898. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.6.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalin D. R., McLaughlin J. C., Rahaman M., Yunus M., Curlin G. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and idiopathic diarrhoea in Bangladesh. Lancet. 1975 Dec 6;2(7945):1116–1119. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picken R. N., Mazaitis A. J., Maas W. K., Rey M., Heyneker H. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for heat-stable enterotoxin II of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):269–275. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.269-275.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ristaino P. A., Levine M. M., Young C. R. Improved GM1-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Oct;18(4):808–815. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.4.808-815.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder R. W., Wachsmuth I. K., Buxton A. E., Evans D. G., DuPont H. L., Mason E., Barrett F. F. Infantile diarrhea produced by heat-stable enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. N Engl J Med. 1976 Oct 14;295(16):849–853. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197610142951601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rönnberg B., Wadström T. Rapid detection by a coagglutination test of heat-labile enterotoxin in cell lysates from blood agar-grown Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;17(6):1021–1025. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.6.1021-1025.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack D. A., Huda S., Neogi P. K., Daniel R. R., Spira W. M. Microtiter ganglioside enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for vibrio and Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxins and antitoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jan;11(1):35–40. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.1.35-40.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack D. A., Merson M. H., Wells J. G., Sack R. B., Morris G. K. Diarrhoea associated with heat-stable enterotoxin-producing strains of Escherichia coli. Lancet. 1975 Aug 9;2(7928):239–241. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90958-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seriwatana J., Echeverria P., Escamilla J., Glass R., Huq I., Rockhill R., Stoll B. J. Identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in patients with diarrhea in Asia with three enterotoxin gene probes. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):152–155. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.152-155.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., Atchison R., Falkow S., Moseley S., McCarthy B. J. A study of the dissemination of Tn1681: a bacterial transposon encoding a heat-stable toxin among enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolates. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):53–58. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staples S. J., Asher S. E., Giannella R. A. Purification and characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by a strain of E. coli pathogenic for man. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4716–4721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundberg L., Porath J. Preparation of adsorbents for biospecific affinity chromatography. Attachment of group-containing ligands to insoluble polymers by means of bifuctional oxiranes. J Chromatogr. 1974 Mar 13;90(1):87–98. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)94777-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm A. M., Wiklund G. Rapid GM1-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with visual reading for identification of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;17(4):596–600. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.4.596-600.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Takeda T., Yano T., Yamamoto K., Miwatani T. Purification and partial characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):978–985. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.978-985.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Yokota T. Plasmids of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli H10407: evidence for two heat-stable enterotoxin genes and a conjugal transfer system. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1352–1360. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1352-1360.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


