Abstract
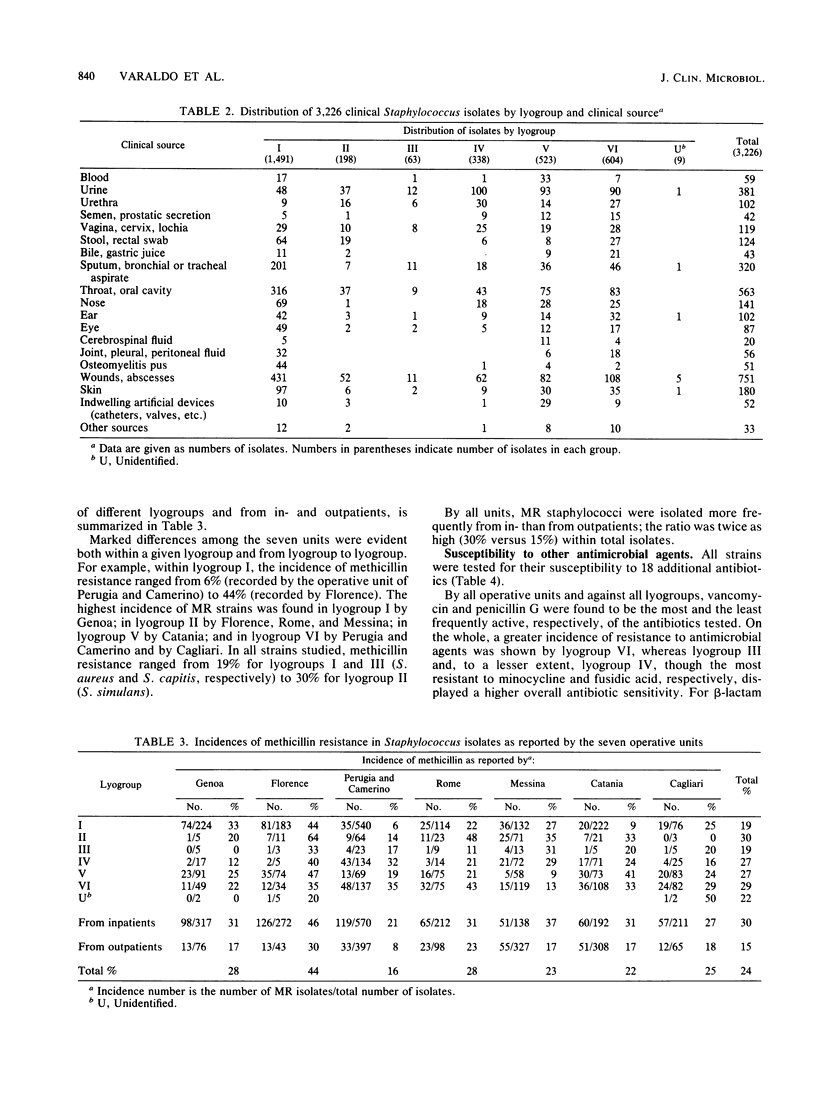
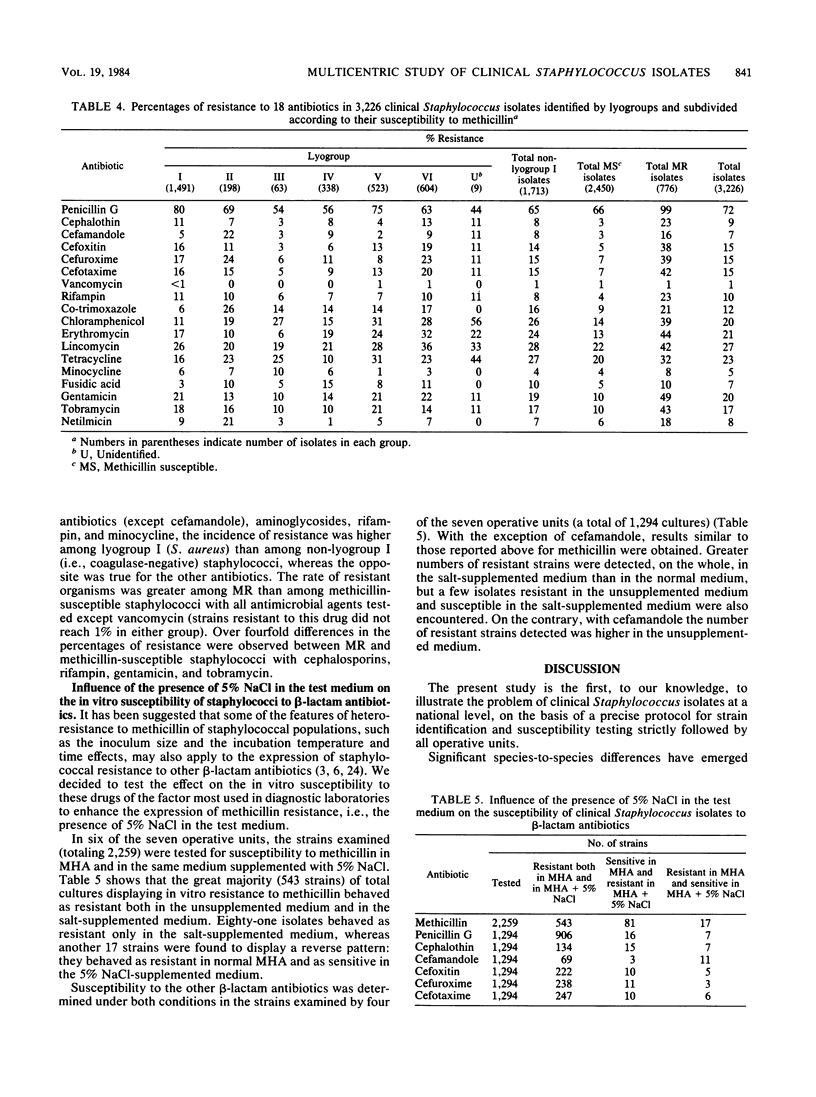
A multicentric study of clinical Staphylococcus isolates was performed by seven operative units working in different areas of Italy. Over a 6-month period, a total of 3,226 staphylococci, isolated from in- and outpatients, were identified and tested for antimicrobial susceptibility by a protocol agreed upon by all units. On the basis of their bacteriolytic-activity patterns and other conventional tests, the isolates were identified by lyogroups , which closely correlate with human Staphylococcus species. Lyogroup I (Staphylococcus aureus) and lyogroup III (Staphylococcus capitis) were the most and the least frequently isolated staphylococci, respectively. Significant differences depending on strain origin from in- or outpatients were only observed with lyogroup IV (i.e., novobiocin- resistant staphylococci), whose isolation from outpatients was three times greater than from inpatients. Lyogroup I was predominant among isolates from most clinical sources. Lyogroup IV predominated in strains isolated from the urinary tract; lyogroup V (Staphylococcus epidermidis) predominated in strains from blood, cerebrospinal fluid, and indwelling artificial devices; and lyogroup VI ( Staphylococcus hominis, Staphylococcus haemolyticus, and Staphylococcus warneri ) predominated in strains from bile and the male genital tract. The incidence of methicillin resistance within the different lyogroups varied from unit to unit, suggesting epidemiological differences among different hospitals and different geographical areas. On the whole, methicillin resistance was more frequent in coagulase-negative staphylococci than in S. aureus and ranged from 19% for lyogroups I and III to 30% for lyogroup II (Staphylococcus simulans). Laboratory testing with 18 additional antibiotics suggested the occurrence of some specific differences in susceptibility among the different lyogroups . The rate of organisms resistant to the various antibiotics was greater among methicillin-resistant than among methicillin -susceptible staphylococci; particularly marked differences occurred with cephalosporins, rifampin, gentamicin, and tobramycin. The results suggested an increasing spread in Italy, during the last few years, of staphylococcal resistance to methicillin and to many other antibiotics. Some questions about the actual reliability of laboratory tests for the determination of staphylococcal susceptibility to methicillin and other beta-lactam antibiotics were raised by parallel test performances in which both unsupplemented and 5% NaCl-supplemented Mueller-Hinton agars were used. The presence of NaCl heightened, on the whole, the number of resistant strains detected; however, a few isolates resistant in the unsupplemented medium and susceptible in the salt-supplemented medium were also encountered. This was true not only for methicillin but also for all other beta-lactam antibiotics tested except cefamandole. With cefamandole, the presence of 5% NaCl reduced the number of resistant strains detected.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldridge K. E., Janney A., Sanders C. V., Marier R. L. Interlaboratory variation of antibiograms of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus strains with conventional and commercial testing systems. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1226–1236. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1226-1236.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. D., Clarke A. M., Anderson M. E., Isaac-Renton J. L., McLoughlin M. G. Urinary tract infections due to Staphylococcus saprophyticus biotype 3. Can Med Assoc J. 1981 Feb 15;124(4):415–418. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer G. L. Antimicrobial susceptibility and selection of resistance among Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates recovered from patients with infections of indwelling foreign devices. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):353–359. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canawati H. N., Witte J. L., Sapico F. L. Temperature effect on the susceptibility of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus to four different cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jan;21(1):173–175. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt R. The classification of staphylococci from colonized ventriculo-atrial shunts. J Clin Pathol. 1969 Jul;22(4):475–482. doi: 10.1136/jcp.22.4.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovelius B., Mårdh P. A., Bygren P. Urinary tract infections caused by Staphylococcus saprophyticus: recurrences and complications. J Urol. 1979 Nov;122(5):645–647. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)56541-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovelius B., Thelin I., Mårdh P. A. Staphylococcus saprophyticus in the aetiology of nongonococcal urethritis. Br J Vener Dis. 1979 Oct;55(5):369–374. doi: 10.1136/sti.55.5.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John J. F., Jr, Gramling P. K., O'Dell N. M. Species identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci from urinary tract isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Oct;8(4):435–437. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.4.435-437.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan P. A., Iravani A., Richard G. A., Baer H. Urinary tract infection caused by Staphylococcus saprophyticus. J Infect Dis. 1980 Oct;142(4):510–515. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.4.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laverdiere M., Peterson P., Verhoef J., Williams D. N., Sabath L. D. In vitro activity of cephalosporins against methicillin-resistant, coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Infect Dis. 1978 Mar;137(3):245–250. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.3.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Kwan C., Noble M. A., West A., Duffield L. Staphylococcus saprophyticus as a cause of urinary tract infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):427–431. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.427-431.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsik F. J., Brake S. Species identification and susceptibility to 17 antibiotics of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Apr;15(4):640–645. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.4.640-645.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maskell R. Importance of coagulase-negative staphylococci as pathogens in the urinary tract. Lancet. 1974 Jun 8;1(7867):1155–1158. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90634-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolle L. E., Hoban S. A., Harding G. K. Characterization of coagulase-negative staphylococci from urinary tract specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;17(2):267–271. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.2.267-271.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price S. B., Flournoy D. J. Comparison of antimicrobial susceptibility patterns among coagulase-negative staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Mar;21(3):436–440. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.3.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. F., Marples R. R. Changing resistance to antimicrobial drugs, and resistance typing in clinically significant strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Med Microbiol. 1982 Nov;15(4):475–484. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-4-475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond A. S., Simberkoff M. S., Schaefler S., Rahal J. J., Jr Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to semisynthetic penicillins and cephalothin. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jan;135(1):108–112. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.1.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D. Chemical and physical factors influencing methicillin resistance of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1977 Nov;3 (Suppl 100):47–51. doi: 10.1093/jac/3.suppl_c.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Garner C., Wilcox C., Finland M. Effect of inoculum and of beta-lactamase on the anti-staphylococcal activity of thirteen penicillins and cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Sep;8(3):344–349. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.3.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satta G., Grazi G., Varaldo P. E., Fontana R. Detection of bacterial phosphatase activity by means of an original and simple test. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Apr;32(4):391–395. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.4.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebert W. T., Moreland N., Williams T. W., Jr Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. South Med J. 1978 Nov;71(11):1353–1355. doi: 10.1097/00007611-197811000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., McDougal L. K. Successful use of broth microdilution in susceptibility tests for methicillin-resistant (heteroresistant) staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1084–1091. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1084-1091.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tselenis-Kotsowilis A. D., Koliomichalis M. P., Papavassiliou J. T. Acute pyelonephritis caused by Staphylococcus xylosus. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):593–594. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.593-594.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varaldo P. E., Debbia E., Schito G. C. In vitro activity of teichomycin and vancomycin alone and in combination with rifampin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Mar;23(3):402–406. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.3.402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varaldo P. E., Grazi G., Cisani G., Satta G. Routine separation of staphylococci from micrococci based on bacteriolytic activity production. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):147–148. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.147-148.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varaldo P. E., Grazi G., Soro O., Cisani G., Satta G. Simplified lyogroup system, a new method for routine identification of staphylococci: description and comparison with three other methods. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jul;12(1):63–68. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.1.63-68.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varaldo P. E., Soro O., Grazi G., Biavasco F. Clinical distribution and antibiotic sensitivities of staphylococcal strains isolated over an eight-month period. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Apr;34(4):443–447. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.4.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. C., Schimpff S. C., Newman K. A., Wiernik P. H. Staphylococcus epidermidis: an increasing cause of infection in patients with granulocytopenia. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Oct;97(4):503–508. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-4-503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallmark G., Arremark I., Telander B. Staphylococcus saprophyticus: a frequent cause of acute urinary tract infection among female outpatients. J Infect Dis. 1978 Dec;138(6):791–797. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.6.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson B. J., Maxwell S., Schaus S. M. Classification and characteristics of coagulase-negative, methicillin-resistant staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Aug;12(2):161–166. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.2.161-166.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


