Abstract
In the Gillies and Govan method of pyocin typing for Pseudomonas aeruginosa a cross-streaking technique was used, and 105 main types and 25 subtypes were identified by the patterns of inhibition observed on 13 indicator strains. Disadvantages of the technique included the need to remove test strain growth before application of the indicator strains, the 48-h period needed to obtain a result, and the inability to reliably type mucoid P. aeruginosa. Recent studies have enabled us to overcome these disadvantages and significantly improve the speed and application of pyocin typing. Our revised technique utilizes the same 13 indicator strains which are already used internationally. Test strains were rapidly applied to the surface of agar plates with a multiple inoculator. After incubation for 6 h and exposure to chloroform, the indicator strains were applied in agar overlays without prior removal of the test strain growth. After 18 h of incubation, the pyocin type was recognized by inhibition of particular indicator strains. Additionally, the activity of particulate (R and F) and nonparticulate (S) pyocins could be distinguished on the basis of inhibition zone size, which thus allowed further discrimination. The revised technique allows typing within 24 h, increases the number of identifiable types, and can be used to type mucoid strains.
Full text
PDF
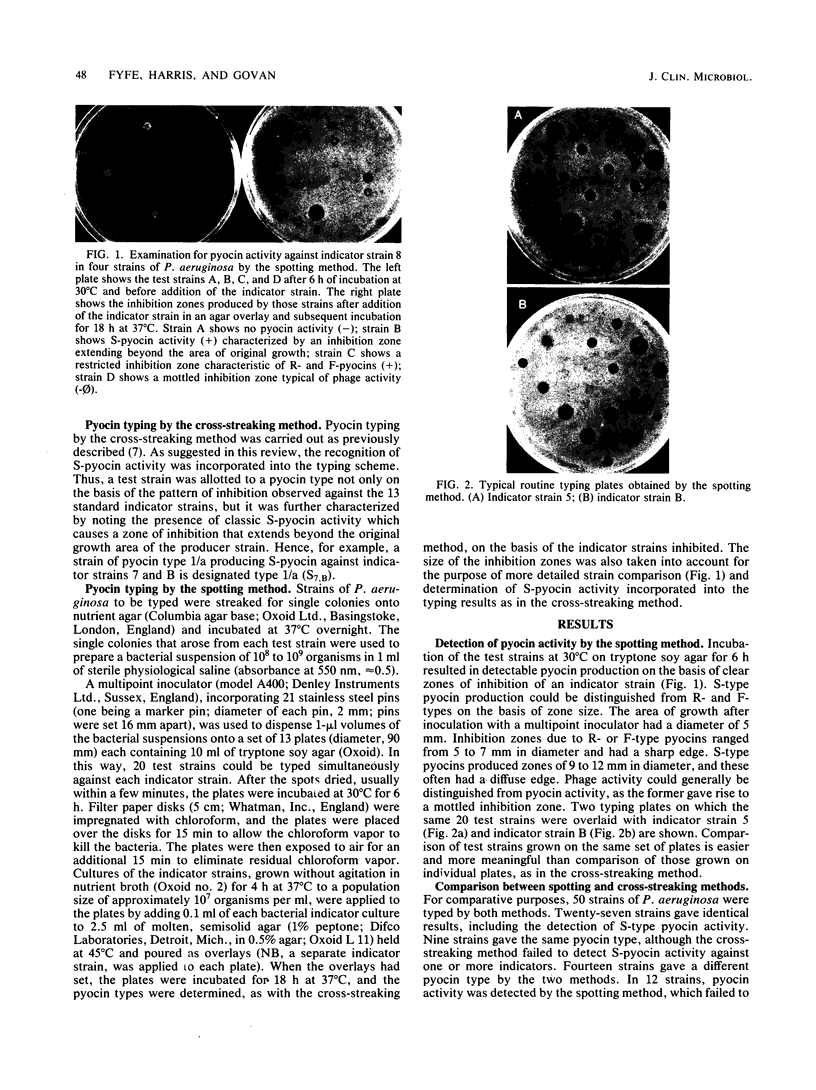


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcock S. R. Acute otitis externa in divers working in the North Sea: a microbiological survey of seven saturation dives. J Hyg (Lond) 1977 Jun;78(3):395–409. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400056291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brokopp C. D., Gomez-Lus R., Farmer J. J., 3rd Serological typing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: use of commercial antisera and live antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jun;5(6):640–649. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.6.640-649.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies R. R., Govan J. R. Typing of Pseudomonas pyocyanea by pyocine production. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(2):339–345. doi: 10.1002/path.1700910207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R., Gillies R. R. Further studies in the pyocine typing of Pseudomonas pyocyanea. J Med Microbiol. 1969 Feb;2(1):17–25. doi: 10.1099/00222615-2-1-17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R. Studies on the pyocins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: morphology and mode of action of contractile pyocins. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jan;80(1):1–15. doi: 10.1099/00221287-80-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. The role of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 May;11 (Suppl B):1–13. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.suppl_b.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penketh A., Pitt T., Roberts D., Hodson M. E., Batten J. C. The relationship of phenotype changes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the clinical condition of patients with cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 May;127(5):605–608. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.5.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt T. L. State of the art: typing Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Hosp Infect. 1980 Sep;1(3):193–199. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(80)90056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarma N. V., Shriniwas, Srinivas R. V. Production of S and R pyocins by Pseudomonas aeruginosa--a preliminary study. Indian J Med Res. 1980 Jan;71:36–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherertz R. J., Sarubbi F. A. A three-year study of nosocomial infections associated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):160–164. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.160-164.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt R., LaRue D., Parry M. F., Brokopp C. D., Klaucke D., Allen J. Pseudomonas aeruginosa skin infections in persons using a whirlpool in Vermont. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Apr;15(4):571–574. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.4.571-574.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. J., Govan J. R. Pyocine typing of mucoid strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from children with cystic fibrosis. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Aug;6(3):409–412. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-3-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]