Abstract
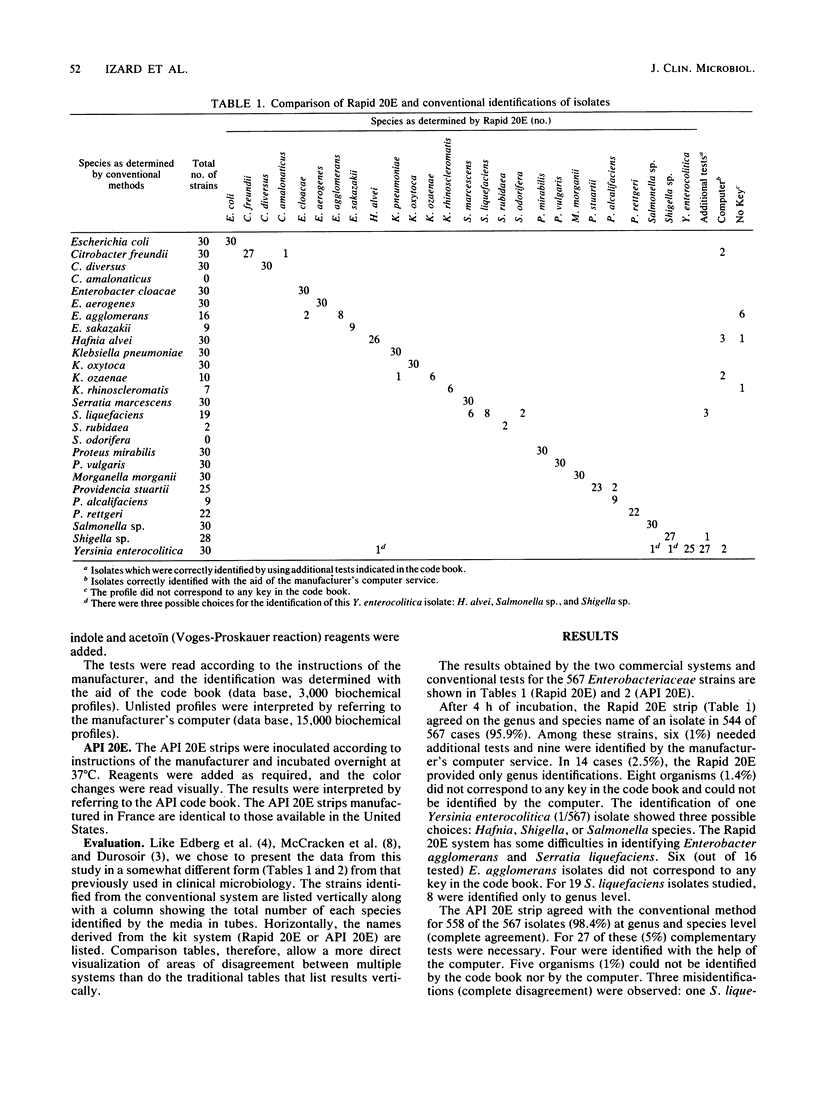
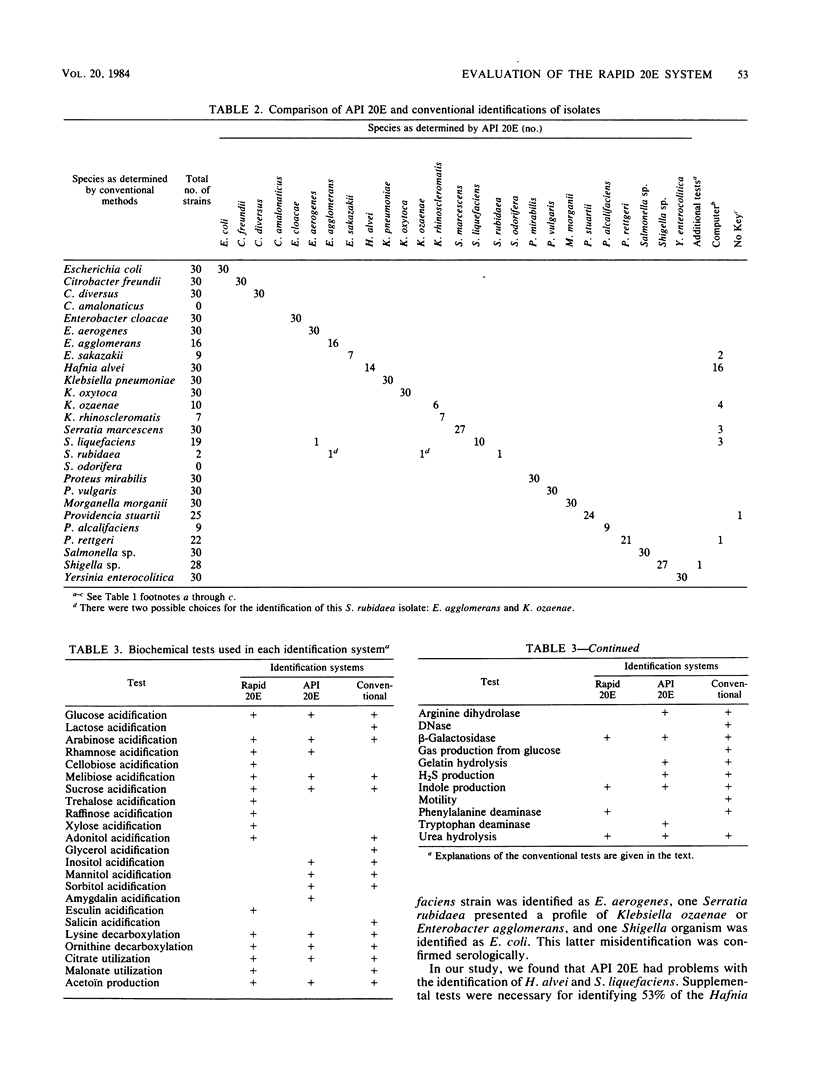
A study was conducted to compare the API Rapid 20E 4-h system (API System S.A., France; commercially available in the U.S.A. under the name DMS Rapid E System; DMS Laboratories, Darts Mill, Flemington, N.J.), the API 20E 18- to 24-h system (Analytab Products, Plainview, N.Y.), and a conventional media system to measure the ability of each to identify members of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Comparison tables rather than simple percentage agreement tables were generated to define the particular strengths and weaknesses of each system and to allow the laboratory to best use the data. The Rapid 20E compared quite favorably with conventional media. It yielded correct identifications with 95.9% of the isolates tested (API 20E, 98% identification rate). In 2.5% of the isolates, the Rapid 20E gave only genus identifications, and in 1.4% the organisms did not correspond to any key in the code book and could not be identified by the manufacturer's computer service. The ease of inoculation and the 4-h capability make the Rapid 20E system an extremely attractive development in the field of bacterial identification.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldridge K. E., Gardner B. B., Clark S. J., Matsen J. M. Comparison of micro-ID, API 20E, and conventional media systems in identification of Enterobacteriaceae. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jun;7(6):507–513. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.6.507-513.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durosoir J. L. ABAC identibiogramme: prototype of an automated system for identification of enterobacteria. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;2(1):26–31. doi: 10.1007/BF02019919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edberg S. C., Atkinson B., Chambers C., Moore M. H., Palumbo L., Zorzon C. F., Singer J. M. Clinical evaluation of the MICRO-ID, API 20E, and conventional media systems for identification of Enterobacteriacea. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Aug;10(2):161–167. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.2.161-167.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izard D., Gavini F., Ochin D., Enayeh E., Leclerc H. Evaluation of Micro-ID, for identification of Enterobacteriaceae. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1980 Dec;28(10):681–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izard D., Savage C., Enayeh E., Leclerc H., Troonen H. Rapid and automated identification of Enterobacteriaceae with the abbott MS-2 system and API-20E versus conventional methods. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1982 May;252(1):26–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken A. W., Martin W. J., McCarthy L. R., Schwab D. A., Cooper B. H., Helgeson N. G., Prowant S., Robson J. Evaluation of the MS-2 system for rapid identification of Enterobacteriaceae. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Nov;12(5):684–689. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.5.684-689.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


