Abstract
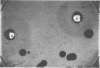
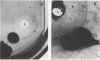
We examined an antiserum agar method to study its reliability in screening Staphylococcus aureus strains for capsule production. The encapsulated S. aureus Smith diffuse strain was compared with its nonencapsulated variant, Smith compact, in CCY medium containing 0.5% NaCl and 5.0% Smith diffuse rabbit antiserum. A halo was visible surrounding colonies of the Smith diffuse strain but not the Smith compact strain. On this same medium, the protein A-producing Cowan I strain possessed a halo that was visible on photographs. Single high-salt medium is known to inhibit protein A production, halo formation by the strains was also compared in 7.5% NaCl medium. The halo surrounding the Cowan I strain was not present when the salt content of the medium was increased. In contrast, the halo surrounding the Smith diffuse strain persisted in the 7.5% NaCl medium. By use of this medium, the antiserum agar technique may be valuable for the identification of encapsulated staphylococci without appreciable interference from protein A.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashton F. E., Ryan A., Diena B. B., Frasch C. E. Evaluation of the antiserum agar method for the serogroup identification of Neisseria meningitidis. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Jun;25(6):784–787. doi: 10.1139/m79-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw M. W., Schneerson R., Parke J. C., Jr, Robbins J. B. Bacterial antigens cross-reactive with the capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Lancet. 1971 May 29;1(7709):1095–1096. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91837-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven D. E., Frasch C. E., Mocca L. F., Rose F. B., Gonzalez R. Rapid serogroup identification of Neisseria meningitidis by using antiserum agar: Prevalence of serotypes in a disease-free military population. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Sep;10(3):302–307. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.3.302-307.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven D. E., Frasch C. E., Robbins J. B., Feldman H. A. Serogroup identification of Neisseria meningitidis: comparison of an antiserum agar method with bacterial slide agglutination. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 May;7(5):410–414. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.5.410-414.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINKELSTEIN R. A., SULKIN S. E. Characteristics of coagulase positive and coagulase negative staphylococci in serum-soft agar. J Bacteriol. 1958 Mar;75(3):339–344. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.3.339-344.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Use of staphylococcal protein A as an immunological reagent. J Immunol Methods. 1978;20:241–253. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90259-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT G. A., MOSES A. J. Acute infection of mice with Smith strain of Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1958 Dec 19;128(3338):1574–1575. doi: 10.1126/science.128.3338.1574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOENIG M. G. Factors relating to the virulence of staphylococci. I. Comparative studies on two colonial variants. Yale J Biol Med. 1962 Jun;34:537–559. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuzemenská P., Burian V., Frasch C. E., Svandová E. A comparison of the serum agar grouping and slide agglutination methods for the identification of Neisseria meningitidis strains. Bull World Health Organ. 1977;55(6):659–661. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind I. Protein A production in different strains of Staphylococcus aureus under varied growth conditions. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Dec;82(6):821–828. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movitz J. Formation of extracellular protein A by Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Sep;68(1):291–299. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickerson D. S., White J. G., Kronvali G., Williams R. C., Jr, Quie P. G. Indirect visualization of Staphylococcus aureus protein A. J Exp Med. 1970 May 1;131(5):1039–1047. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.5.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OEDING P. Agglutinability of pyogenic staphylococci at various conditions. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1957;41(4):310–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1957.tb01028.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH J. M., DUBOS R. J. The behavior of virulent and avirulent staphylococci in the tissues of normal mice. J Exp Med. 1956 Jan 1;103(1):87–108. doi: 10.1084/jem.103.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Bradshaw M., Whisnant J. K., Myerowitz R. L., Parke J. C., Jr, Robbins J. B. An Escherichia coli antigen cross-reactive with the capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b: occurrence among known serotypes, and immunochemical and biologic properties of E. coli antisera toward H. influenzae type b. J Immunol. 1972 Jun;108(6):1551–1562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivonen A., Renkonen O. V., Robbins J. B. Use of antiserum agar plates for serogrouping of meningococci. J Clin Pathol. 1977 Sep;30(9):834–837. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.9.834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]