Abstract
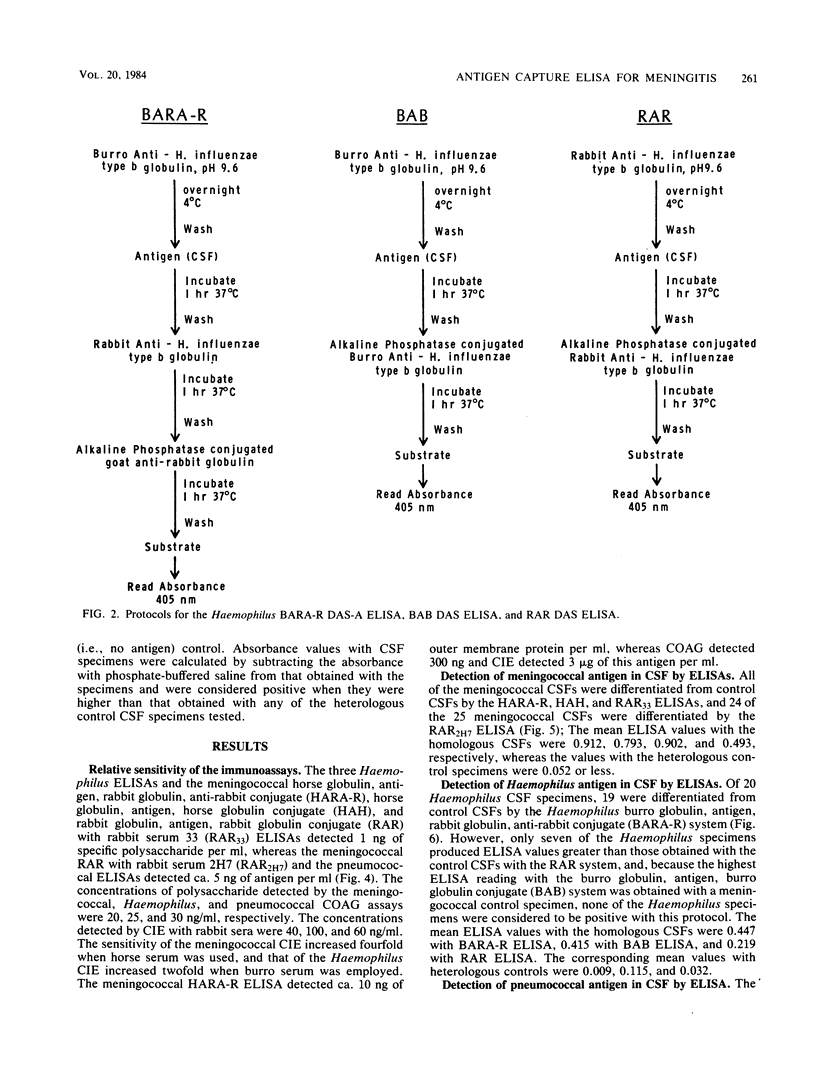
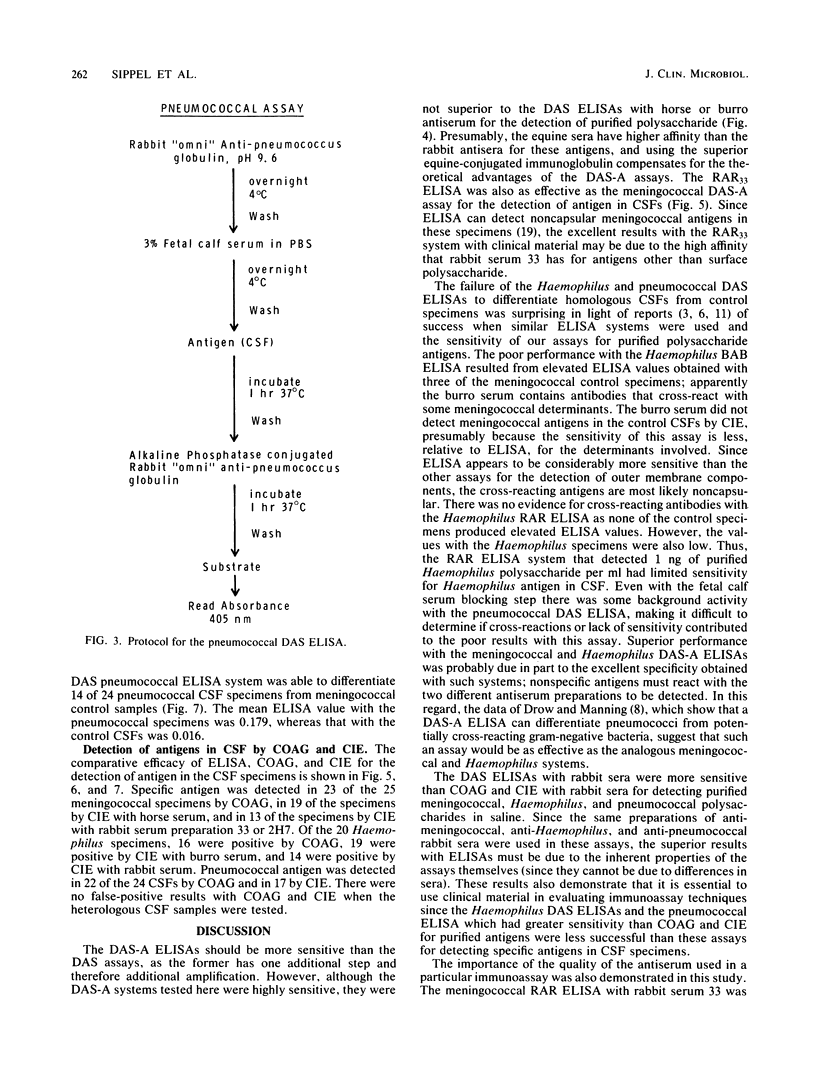
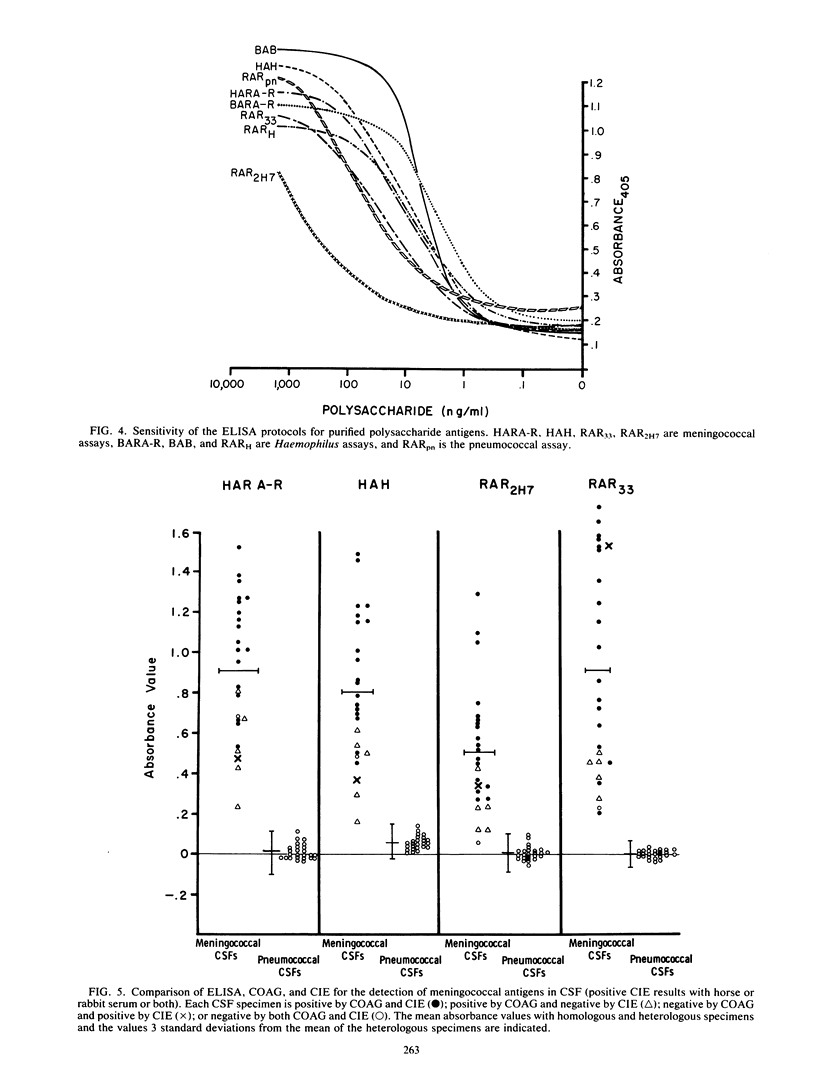
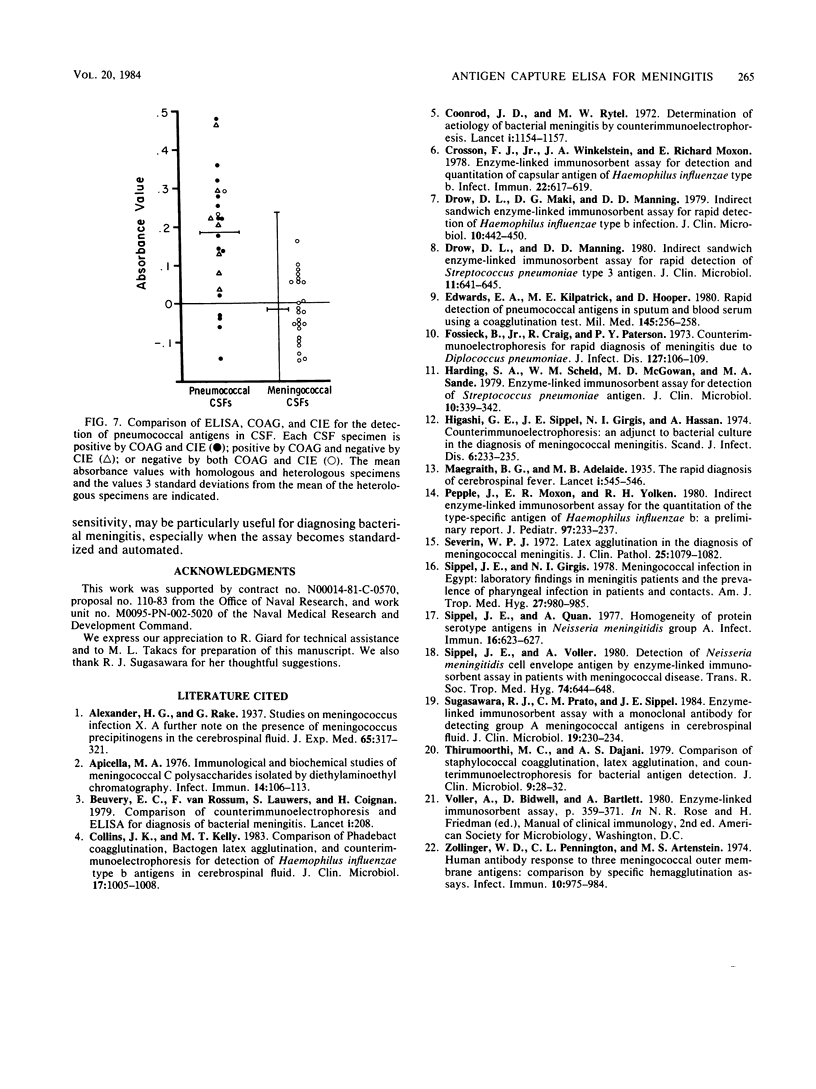
Antigen capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was compared to coagglutination and counterimmunoelectrophoresis for the detection of meningococcal, Haemophilus, and pneumococcal antigens. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay detected 1 ng of purified meningococcal and Haemophilus polysaccharides per ml and 5 ng of pneumococcal polysaccharide per ml; coagglutination detected 20, 25, and 30 ng/ml, respectively, of these polysaccharides; and counterimmunoelectrophoresis detected 10, 50, and 60 ng/ml. Double-antibody sandwich-antiglobulin enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays, which employed antibodies produced in two animal species, differentiated 100% of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) specimens from meningococcal meningitis patients and 95% of the CSFs from Haemophilus patients from heterologous control CSFs. Double-antibody sandwich procedures, which use the same antiserum preparation for coating the wells of microtiter plates and for alkaline phosphatase-conjugated immunoglobulin, differentiated meningococcal CSFs from control specimens but were unable to effectively differentiate the Haemophilus or pneumococcal specimens from control CSFs. Coagglutination detected specific antigen in 92% of the meningococcal CSFs, 80% of the Haemophilus CSFs, and 92% of the pneumococcal specimens. The comparable percentages for counterimmunoelectrophoresis were 76, 95, and 71%.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apicella M. A. Immunological and biochemical studies of meningococcal C polysaccharides isolated by diethylaminoethyl chromatography. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):106–113. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.106-113.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beuvery E. C., van Rossum F., Lauwers S., Coignau H. Comparison of counterimmunoelectrophoresis and ELISA for diagnosis of bacterial meningitis. Lancet. 1979 Jan 27;1(8109):208–208. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90599-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. K., Kelly M. T. Comparison of Phadebact coagglutination, Bactogen latex agglutination, and counterimmunoelectrophoresis for detection of Haemophilus influenzae type b antigens in cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;17(6):1005–1008. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.6.1005-1008.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coonrod J. D., Rytel M. W. Determination of aetiology of bacterial meningitis by counter-immunoelectrophoresis. Lancet. 1972 May 27;1(7761):1154–1157. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91376-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosson F. J., Jr, Winkelstein J. A., Moxon E. R. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection and quantitation of capsular antigen of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):617–619. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.617-619.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drow D. L., Maki D. G., Manning D. D. Indirect sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for rapid detection of Haemophilus influenzae type b infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):442–450. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.442-450.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drow D. L., Manning D. D. Indirect sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for rapid detection of Streptococcus pneumoniae type 3 antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jun;11(6):641–645. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.6.641-645.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards E. A., Kilpatrick M. E., Hooper D. Rapid detection of pneumococcal antigens in sputum and blood serum using a coagglutination test. Mil Med. 1980 Apr;145(4):256–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fossieck B., Jr, Craig R., Paterson P. Y. Counterimmunoelectrophoresis for rapid diagnosis of meningitis due to Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jan;127(1):106–109. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.1.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding S. A., Scheld W. M., McGowan M. D., Sande M. A. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Streptococcus pneumoniae antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Sep;10(3):339–342. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.3.339-342.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi G. I., Sippel J. E., Girgis N. I., Hassan A. Counterimmunoelectrophoresis: an adjunct to bacterial culture in the diagnosis of meningococcal meningitis. Scand J Infect Dis. 1974;6(3):233–235. doi: 10.3109/inf.1974.6.issue-3.04. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepple J., Moxon E. R., Yolken R. H. Indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the quantitation of the type-specific antigen of Haemophilus influenzae b: a preliminary report. J Pediatr. 1980 Aug;97(2):233–237. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80480-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severin W. P. Latex agglutination in the diagnosis of meningococcal meningitis. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Dec;25(12):1079–1082. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.12.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippel J. E., Girgis N. I. Meningococcal infection in Egypt: laboratory findings in meningitis patients and the prevalence of pharyngeal infection in patients and contacts. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 Sep;27(5):980–985. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippel J. E., Quan A. Homogeneity of protein serotype antigens in Neisseria meningitidis group A. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):623–627. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.623-627.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippel J. E., Voller A. Detection of Neisseria meningitidis cell envelope antigen by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in patients with meningococcal disease. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(5):644–648. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90156-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugasawara R. J., Prato C. M., Sippel J. E. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with a monoclonal antibody for detecting group A meningococcal antigens in cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):230–234. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.230-234.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thirumoorthi M. C., Dajani A. S. Comparison of staphylococcal coagglutination, latex agglutination, and counterimmunoelectrophoresis for bacterial antigen detection. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):28–32. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.28-32.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Pennington C. L., Artenstein M. S. Human antibody response to three meningococcal outer membrane antigens: comparison by specific hemagglutination assays. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):975–984. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.975-984.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


