Abstract
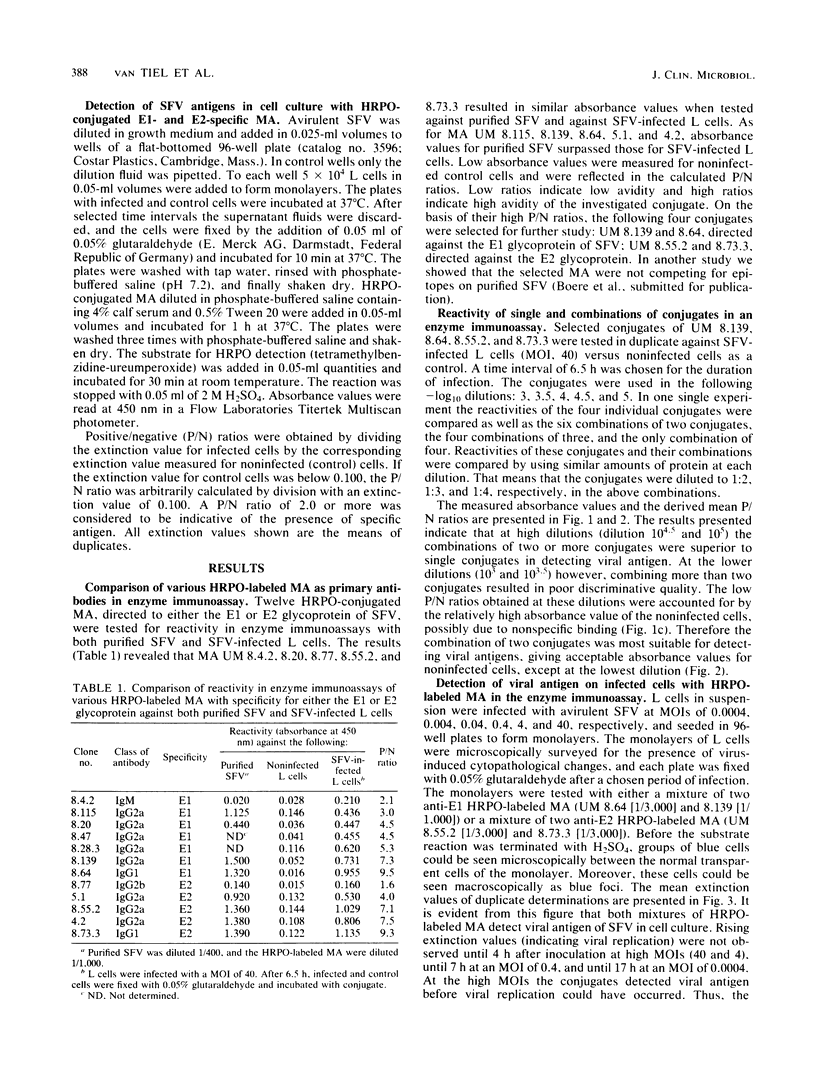
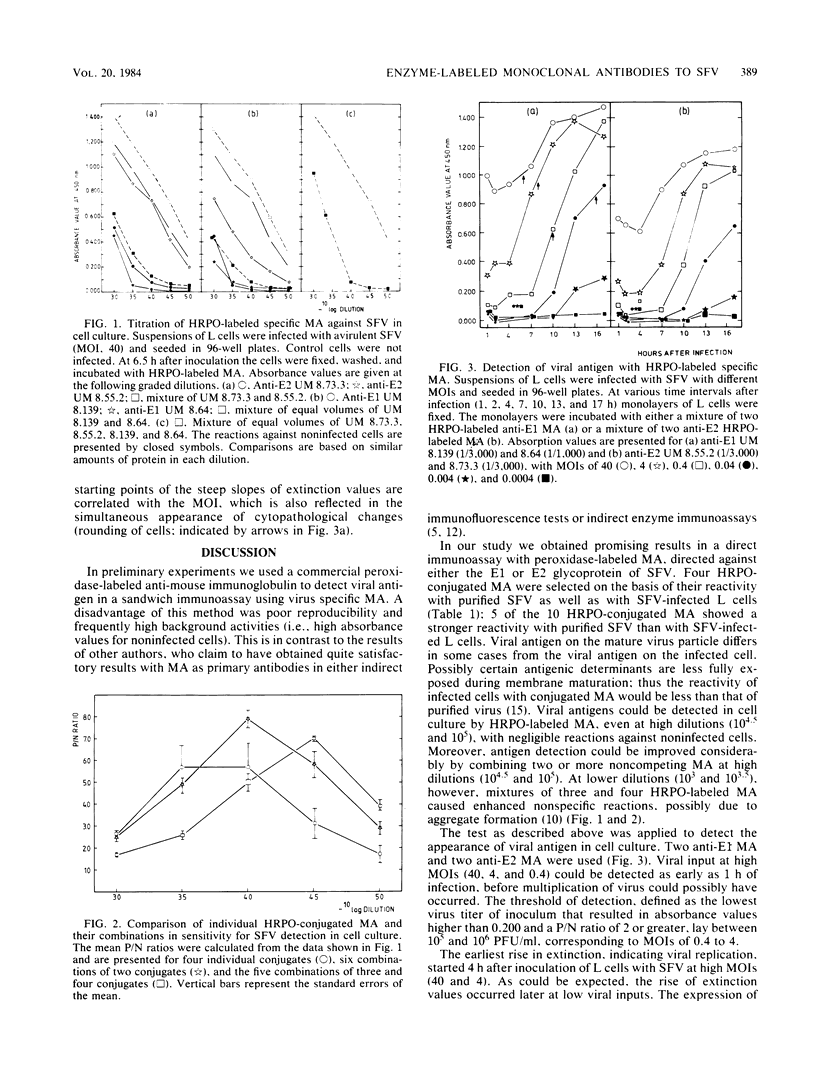
Four noncompeting monoclonal antibodies (MA) directed against either the E1 (UM 8.64 and 8.139) or E2 (UM 8.55 and 8.73) glycoprotein of Semliki Forest virus were purified and labeled with horseradish peroxidase. Each enzyme-labeled MA was tested alone and in combination with others for its sensitivity to detect virus-infected cells. Semliki Forest virus-infected L cells seeded as monolayers in 96-well plates were screened for the virus after incubation with enzyme-labeled MA and a substrate. In this system single enzyme-labeled MA even at high dilution (10(3.0) to 10(4.5] were able to detect virus-infected cells. The sensitivity of the test could be enhanced by combining two noncompeting MA (10(4.5) to 10(5.0]. Combinations of three and four MA were less effective, due to high absorbance values for noninfected cells. The threshold of virus defection was between 10(5) and 10(6) PFU/ml. This test is sensitive and specific and therefore may be useful for diagnostic purposes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson N. H., Tamm I. Replication of Semliki Forest virus: an electron microscopic study. Virology. 1967 May;32(1):128–143. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boere W. A., Benaissa-Trouw B. J., Harmsen M., Kraaijeveld C. A., Snippe H. Neutralizing and non-neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to the E2 glycoprotein of Semliki Forest virus can protect mice from lethal encephalitis. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jun;64(Pt 6):1405–1408. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-6-1405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter G. B. The rapid titration of Semliki forest virus in cell monolayers by immunofluorescence. J Gen Virol. 1969 Jan;4(1):139–143. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-4-1-139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cevenini R., Donati M., Moroni A., Franchi L., Rumpianesi F. Rapid immunoperoxidase assay for detection of respiratory syncytial virus in nasopharyngeal secretions. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Oct;18(4):947–949. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.4.947-949.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein L. C., McDougall J., Hackman R., Meyers J. D., Thomas E. D., Nowinski R. C. Monoclonal antibodies to cytomegalovirus: rapid identification of clinical isolates and preliminary use in diagnosis of cytomegalovirus pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):273–281. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.273-281.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson B. E., Metselaar D., Kirya G. B., Timms G. L. Investigations into yellow fever virus and other arboviruses in the northern regions of Kenya. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;42(5):787–795. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King B., Wust C. J., Brown A. Antibody-dependent, complement-mediated homologous and cross-cytolysis of togavirus-infected cells. J Immunol. 1977 Oct;119(4):1289–1292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraaijeveld C. A., Harmsen M., Khader Boutahar-Trouw B. Delayed-type hypersensitivity against Semliki Forest virus in mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):219–223. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.219-223.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensson K., Orvell C. Cellular localization of five structural proteins of Sendai virus studied with peroxidase-labelled Fab fragments of monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1983 Aug;64(Pt 8):1673–1678. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-8-1673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane P. K., Kawaoi A. Peroxidase-labeled antibody. A new method of conjugation. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1084–1091. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilheden E., Jeansson S., Vahlne A. Typing of herpes simplex virus by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;17(4):677–680. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.4.677-680.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowinski R. C., Tam M. R., Goldstein L. C., Stong L., Kuo C. C., Corey L., Stamm W. E., Handsfield H. H., Knapp J. S., Holmes K. K. Monoclonal antibodies for diagnosis of infectious diseases in humans. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):637–644. doi: 10.1126/science.6297006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Ota M., Gallo D., Fox V. L. Monoclonal antibodies for rapid, strain-specific identification of influenza virus isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Oct;16(4):763–765. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.4.763-765.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolcott J. A., Wust C. J., Brown A. Identification of immunologically cross-reactive proteins of Sindbis virus: evidence for unique conformation of E1 glycoprotein from infected cells. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):379–385. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.379-385.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yelton D. E., Scharff M. D. Monoclonal antibodies: a powerful new tool in biology and medicine. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:657–680. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


