Abstract
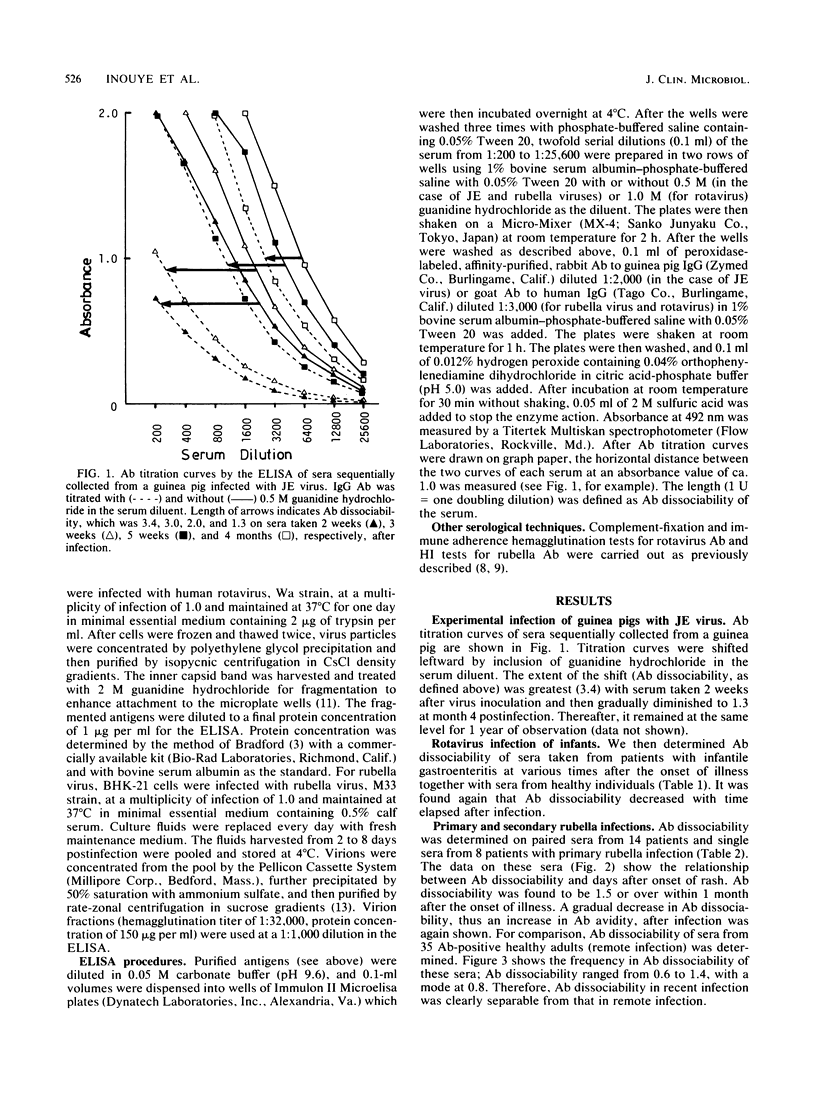
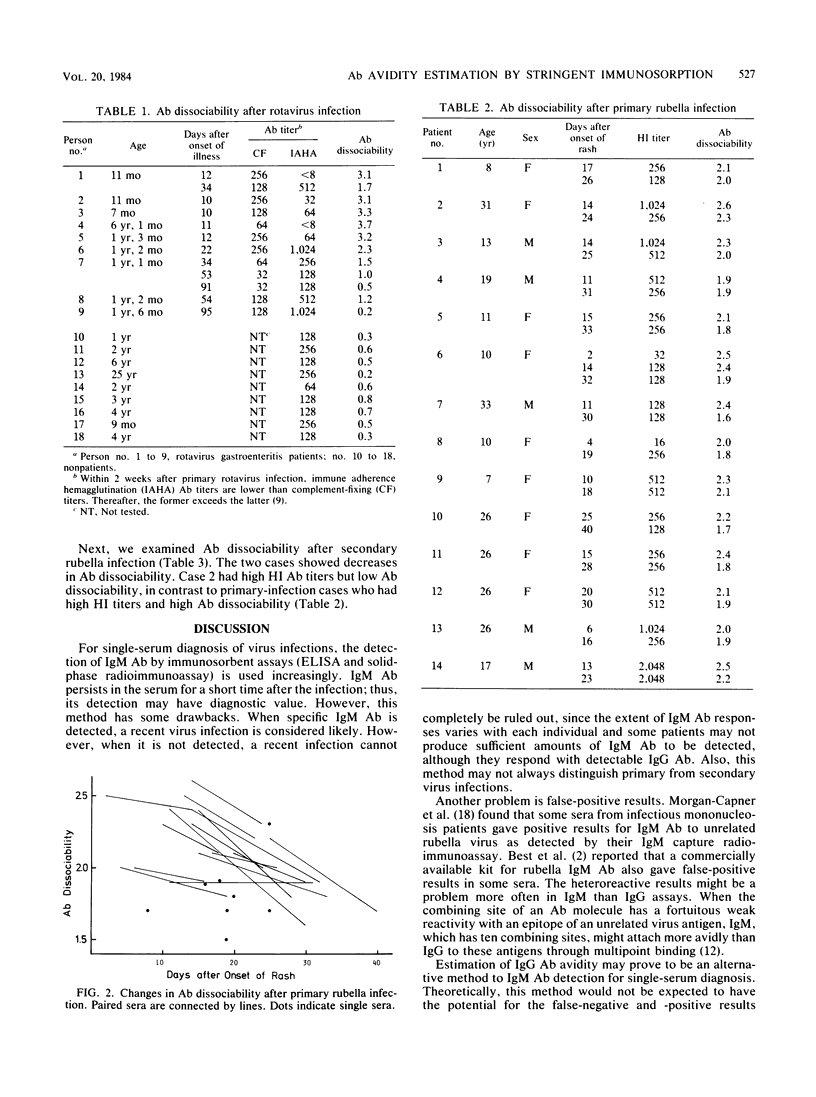
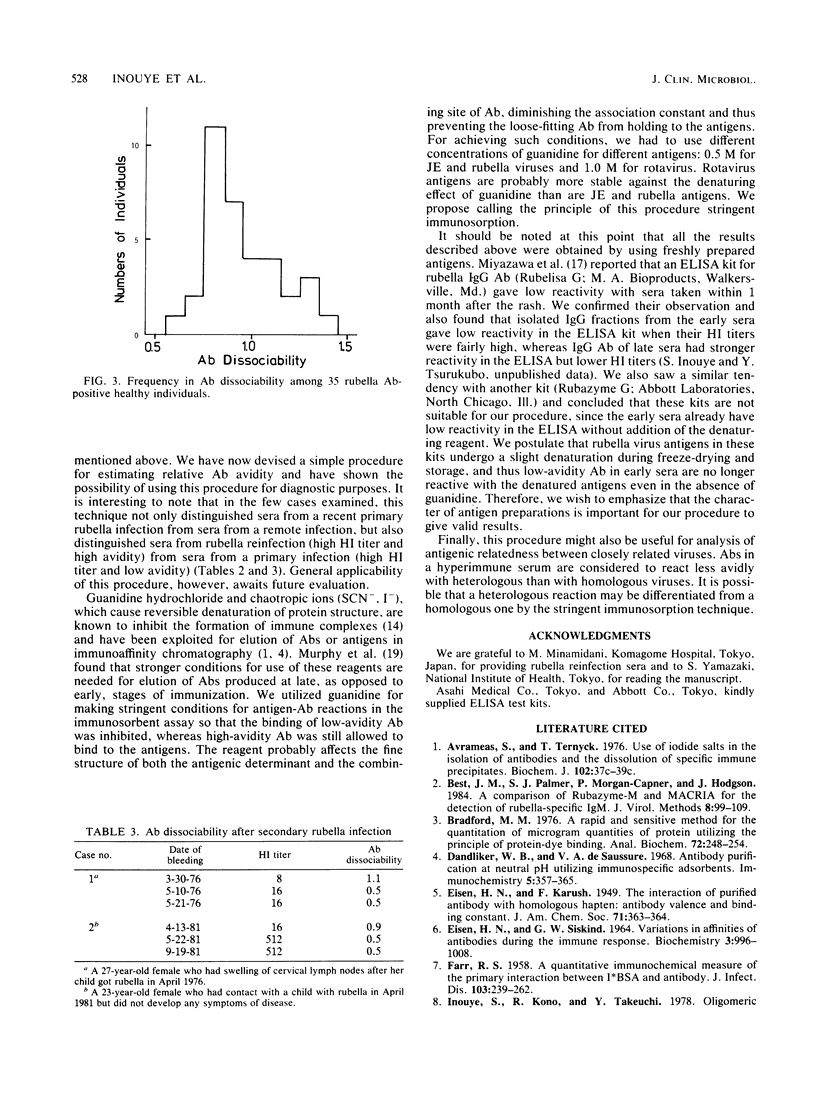
In titrating serum immunoglobulin G antibody to viruses by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, we used two rows of wells for serial twofold dilutions of the serum; in one row, a low concentration of a protein denaturant, 0.5 or 1.0 M guanidine hydrochloride, was added to the diluent so that the binding of low-avidity antibodies to viral antigens on the solid phase was inhibited. We then compared the antibody titration curves obtained in the two rows. We found that the addition of the reagent resulted in a parallel leftward shift of the curves and that the extent of the shift was greater in early than in late sera from all of the three infections studied (Japanese encephalitis virus, rotavirus, and rubella virus infections). This procedure may be useful for estimation of the avidity of antibody in serum and, with further evaluation, may prove to be applicable to single-serum diagnosis of virus infections.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashihara Y., Miyazawa H., Tokieda M., Yamabe H. [Serological investigation of the hemagglutination inhibition test and enzyme linked immunosorbent assay to rubella infection (author's transl)]. Rinsho Byori. 1982 Mar;30(3):269–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. Use of iodide salts in the isolation of antibodies and the dissolution of specific immune precipitates. Biochem J. 1967 Mar;102(3):37C–39C. doi: 10.1042/bj1020037c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best J. M., Palmer S. J., Morgan-Capner P., Hodgson J. A comparison of Rubazyme-M and MACRIA for the detection of rubella-specific IgM. J Virol Methods. 1984 Feb;8(1-2):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(84)90044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dandliker W. B., De Saussure V. A. Antibody purification at neutral pH utilizing immunospecific adsorbents. Immunochemistry. 1968 Jul;5(4):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(68)90131-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISEN H. N., SISKIND G. W. VARIATIONS IN AFFINITIES OF ANTIBODIES DURING THE IMMUNE RESPONSE. Biochemistry. 1964 Jul;3:996–1008. doi: 10.1021/bi00895a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARR R. S. A quantitative immunochemical measure of the primary interaction between I BSA and antibody. J Infect Dis. 1958 Nov-Dec;103(3):239–262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Kono R., Takeuchi Y. Oligomeric immunoglobulin A antibody response to rubella virus infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jul;8(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.1.1-6.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Matsuno S., Kono R. Difference in antibody reactivity between complement fixation and immune adherence hemagglutination tests with virus antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):241–246. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.241-246.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Matsuno S., Tsurukubo Y. "Original antigenic sin" phenomenon in experimental flavivirus infections of guinea pigs: studies by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Microbiol Immunol. 1984;28(5):569–574. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1984.tb00709.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Matsuno S., Yamaguchi H. Efficient coating of the solid phase with rotavirus antigens for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of immunoglobulin A antibody in feces. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):259–263. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.259-263.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEINSCHMIDT W. J., BOYER P. D. Interaction of protein antigens and antibodies. I. Inhibition studies with the egg albumin-antiegg albumin system. J Immunol. 1952 Sep;69(3):247–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katow S., Matsuno T. Base composition of rubella virus RNA. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1980;65(1):67–70. doi: 10.1007/BF01340542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehtonen O. P., Meurman O. H. An ELISA for the estimation of high-avidity and total specific IgG and IgM antibodies to rubella virus. J Virol Methods. 1982 Sep;5(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(82)90091-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno S., Nagayoshi S. Quantitative estimation of infantile gastroenteritis virus antigens in stools by immune adherence hemagglutination test. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Mar;7(3):310–311. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.3.310-311.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan-Capner P., Tedder R. S., Mace J. E. Rubella-specific IgM reactivity in sera from cases of infectious mononucleosis. J Hyg (Lond) 1983 Jun;90(3):407–413. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400029041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. F., Imam A., Hughes A. E., McGucken M. J., Buchanan K. D., Conlon J. M., Elmore D. T. Avoidance of strongly chaotropic eluents for immunoaffinity chromatography by chemical modification of immobilized ligand. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 20;420(1):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90347-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodkey L. S., Freeman M. J. Variations in the properties of rabbit antibodies during prolonged immunization by various routes with serum albumin in Freund's complete adjuvant. Immunology. 1970 Aug;19(2):219–224. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siskind G. W., Benacerraf B. Cell selection by antigen in the immune response. Adv Immunol. 1969;10:1–50. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60414-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G. The immune response to influenza virus. 3. Changes in the avidity and specificity of early IgM and IgG antibodies. Immunology. 1968 Jan;14(1):39–52. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


