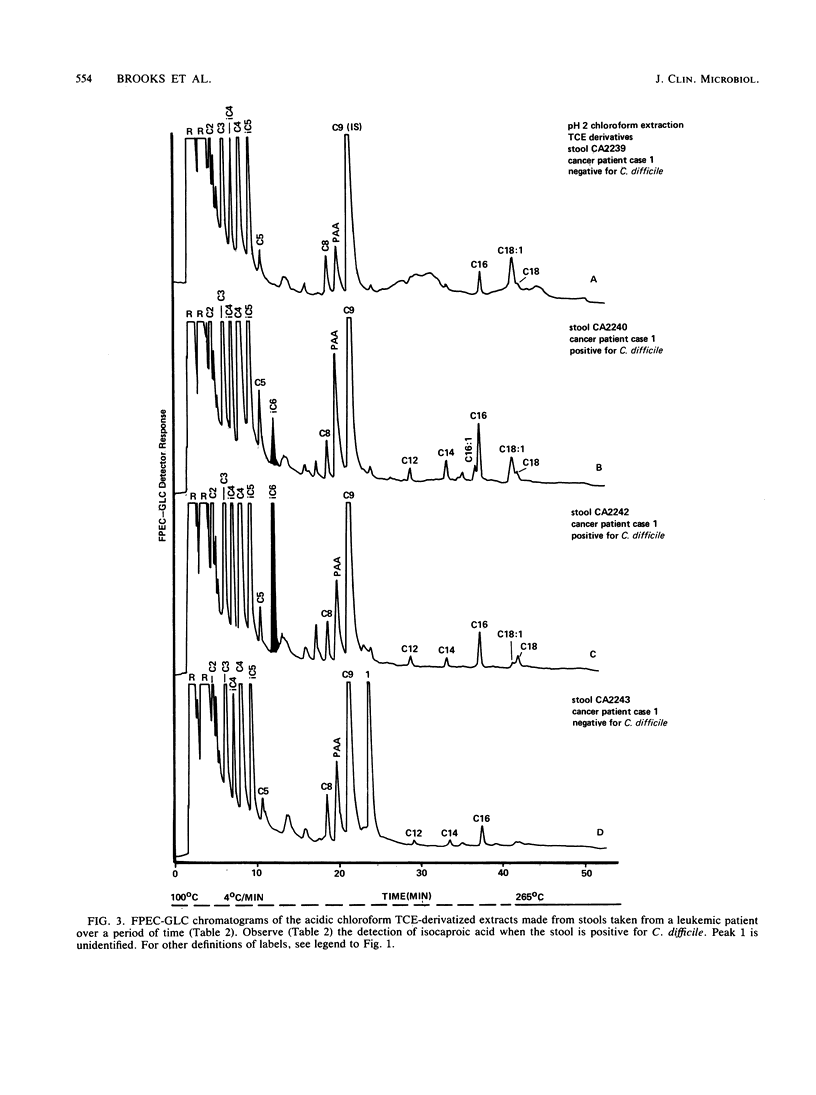
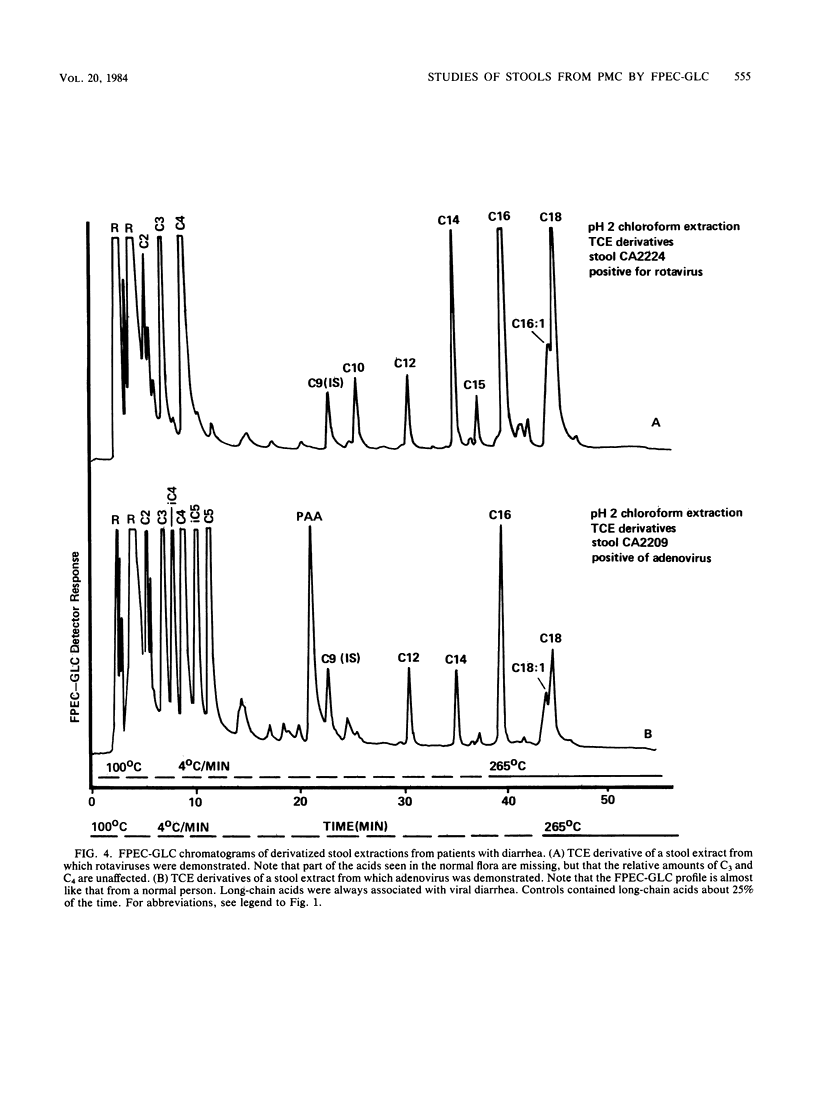
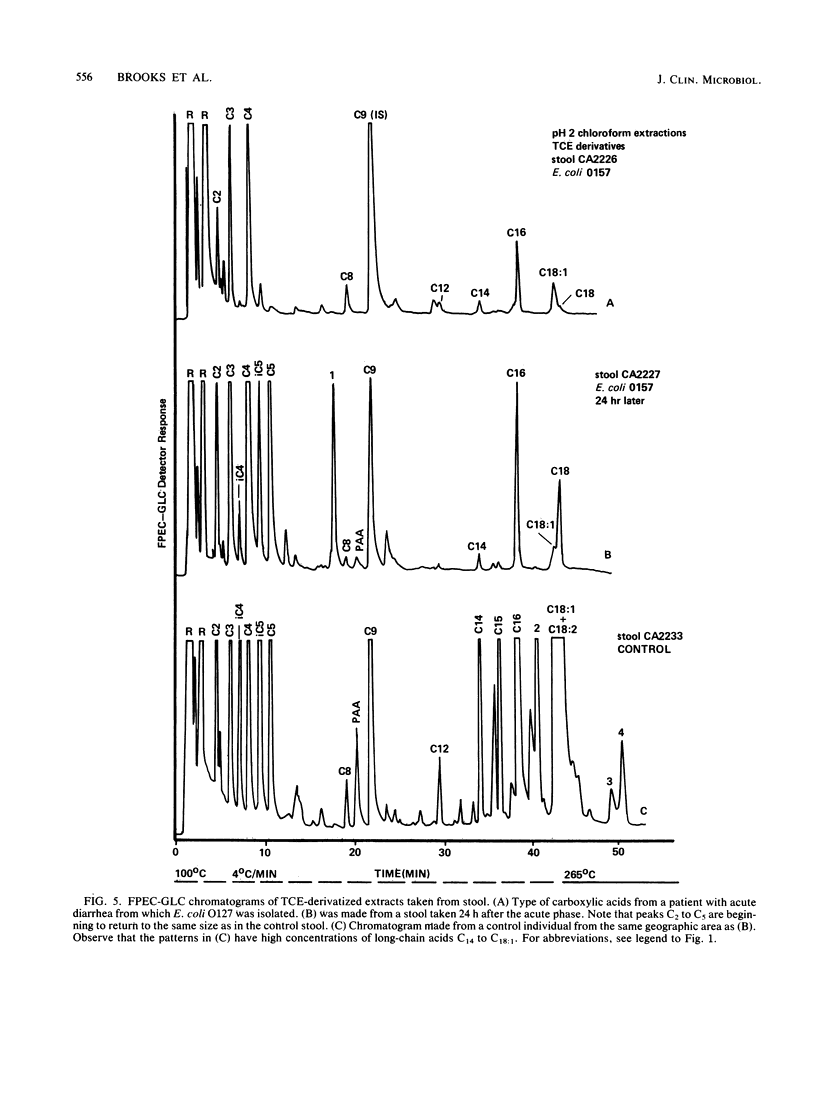
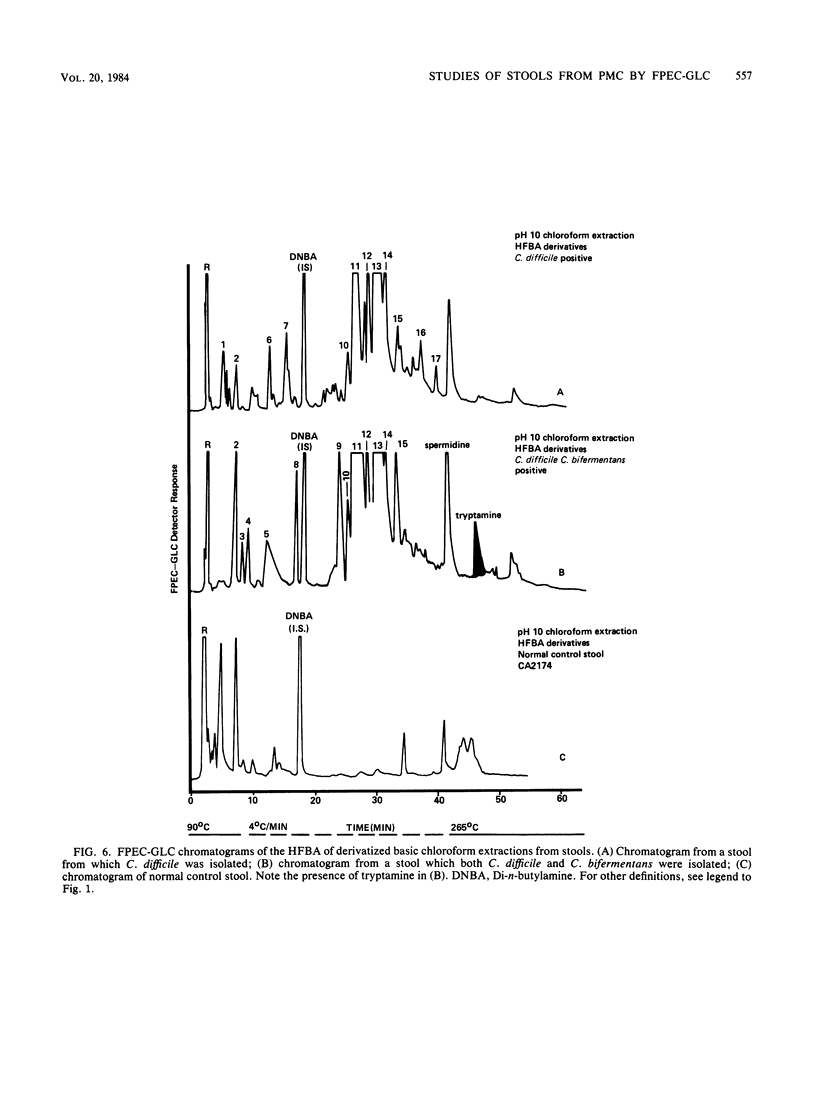
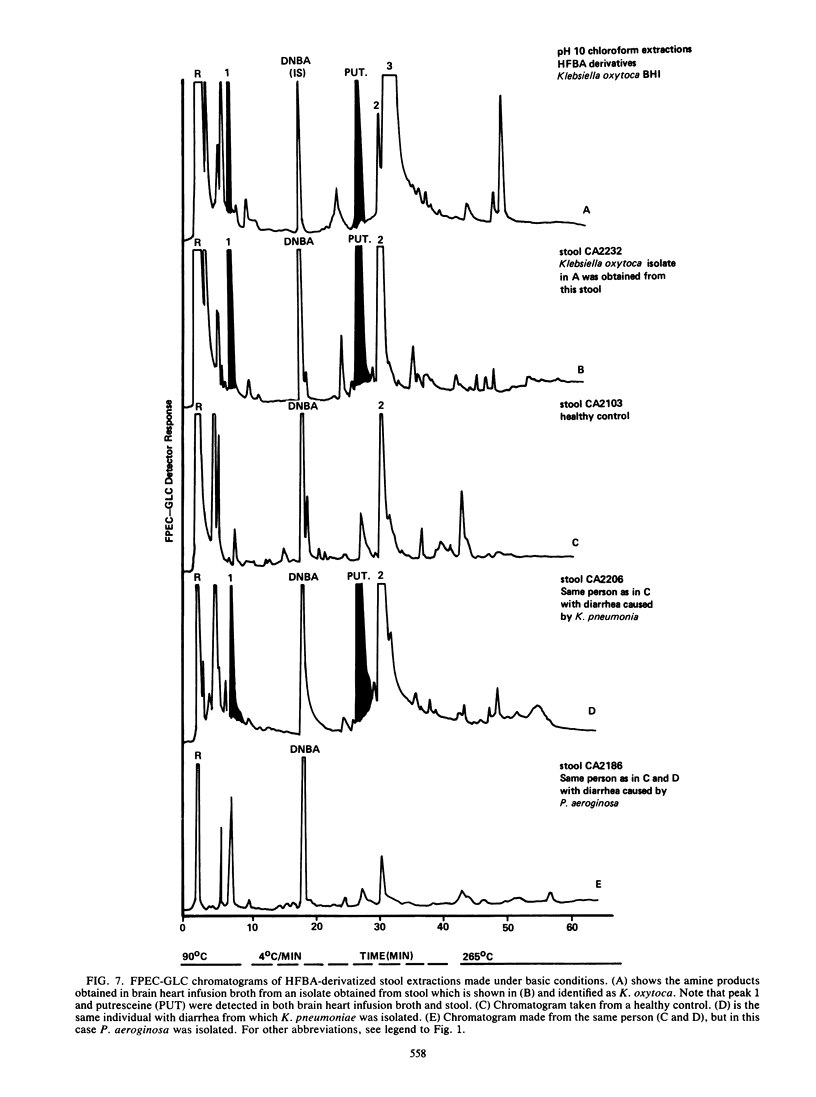
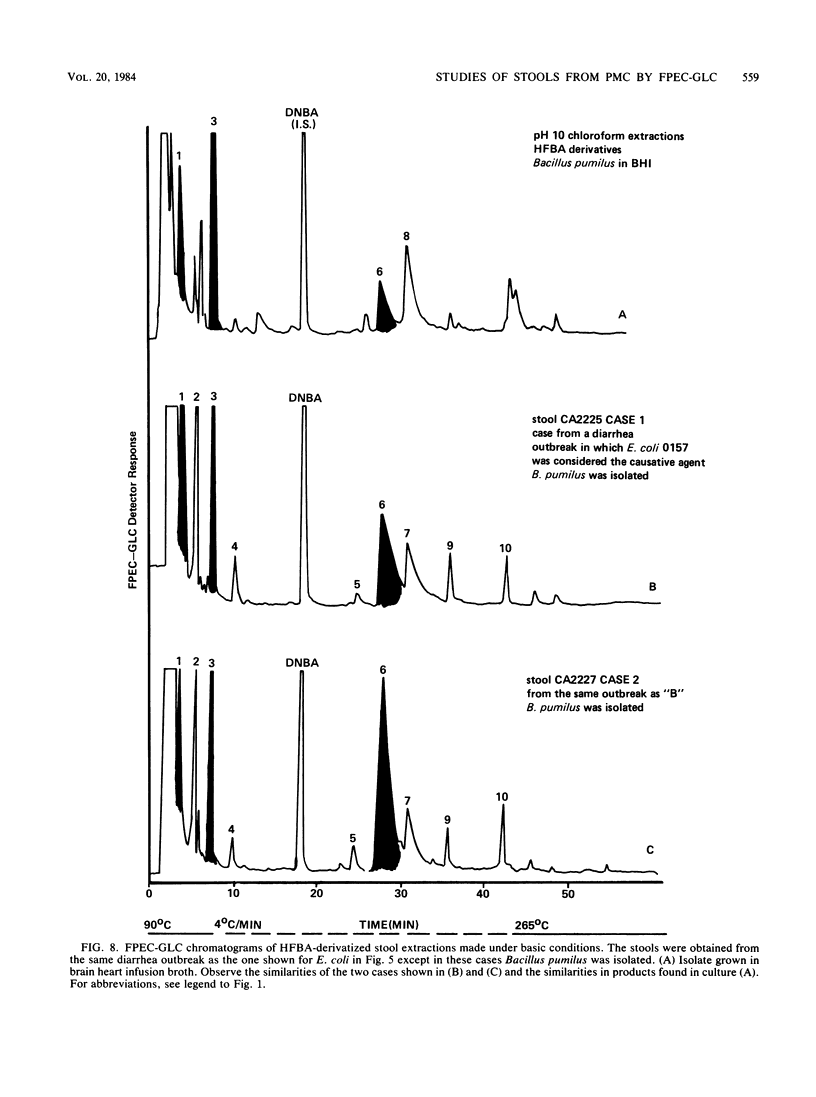
Abstract
Thirty-five patients with various diarrheal syndromes and 22 controls were studied. All stool samples were carefully cultured for Clostridium difficile, using selective isolation media. Cytotoxin assays with proper antitoxin neutralization were done in MRC-5 cells. The stool samples were extracted four times, three times at pH 2 and once at pH 10, using CHCl3 or ether. Derivatizations of extracts were done with trichloroethanol, heptafluorobutyric anhydride, and heptafluorobutyric anhydride-ethanol, and all derivatives were analyzed by frequency-pulsed electron capture gas-liquid chromatography (FPEC-GLC). A dedicated computer was used to assist in both qualitative and quantitative data analysis. Isocaproic acid (iC6) was always found in stool from which C. difficile was isolated and was absent in C. difficile-negative specimens. p-Cresol was found frequently in both persons with pseudomembranous colitis and controls. Tryptamine was found in stool containing C. bifermentans. The FPEC-GLC profiles of persons with acute diarrhea were very different from those of normal persons. Diarrhea associated with adenovirus and rotavirus, Klebsiella spp., and Escherichia spp. showed different FPEC-GLC patterns. Stools from well persons consistently contained full-scale peaks of pyruvic, acetic, propionic, isobutyric, butyric, isovaleric, and valeric acids. In rotavirus stools isobutyric, isovaleric, and valeric acids were reduced in quantity from those found in control stools, whereas propionic and butyric acids were increased.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alley C. C., Brooks J. B., Kellogg D. S., Jr Electron capture gas-liquid chromatographic-mass spectral identification of acids produced by Neisseria meningitidis in a defined medium. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):97–102. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.97-102.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., Chang T. W., Moon N., Onderdonk A. B. Antibiotic-induced lethal enterocolitis in hamsters: studies with eleven agents and evidence to support the pathogenic role of toxin-producing Clostridia. Am J Vet Res. 1978 Sep;39(9):1525–1530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borriello S. P. Gas-liquid chromatography and Clostridium difficile. Lancet. 1981 Dec 5;2(8258):1283–1283. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91515-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. B., Kellogg D. S., Jr, Shepherd M. E., Alley C. C. Rapid differentiation of the major causative agents of bacterial meningitis by use of frequency-pulsed electron capture gas-liquid chromatograph: analysis of acids. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jan;11(1):45–51. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.1.45-51.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. B., Kellogg D. S., Jr, Shepherd M. E., Alley C. C. Rapid differentiation of the major causative agents of bacterial meningitis by use of frequency-pulsed electron capture gas-liquid chromatography: analysis of amines. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jan;11(1):52–58. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.1.52-58.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. B., Moore W. E. Gas chromatographic analysis of amines and other compounds produced by several species of Clostridium. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Dec;15(12):1433–1447. doi: 10.1139/m69-257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. B., Moss C. W., Dowell V. R. Differentiation between Clostridium sordellii and Clostridi- um bifermentans by gas chromatography. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):528–530. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.528-530.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Blacklow N. R., Cukor G. G., Vibulbandhitkit S., Changchawalit S., Boonthai P. Rotavirus as a cause of severe gastroenteritis in adults. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):663–667. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.663-667.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George R. H., Symonds J. M., Dimock F., Brown J. D., Arabi Y., Shinagawa N., Keighley M. R., Alexander-Williams J., Burdon D. W. Identification of Clostridium difficile as a cause of pseudomembranous colitis. Br Med J. 1978 Mar 18;1(6114):695–695. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6114.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. L., Rolfe R. D., Finegold S. M. Clostridium difficile and its cytotoxin in feces of patients with antimicrobial agent-associated diarrhea and miscellaneous conditions. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1049–1053. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1049-1053.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. L., Sutter V. L., Citron D., Finegold S. M. Selective and differential medium for isolation of Clostridium difficile. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):214–219. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.214-219.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Nunez-Montiel O. L. Analysis of short-chain acids from bacteria by gas-liquid chromatography with a fused-silica capillary column. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):308–311. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.308-311.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunez-Montiel O. L., Thompson F. S., Dowell V. R., Jr Norleucine-tyrosine broth for rapid identification of Clostridium difficile by gas-liquid chromatography. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;17(2):382–385. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.2.382-385.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potvliege C., Labbé M., Yourassowsky E. Gas-liquid chromatography as screening test for Clostridium difficile. Lancet. 1981 Nov 14;2(8255):1105–1105. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91296-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Wachsmuth I. K., Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Sokolow R., Morris G. K. Laboratory investigation of hemorrhagic colitis outbreaks associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):512–520. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.512-520.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong J. C., Wigand R., Kidd A. H., Wadell G., Kapsenberg J. G., Muzerie C. J., Wermenbol A. G., Firtzlaff R. G. Candidate adenoviruses 40 and 41: fastidious adenoviruses from human infant stool. J Med Virol. 1983;11(3):215–231. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890110305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


