Abstract
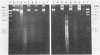
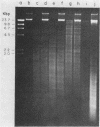
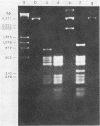
We used the restriction endonuclease HaeIII to differentiate Neisseria gonorrhoeae from other Neisseria species and Branhamella catarrhalis. A total of 16 clinical isolates and four American Type Culture Collection strains of N. gonorrhoeae were resistant to HaeIII digestion, whereas 17 isolates and four American Type Culture Collection strains from eight different bacterial species were susceptible. This resistance was not caused by an enzyme inhibitor. We propose that protection of the HaeIII recognition sequence by methylation is the mechanism of resistance since N. gonorrhoeae DNA became susceptible to digestion when passed in Escherichia coli as part of a plasmid clone.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anand C. M., Kadis E. M. Evaluation of the Phadebact Gonococcus Test for confirmation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jul;12(1):15–17. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.1.15-17.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler L. O., Knight R. D. Laboratory diagnosis of gonococcal infection by genetic transformation. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):810–814. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.810-814.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clanton D. J., Woodward J. M., Miller R. V. Identification of a new sequence-specific endonuclease, NgoII, from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):270–273. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.270-273.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amato R. F., Eriquez L. A., Tomfohrde K. M., Singerman E. Rapid identification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis by using enzymatic profiles. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jan;7(1):77–81. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.1.77-81.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson D., Moi H., Forslin L. Diagnosis of urogenital gonorrhoea by detecting gonococcal antigen with a solid phase enzyme immunoassay (Gonozyme). J Clin Pathol. 1983 Jun;36(6):674–677. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.6.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janik A., Juni E., Heym G. A. Genetic Transformation as a tool for detection of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jul;4(1):71–81. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.1.71-81.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korch C., Hagblom P., Normark S. Sequence-specific DNA modification in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1324–1332. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1324-1332.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer P. R., Waldrop A. A., Ward D. C. Enzymatic synthesis of biotin-labeled polynucleotides: novel nucleic acid affinity probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6633–6637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann M. B., Smith H. O. Specificity of Hpa II and Hae III DNA methylases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Dec;4(12):4211–4221. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.12.4211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Huq I., Alim A. R., So M., Samadpour-Motalebi M., Falkow S. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by DNA colony hybridization. J Infect Dis. 1980 Dec;142(6):892–898. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.6.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanker S., Daley D. A., Sorrell T. C. A rapid slid coagglutination test-an alternative to the fluorescent antibody test for the identification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Apr;34(4):420–423. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.4.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitkins S. A., Anderson R. D. Failure of the fluorescent antibody reaction to identify penicillinase-producing gonococci. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Feb;35(2):215–218. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]