Abstract
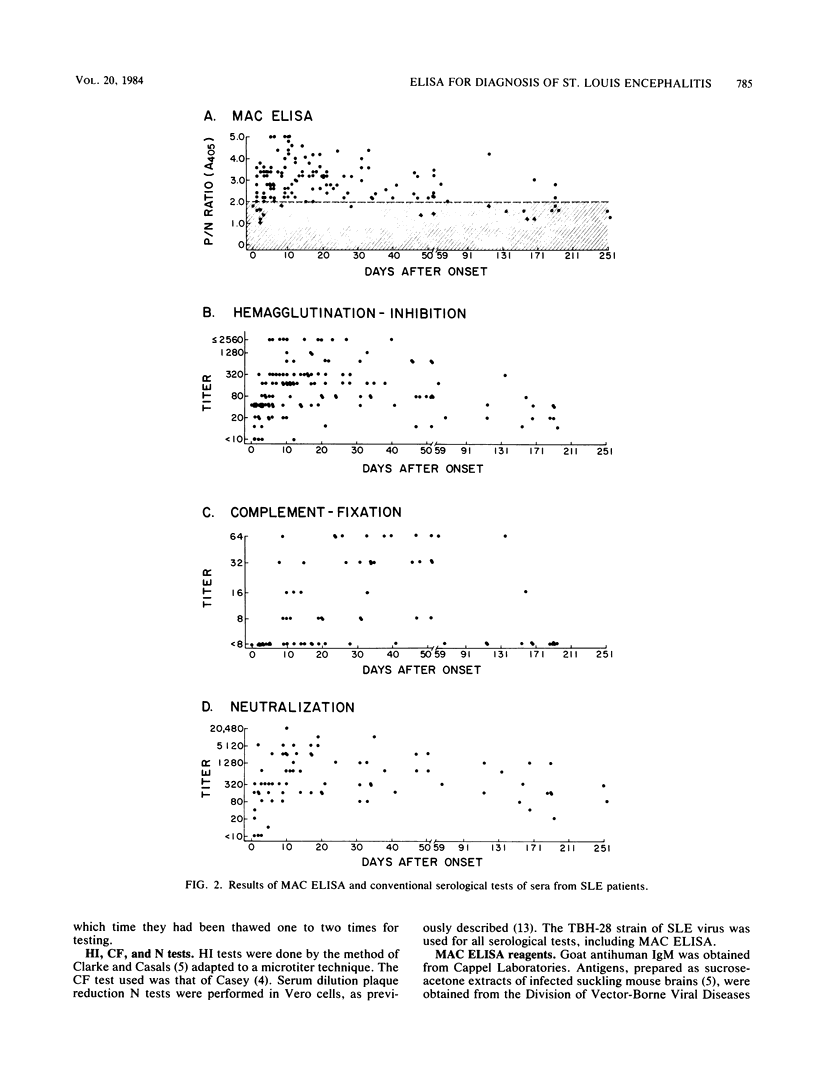
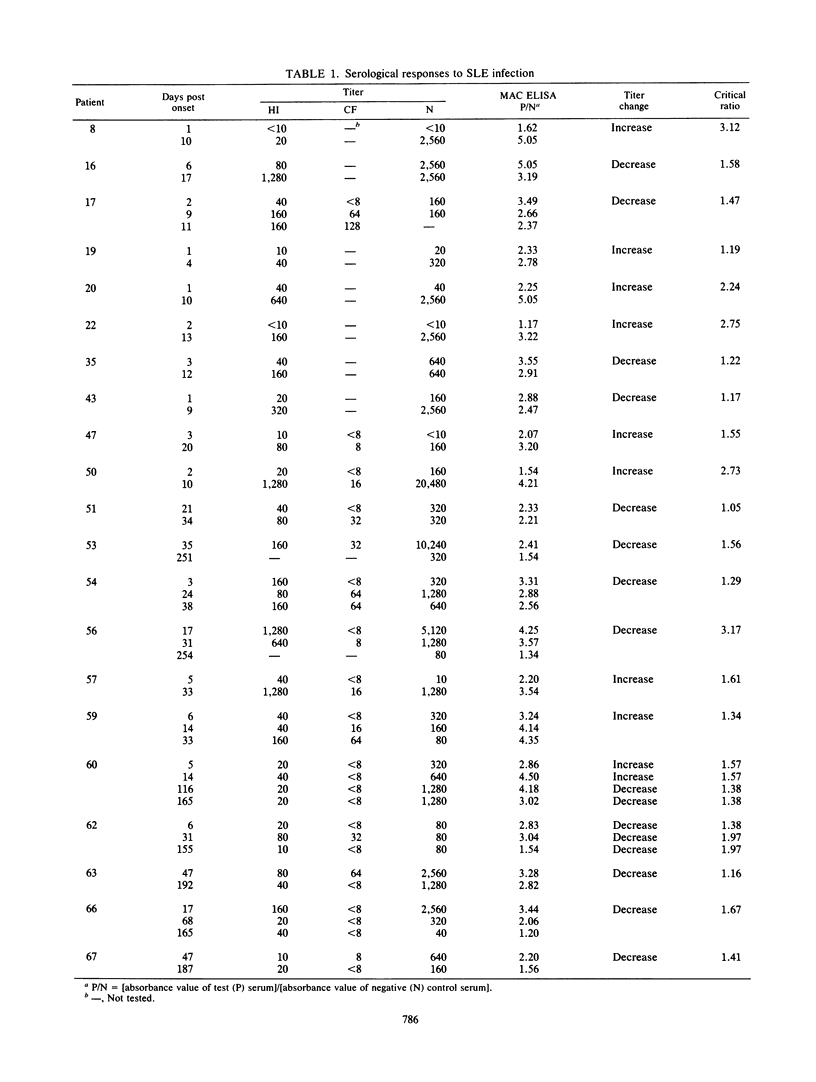
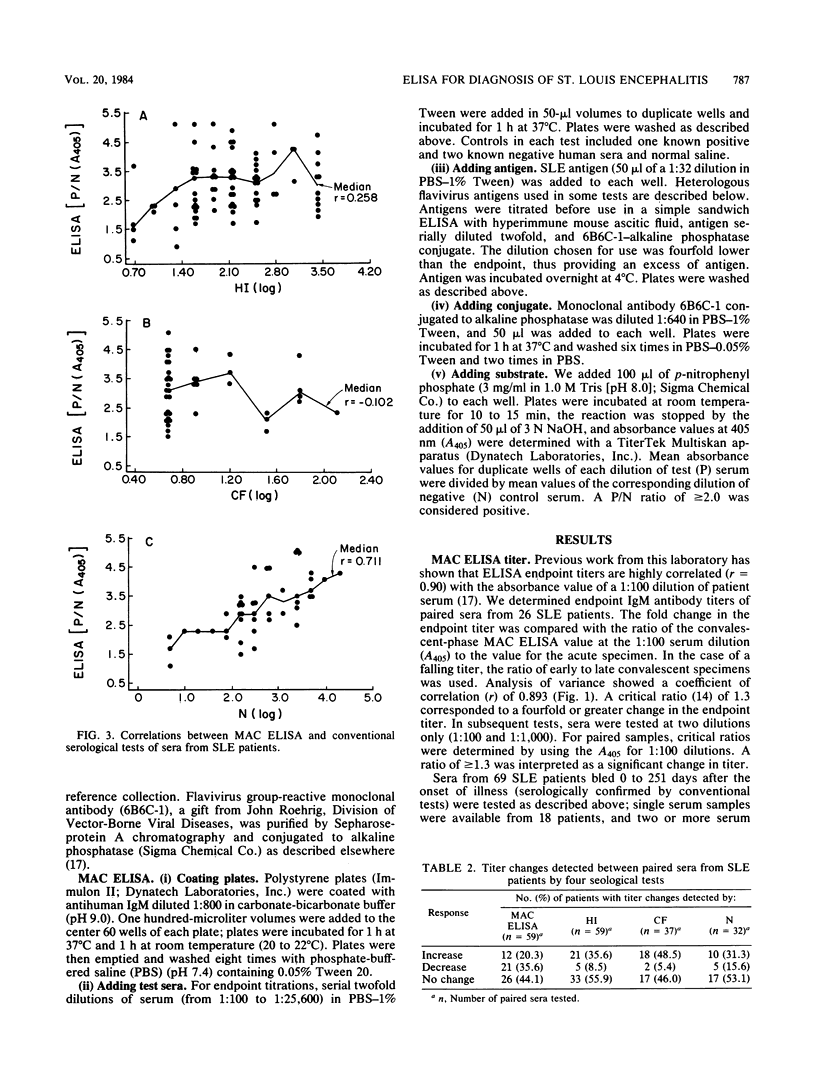
Sera from patients with St. Louis encephalitis were tested with an immunoglobulin M (IgM) antibody capture enzyme immunoassay (MAC ELISA). The assay used five reagents: antihuman IgM, test serum, sucrose-acetone-extracted mouse brain antigen, broadly cross-reactive flavivirus monoclonal antibody conjugated to alkaline phosphatase, and substrate (p-nitrophenyl phosphate). MAC ELISA endpoint titers correlated (r = 0.893) with the absorbance value of a 1:100 dilution of patient serum. Significant (fourfold or greater) changes in the endpoint titers between paired sera corresponded to a critical ratio (ratio of absorbance values at the 1:100 dilution) of greater than or equal to 1.3. IgM antibodies were detected in 71% of patients bled at 0 to 3 days after the onset of illness, in 99% bled at 4 to 21 days, and in 91% bled at 22 to 67 days. Thereafter, the IgM seropositivity rate declined; however, 29% of sera were still positive at 115 to 251 days after the onset of illness. MAC ELISA titers were significantly correlated with hemagglutination inhibition (r = 0.258) and neutralization (r = 0.711) titers. Because IgM antibodies appeared early and waned rapidly, a diagnosis was made on the basis of a decrease in titer more often by MAC ELISA than by hemagglutination inhibition, complement fixation, or neutralization tests. IgM antibodies generally showed a high degree of specificity; heterologous cross-reactions were, however, present in 4 of 14 sera examined. The MAC ELISA is useful for the rapid, early diagnosis of St. Louis encephalitis.
Full text
PDF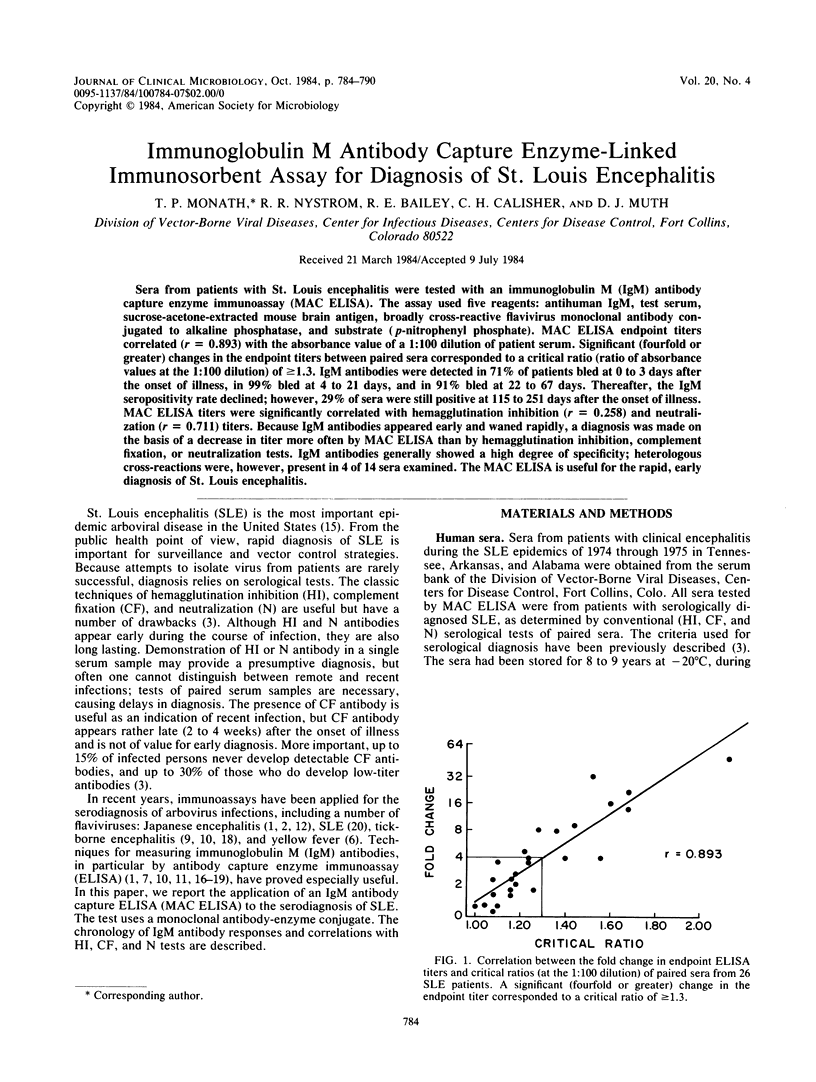


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burke D. S., Nisalak A. Detection of Japanese encephalitis virus immunoglobulin M antibodies in serum by antibody capture radioimmunoassay. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Mar;15(3):353–361. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.3.353-361.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. S., Nisalak A., Ussery M. A. Antibody capture immunoassay detection of japanese encephalitis virus immunoglobulin m and g antibodies in cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Dec;16(6):1034–1042. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.6.1034-1042.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE D. H., CASALS J. Techniques for hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition with arthropod-borne viruses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Sep;7(5):561–573. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deubel V., Mouly V., Salaun J. J., Adam C., Diop M. M., Digoutte J. P. Comparison of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) with standard tests used to detect yellow fever virus antibodies. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1983 May;32(3):565–568. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1983.32.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duermeyer W., Wielaard F., van der Veen J. A new principle for the detection of specific IgM antibodies applied in an ELISA for hepatitis A. J Med Virol. 1979;4(1):25–32. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890040104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinz F. X., Roggendorf M., Hofmann H., Kunz C., Deinhardt F. Comparison of two different enzyme immunoassays for detection of immunoglobulin M antibodies against tick-borne encephalitis virus in serum and cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Aug;14(2):141–146. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.2.141-146.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann H., Frisch-Niggemeyer W., Heinz F. Rapid diagnosis of tick-borne encephalitis by means of enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. J Gen Virol. 1979 Mar;42(3):505–511. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-42-3-505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamnback T. L., Beaty B. J., Hildreth S. W., Brown K. L., Gundersen C. B. Capture immunoglobulin M system for rapid diagnosis of La Crosse (California encephalitis) virus infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):577–580. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.577-580.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi E., Yamaoka M. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibodies to Japanese encephalitis virus in swine sera. Kobe J Med Sci. 1982 Feb;28(1):7–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsey H. S., Calisher C. H., Mathews J. H. Serum dilution neutralization test for California group virus identification and serology. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Dec;4(6):503–510. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.6.503-510.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monath T. P. Arthropod-borne encephalitides in the Americas. Bull World Health Organ. 1979;57(4):513–533. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roehrig J. T. Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the identification of arthropod-borne togavirus antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1982 Nov;63(Pt 1):237–240. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-63-1-237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roggendorf M., Heinz F., Deinhardt F., Kunz C. Serological diagnosis of acute tick-borne encephalitis by demonstration of antibodies of the IgM class. J Med Virol. 1981;7(1):41–50. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890070105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz H., von Deimling U., Flehmig B. Detection of IgM antibodies to cytomegalovirus (CMV) using an enzyme-labelled antigen (ELA). J Gen Virol. 1980 Sep;50(1):59–68. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff K. L., Muth D. J., Hudson B. W., Trent D. W. Evaluation of the solid-phase radioimmunoassay for diagnosis of St. Louis encephalitis infection in humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Aug;14(2):135–140. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.2.135-140.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


