Abstract
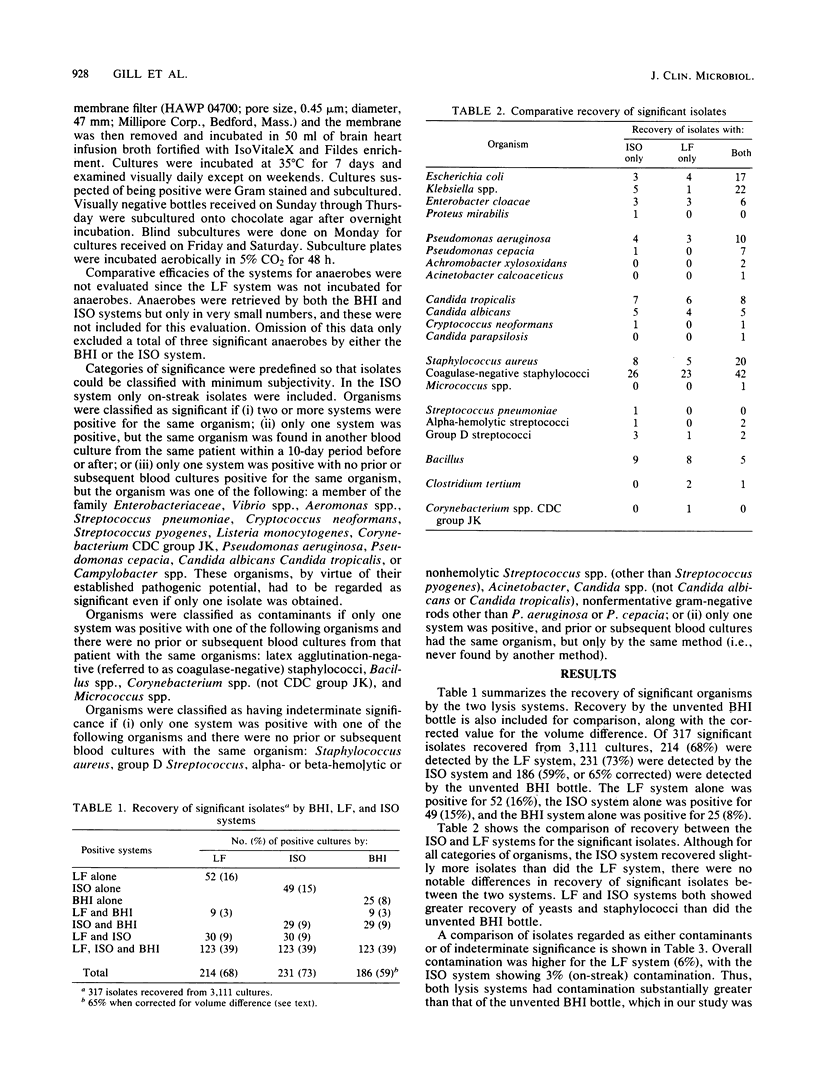
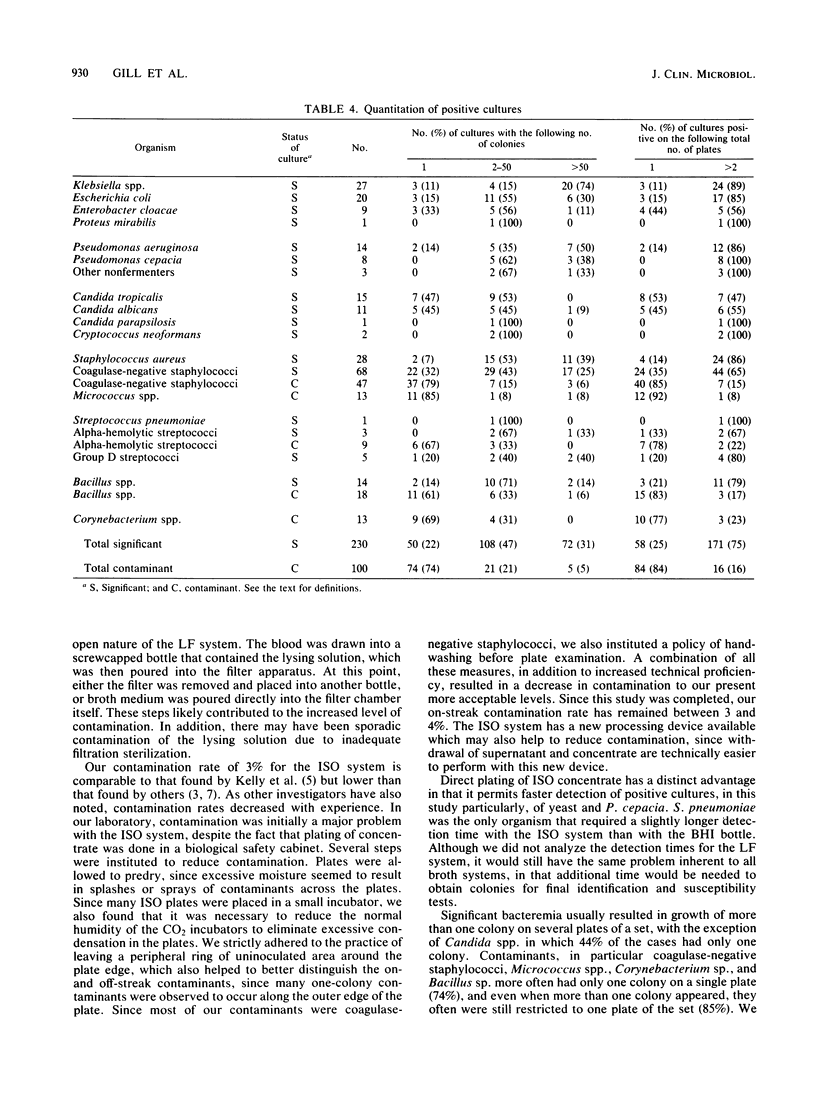
Evaluation of a commercially available lysis-centrifugation blood culture system (Isolator, DuPont Co., Wilmington, Del.) and a lysis-filtration blood culture system for 3,111 cultures showed that both methods had comparable recoveries (73 and 68%, respectively) of significant aerobic and facultatively anaerobic isolates. The unvented conventional blood culture bottle had a recovery rate of 59%. Although the lysis-centrifugation and lysis-filtration systems had comparable recoveries of pathogens, the lysis-centrifugation system had the advantage of having colonies immediately available for further testing. The contamination rate with the lysis-centrifugation system was 3%, compared with 6% with the lysis-filtration system and 0.4% with brain heart infusion.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dorn G. L., Smith K. New centrifugation blood culture device. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jan;7(1):52–54. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.1.52-54.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry N. K., McLimans C. A., Wright A. J., Thompson R. L., Wilson W. R., Washington J. A., 2nd Microbiological and clinical evaluation of the isolator lysis-centrifugation blood culture tube. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):864–869. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.864-869.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan R. L., Schuette W. H., Zierdt C. H., MacLowry J. D. Rapid automated disgnosis of bacteremia by impedance detection. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jan;5(1):51–57. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.1.51-57.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. T., Buck G. E., Fojtasek M. F. Evaluation of a lysis-centrifugation and biphasic bottle blood culture system during routine use. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):554–557. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.554-557.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. T., Fojtasek M. F., Abbott T. M., Hale D. C., Dizikes J. R., Boshard R., Buck G. E., Martin W. J., Matsen J. M. Clinical evaluation of a lysis-centrifugation technique for the detection of septicemia. JAMA. 1983 Oct 28;250(16):2185–2188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson R. B., Jr, Vanzo S. J., Henry N. K., Guenther K. L., Washington J. A., 2nd Contamination of cultures processed with the isolator lysis-centrifugation blood culture tube. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):97–99. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.97-99.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whimbey E., Wong B., Kiehn T. E., Armstrong D. Clinical correlations of serial quantitative blood cultures determined by lysis-centrifugation in patients with persistent septicemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):766–771. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.766-771.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierdt C. H. Blood-lysing solution nontoxic to pathogenic bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):172–174. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.172-174.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierdt C. H. Evidence for transient Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteremia in patients and in healthy humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;17(4):628–630. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.4.628-630.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierdt C. H., Kagan R. L., MacLowry J. D. Development of a lysis-filtration blood culture technique. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jan;5(1):46–50. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.1.46-50.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierdt C. H., Peterson D. L., Swan J. C., MacLowry J. D. Lysis-filtration blood culture versus conventional blood culture in a bacteremic rabbit model. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):74–77. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.74-77.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


