Abstract
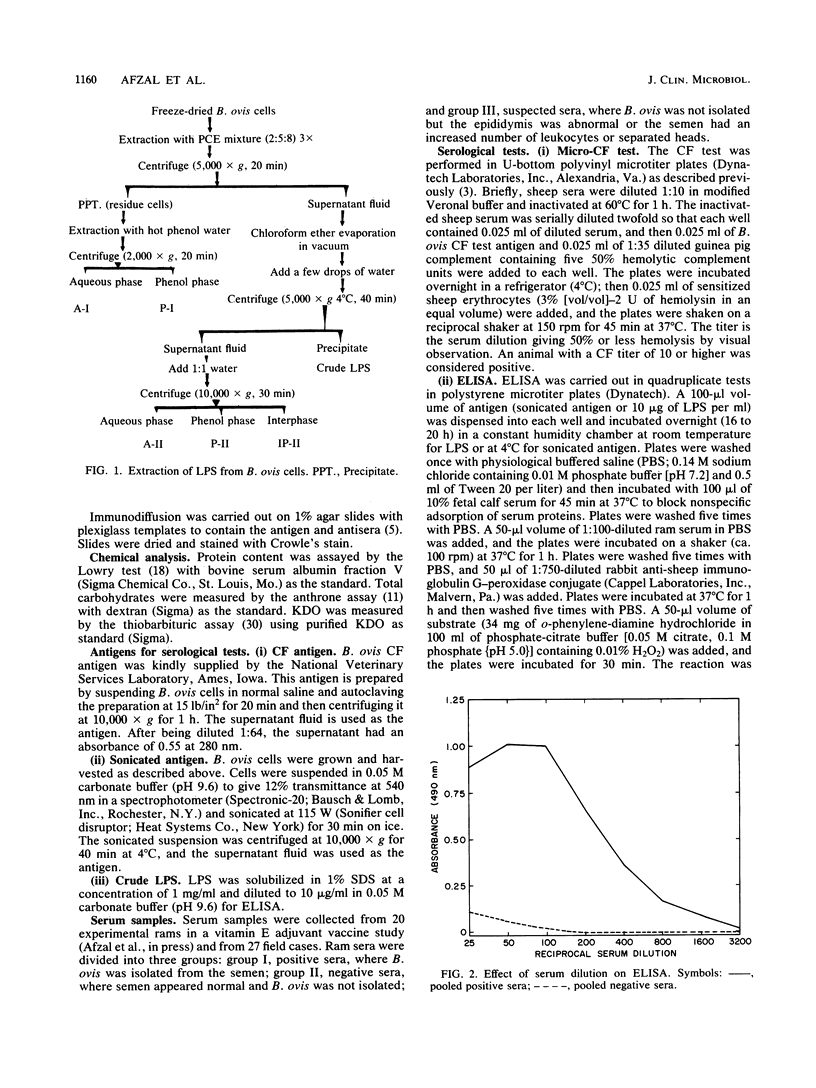
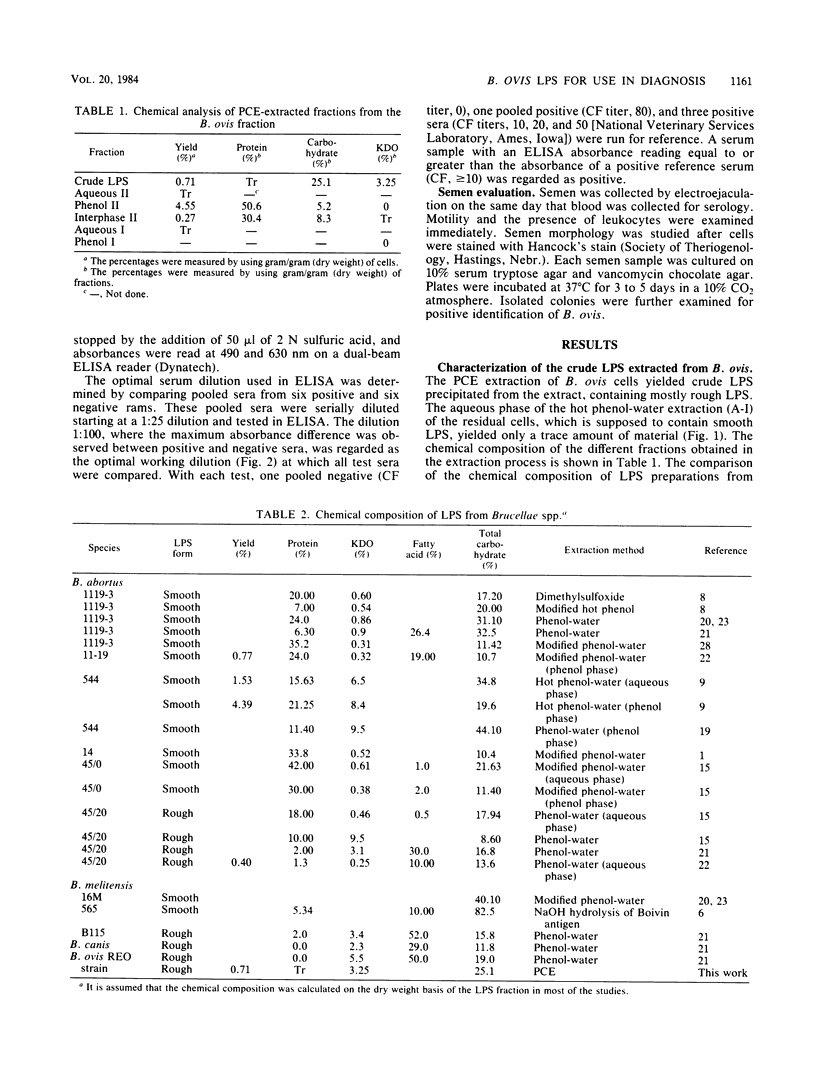
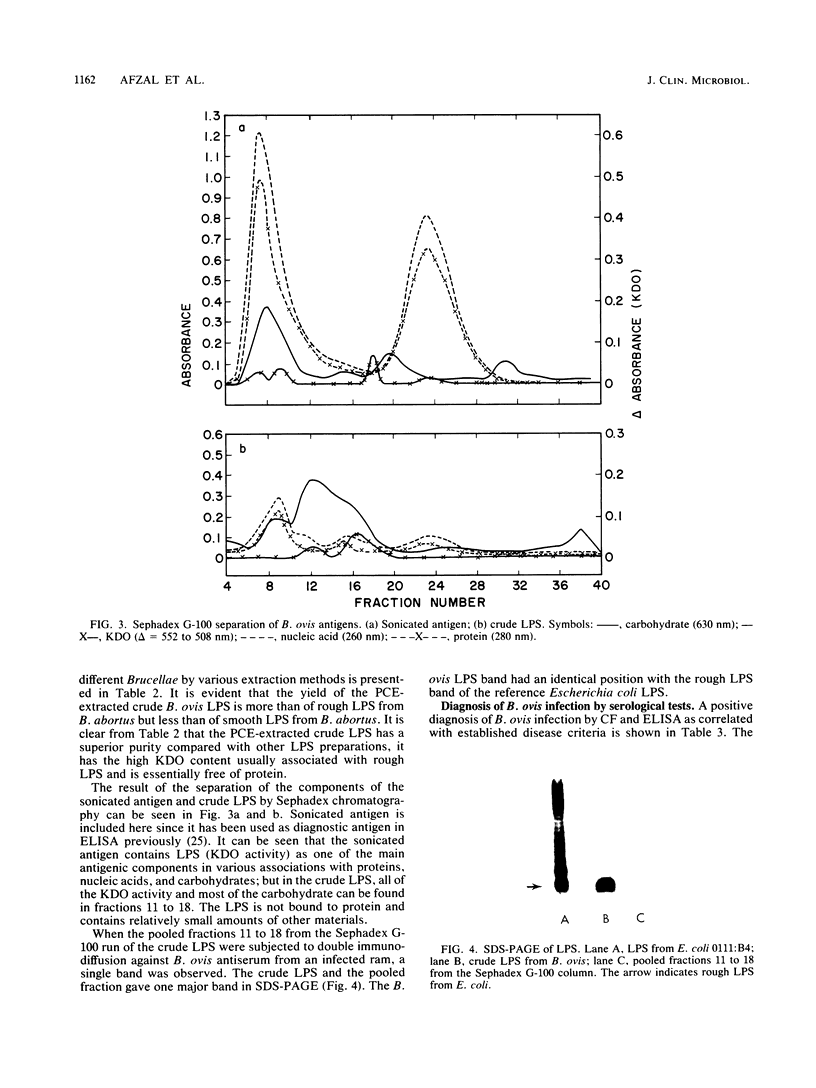
Rough lipopolysaccharide, extracted by a mixture of phenol, chloroform, and petroleum ether from freeze-dried Brucella ovis cells with a yield of 0.71%, contained relatively small amounts of protein and nucleic acid contaminants as compared with lipopolysaccharides from other Brucellae. The crude lipopolysaccharide was suitable as a diagnostic antigen in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the sensitive and specific detection of ram epididymitis caused by B. ovis infection. In comparative serological tests, the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with B. ovis lipopolysaccharide gave better identification of infections and fewer false-negative results than the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with sonicated antigen or the complement fixation test.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birmingham J. R., Tabatabai L. B., Deyoe B. L., Jeska E. L., Nuessen M. E. Generation of chemotactic factor for granulocytes and monocytes from serum by fractions of Brucella abortus. Immunology. 1982 May;46(1):17–22. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. W., Norris M. J. Evaluation of the cold complement fixation test for diagnosis of ovine brucellosis. Aust Vet J. 1982 Jul;59(1):23–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1982.tb02706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson H. E., Hurvell B., Lindberg A. A. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for titration of antibodies against Brucella abortus and Yersinia enterocolitica. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1976 Jun;84(3):168–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb00016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dranovskaya E. A., Shibayeva I. V., Khabakpasheva H. A., Rostovtseva N. A. Immunobiological biochemical and physico-chemical characteristics of Brucella lipopolysaccharide subjected to various doses of gamma radiation. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1975;19(1):116–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann E. M., Houle J. J. Failure of Brucella abortus lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to activate the alternative pathway of complement. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Nov;5(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(83)90032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurvell B. Serological cross-reactions between different Brucella species and Yersinia enterocolitica. Biological and chemical investigations of lipopolysaccharides from Brucella abortus and Yersinia enterocolitica type IX. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Feb;81(1):105–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02193.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jermyn M. A. Increasing the sensitivity of the anthrone method for carbohydrate. Anal Biochem. 1975 Sep;68(1):332–335. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90713-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. M., Berman D. T. Studies of Brucella lipopolysaccharide. Dev Biol Stand. 1976;31:62–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. M., Diaz R., Berman D. T. Endotoxic activity of rough organisms of Brucella species. Infect Immun. 1976 Jun;13(6):1638–1641. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.6.1638-1641.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreutzer D. L., Buller C. S., Robertson D. C. Chemical characterization and biological properties of lipopolysaccharides isolated from smooth and rough strains of Brucella abortus. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):811–818. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.811-818.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb V. L., Jones L. M., Schurig G. G., Berman D. T. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for bovine immunoglobulin subclass-specific response to Brucella abortus lipopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):240–247. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.240-247.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx A., Ionescu J., Pop A. Immunochemical studies on Brucella abortus lipopolysaccharides. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1983 Feb;253(4):544–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Berman D. T., Boettcher L. A. Biological activities of Brucella abortus lipopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):362–370. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.362-370.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Jones L. M., Berman D. T. Immunochemical characterization of rough Brucella lipopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):779–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.779-782.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Pitt M. W., Jones L. M., Schurig G. G., Berman D. T. Purification and characterization of smooth and rough lipopolysaccharides from Brucella abortus. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):361–369. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.361-369.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Speth S. L., Jones L. M., Berman D. T. Immunochemical characterization of Brucella lipopolysaccharides and polysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):214–222. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.214-222.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers D. M., Jones L. M., Varela-Diaz V. M. Studies of antigens for complement fixation and gel diffusion tests in the diagnosis of infections caused by Brucella ovis and other Brucella. Appl Microbiol. 1972 May;23(5):894–902. doi: 10.1128/am.23.5.894-902.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahaley R. S., Dennis S. M., Smeltzer M. S. Comparison of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and complement fixation test for detecting Brucella ovis antibodies in sheep. Vet Rec. 1983 Nov 12;113(20):467–470. doi: 10.1136/vr.113.20.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurig G. G., Jones L. M., Speth S. L., Berman D. T. Antibody response to antigens distinct from smooth lipopolysaccharide complex in Brucella infection. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):994–1002. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.994-1002.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spellman J. M., Reed N. D. Immune and mitogenic responses by BALB/c, C3H/HeJ, and nude mice to Brucella abortus bacterin and lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):371–378. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.371-378.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARAVDEKAR V. S., SASLAW L. D. A sensitive colorimetric method for the estimation of 2-deoxy sugars with the use of the malonaldehyde-thiobarbituric acid reaction. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1945–1950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]