Abstract
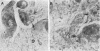
In 12 of 20 (60%) biopsy-proven cases of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia, the diagnosis was first suggested by examination of routine Gram stains of impression smears made from infected lung tissue and later confirmed by methenamine-silver staining. The cysts appeared as 5- to 7-microns unstained spheres, each containing six to eight intracystic gram-negative bodies (sporozoites). Although the Gram stain does not appear to be as sensitive as more traditional staining techniques for the detection of P. carinii, clinical microbiologists should be aware of the morphology of this organism in gram-stained specimens because this relatively simple procedure gives quick results.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GAJDUSEK D. C. Pneumocystis carinii; etiologic agent of interstitial plasma cell pneumonia of premature and young infants. Pediatrics. 1957 Apr;19(4 Pt 1):543–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROCOTT R. G. A stain for fungi in tissue sections and smears using Gomori's methenamine-silver nitrate technic. Am J Clin Pathol. 1955 Aug;25(8):975–979. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/25.8_ts.0975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverkos H. W., Dowling J. N., Pasculle A. W., Myerowitz R. L., Lerberg D. B., Hakala T. R. Diagnosis of pneumonitis in immunocompromised patients by open lung biopsy. Cancer. 1983 Sep 15;52(6):1093–1097. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19830915)52:6<1093::aid-cncr2820520627>3.0.co;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LE TAN-VINH, COCHARD A. M., VU-TRIEU-DONG, SOLONAR W. DIAGNOSTIC "IN VIVO" DE LA PNEUMONIE 'A "PNEUMOCYSTIS". Arch Fr Pediatr. 1963 Aug-Sep;20:773–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macher A. M., Shelhamer J., MacLowry J., Parker M., Masur H. Pneumocystis carinii identified by gram stain of lung imprints. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Oct;99(4):484–485. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-4-484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahan C. T., Sale G. E. Rapid methenamine silver stain for Pneumocystis and fungi. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1978 Jul;102(7):351–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masur H., Michelis M. A., Greene J. B., Onorato I., Stouwe R. A., Holzman R. S., Wormser G., Brettman L., Lange M., Murray H. W. An outbreak of community-acquired Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: initial manifestation of cellular immune dysfunction. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1431–1438. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Perl D. P., Krogstad D. J., Rawson P. G., Schultz M. G. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the United States. Epidemiologic, diagnostic, and clinical features. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Jan;80(1):83–93. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-1-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]