Abstract
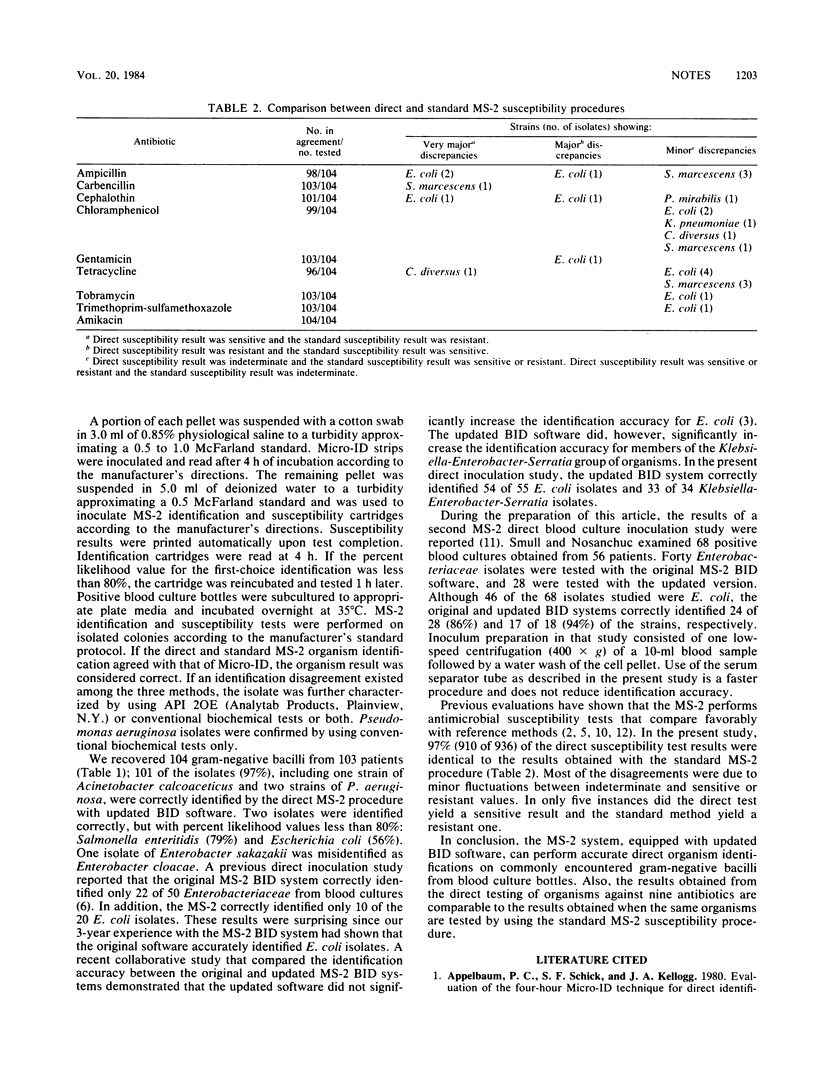
The Abbott MS-2 system (Abbott Laboratories, Diagnostic Division, Irving, Tex.), equipped with updated bacterial identification software (version 03.02), was used to perform both direct identification and susceptibility tests on gram-negative bacilli from positive BACTEC blood culture bottles. Ninety-eight of 101 Enterobacteriaceae strains, one strain of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus, and two strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa were correctly identified by following a direct inoculation procedure. One Enterobacter sakazakii isolate was misidentified as Enterobacter cloacae. Ninety-seven percent of 936 direct susceptibility results were identical to the results obtained by using the standard MS-2 susceptibility procedure. Only five tests yielded a sensitive-direct and a resistant-standard MS-2 susceptibility result.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes W. G., Green L. R., Talley R. L. Clinical evaluation of automated antibiotic susceptibility testing with the MS-2 system. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Oct;12(4):527–532. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.4.527-532.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPersio J. R., Dyke J. W., Vannest R. D. Evaluation of the updated MS-2 Bacterial Identification system in comparison with the API 20E system. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):128–135. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.128-135.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edberg S. C., Clare D., Moore M. H., Singer J. M. Rapid identification of Enterobacteriaceae from blood cultures with the Micro-ID system. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):693–697. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.693-697.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malloy P. J., Ducate M. J., Schreckenberger P. C. Comparison of four rapid methods for identification of Enterobacteriaceae from blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Mar;17(3):493–499. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.3.493-499.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken A. W., Martin W. J., McCarthy L. R., Schwab D. A., Cooper B. H., Helgeson N. G., Prowant S., Robson J. Evaluation of the MS-2 system for rapid identification of Enterobacteriaceae. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Nov;12(5):684–689. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.5.684-689.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore D. F., Hamada S. S., Marso E., Martin W. J. Rapid identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing of gram-negative bacilli from blood cultures by the AutoMicrobic system. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 May;13(5):934–939. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.5.934-939.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifman R. B., Ryan K. J. Rapid automated identification of gram-negative bacilli from blood cultures with the AutoMicrobic system. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):260–264. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.260-264.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sewell D. L., Makler M. T. Clinical evaluation of the Abbott MS-2 antimicrobial susceptibility testing system. Am J Clin Pathol. 1981 Jul;76(1):82–85. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/76.1.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., Anhalt J. P., Washington J. A., 2nd, McCarthy L. R., Schoenknecht F. D., Sherris J. C., Spencer H. J. Clinical laboratory evaluation of the Abbott MS-2 automated antimicrobial susceptibility testing system: report of a collaborative study. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):375–390. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.375-390.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


