Abstract
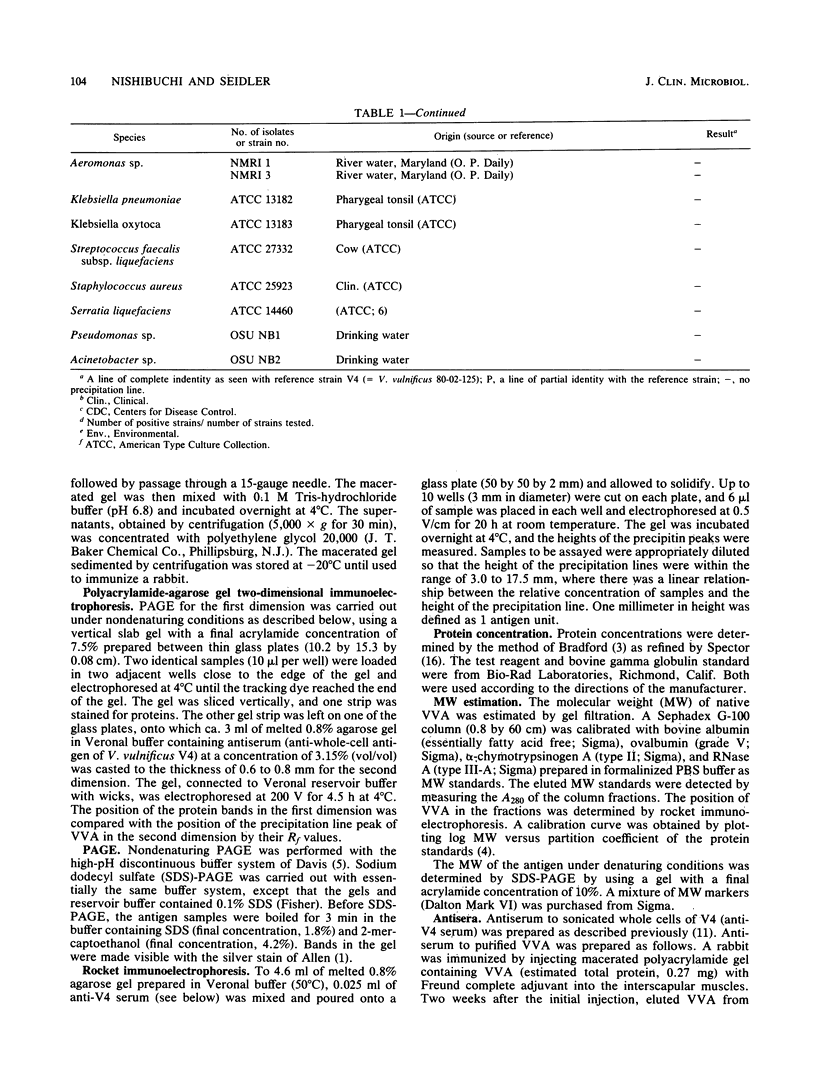
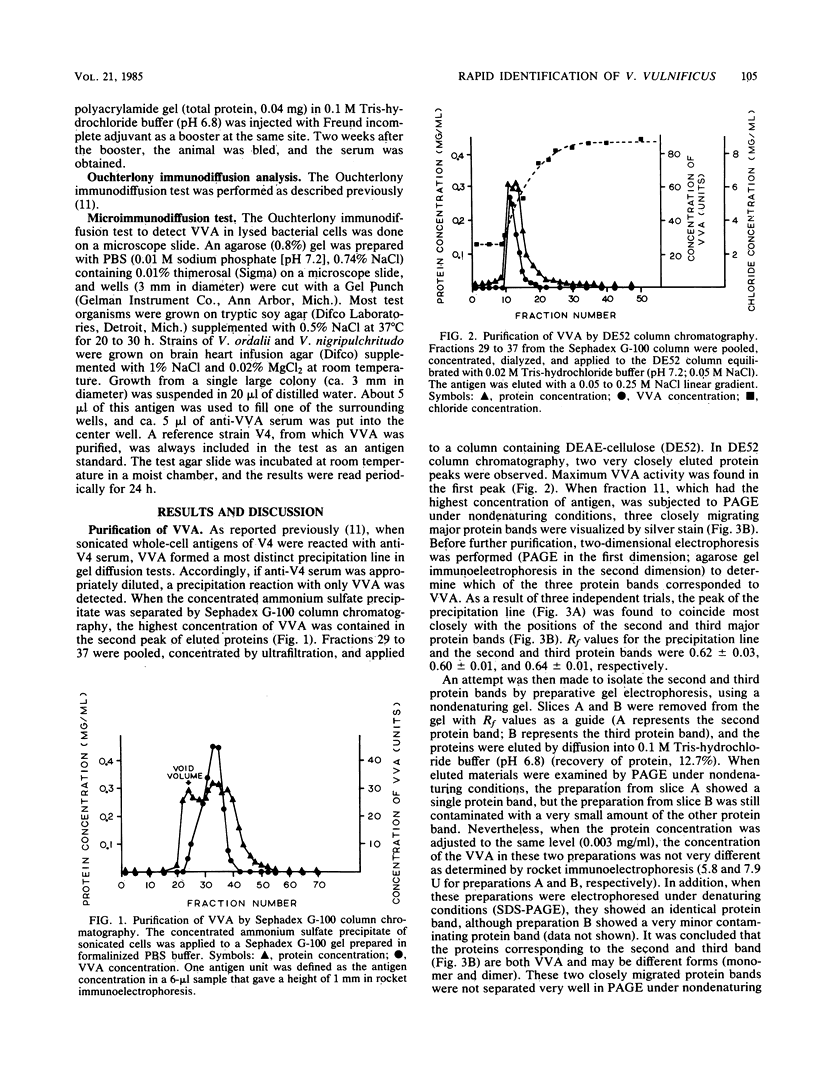
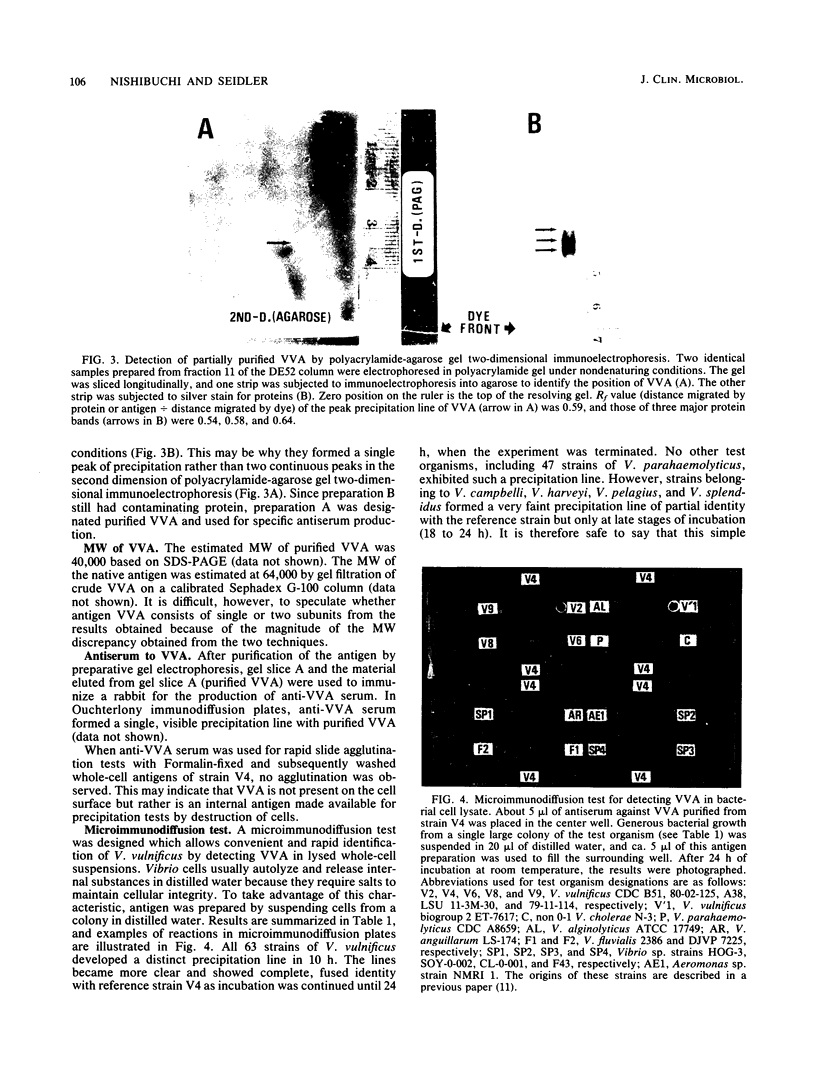
An antigen common to Vibrio vulnificus strains, designated VVA, was purified by ammonium sulfate precipitation, gel filtration, ion-exchange column chromatography, and preparative gel electrophoresis. The molecular weight of VVA was 64,000 when estimated by gel filtration and 40,000 when measured by denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Antiserum prepared against purified VVA (anti-VVA serum) did not agglutinate whole cells of V. vulnificus. Therefore, VVA was considered a possible internal antigen. By using anti-VVA serum, a microimmunodiffusion method was designed to detect the antigen VVA in bacterial cell lysates prepared from a single colony. This simple method allowed the specific identification of V. vulnificus as soon as 10 h after antigen preparation and therefore can be a useful tool in the identification of V. vulnificus from environmental or clinical specimens. VVA was not detected as a line of complete identity in some 20 other Vibrio species or in 7 other bacterial genera. VVA was present in all 63 isolates of V. vulnificus obtained from clinical and nonclinical sources.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E., Baker C. N., Thornsberry C. Halophilic Vibrio species isolated from blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Apr;3(4):425–431. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.4.425-431.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jean-Jacques W., Rajashekaraiah K. R., Farmer J. J., 3rd, Hickman F. W., Morris J. G., Kallick C. A. Vibrio metschnikovii bacteremia in a patient with cholecystitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Dec;14(6):711–712. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.6.711-712.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. G., Jr, Miller H. G., Wilson R., Tacket C. O., Hollis D. G., Hickman F. W., Weaver R. E., Blake P. A. Illness caused by Vibrio damsela and Vibrio hollisae. Lancet. 1982 Jun 5;1(8284):1294–1297. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92853-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibuchi M., Seidler R. J. Demonstration of a common antigen in sonicated cells for identification of Vibrio vulnificus serotypes. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):97–101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.97-101.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland F. P. Leg gangrene and endotoxin shock due to vibrio parahaemolyticus--an infection acquired in New England coastal waters. N Engl J Med. 1970 Jun 4;282(23):1306–1306. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197006042822306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidler R. J., Allen D. A., Colwell R. R., Joseph S. W., Daily O. P. Biochemical characteristics and virulence of environmental group F bacteria isolated in the United States. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Oct;40(4):715–720. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.4.715-720.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector T. Refinement of the coomassie blue method of protein quantitation. A simple and linear spectrophotometric assay for less than or equal to 0.5 to 50 microgram of protein. Anal Biochem. 1978 May;86(1):142–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90327-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tison D. L., Nishibuchi M., Greenwood J. D., Seidler R. J. Vibrio vulnificus biogroup 2: new biogroup pathogenic for eels. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Sep;44(3):640–646. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.3.640-646.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. E., Ehrenkranz N. J. Letter: Vibrio parahaemolyticus septicemia. Arch Intern Med. 1975 Jan;135(1):197–197. doi: 10.1001/archinte.135.1.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zide N., Davis J., Ehrenkranz N. J. Fulminating vibrio parahemolyticus septicemia. A syndrome of erythemia multiforme, hemolytic anemia, and hypotension. Arch Intern Med. 1974 Mar;133(3):479–481. doi: 10.1001/archinte.133.3.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]