Abstract
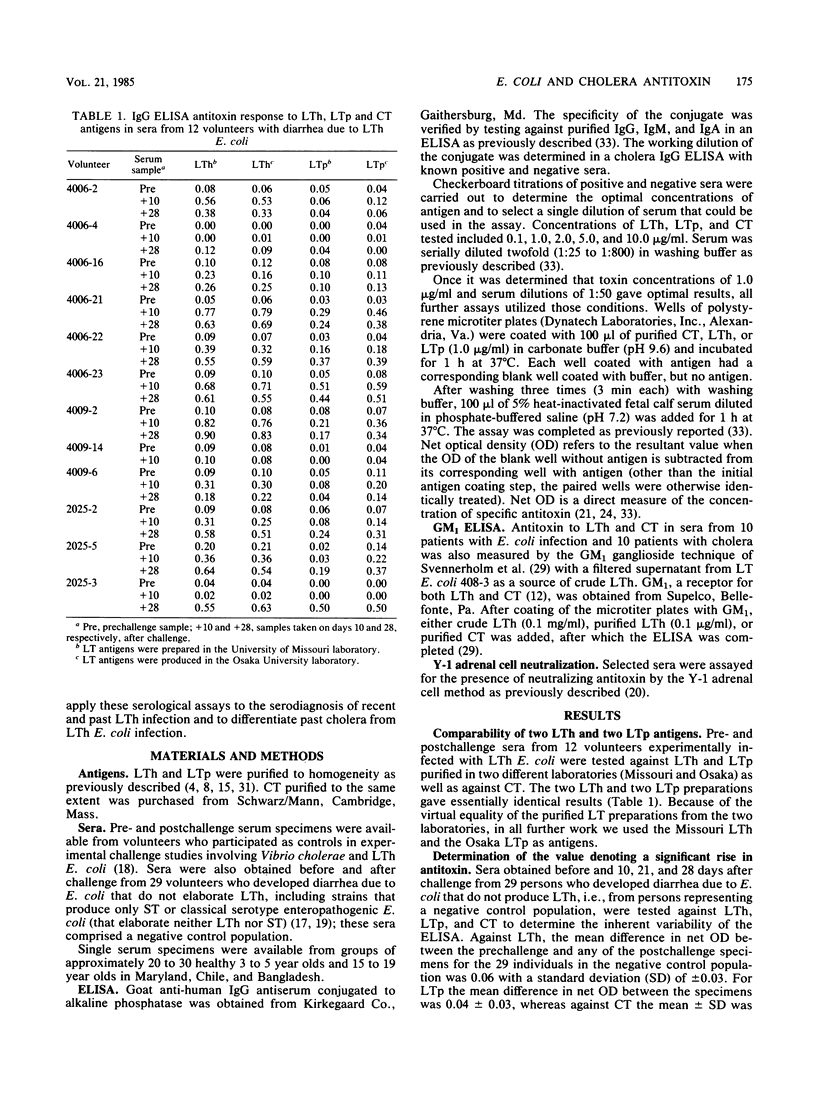
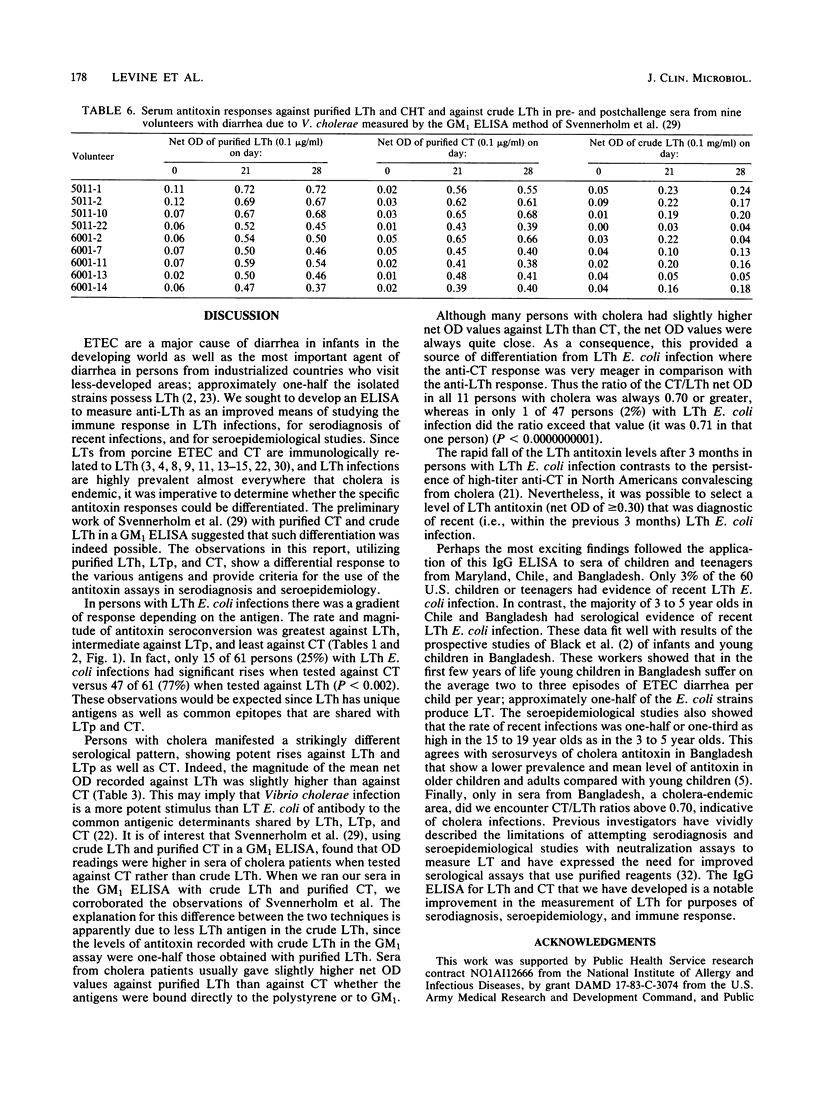
Serum immunoglobulin G antibodies to purified heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) from human (LTh) and porcine (LTp) Escherichia coli strains and cholera enterotoxin (CT) were measured by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Sera from patients with LTh E. coli infection showed a prominent response with LTh, an intermediate response with LTp, and a meager response with CT. Of 47 persons with clinical LTh-producing E. coli (herein shortened to LTh E. coli) infections, significant rises in antitoxin were detected against LTh in 36 (77%), against LTp in 30 (64%), and against CT in only 13 (28%) patients; seroconversions also occurred in 11 of 14 (79%) patients with subclinical LTh E. coli infections. In North Americans with experimental LTh E. coli infection, anti-Lth did not remain at high levels for more than 3 months. Persons with cholera manifested antitoxin responses that were similarly potent against all three toxin antigens; in fact, net optical density values were often slightly higher against LTh than against CT. The ratio of CT/LTh ELISA net optical density in convalescent sera proved to be a sensitive means to differentiate LT E. coli from cholera infection. All 11 cholera patients tested had CT/LTh ratios of greater than 0.70, whereas in only 1 of 47 LTh E. coli infections did the ratio exceed that value (it was 0.71) (P less than 0.0000000001). In single serum specimens, a net optical density of greater than or equal to 0.30 against LTh was shown to be a useful cutoff in screening sera for recent LTh E. coli or past cholera infection. The CT/LTh ratio was then used to differentiate definitively. Sera from healthy 3- to 5-year -olds and 15- to 19-year-olds in Maryland, Chile, and Bangladesh were tested against LTh and CT. The serological results fit known epidemiological observations. (i) LTh infections are rare in the United States (only 2 of 60 sera had LTh net optical density values of >/= 0.30. (ii) In contrast, evidence of recent LTh E. coli infections was very common in Chilean (69%) and Bangladeshi (57%) 3- to 5-year-olds and not uncommon in 15- to 19-year-olds (38 and 31%, respectively) in those countries. (iii) Only Bangladeshi sera showed serological evidence of cholera infections (CT/LTh ratios of > 0.70). The immunoglobulin G enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay measuring antibodies to purified LTh and CT represents a practical and effective tool for the serological study of LTh E. coli and cholera diarrheal infections.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aust-Kettis A., Gebre-Medhin M., Habte D., Khosla N., Wadström T. Antibodies to heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxins in human milk and sera. A study of Ethiopian and Swedish mothers and their children. Trop Geogr Med. 1981 Sep;33(3):225–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black R. E., Brown K. H., Becker S., Alim A. R., Huq I. Longitudinal studies of infectious diseases and physical growth of children in rural Bangladesh. II. Incidence of diarrhea and association with known pathogens. Am J Epidemiol. 1982 Mar;115(3):315–324. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Demonstration of shared and unique immunological determinants in enterotoxins from Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):709–713. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.709-713.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Isolation and characterization of homogeneous heat-labile enterotoxins with high specific activity from Escherichia coli cultures. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):760–769. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.760-769.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Sack D. A., Wallace R. B., Dupont H. L., Sack R. B. Tissue-culture assay of antibodies to heat-liable Escherichia coli enterotoxins. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jul 18;291(3):117–121. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197407182910302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Ruiz-Palacios G., Evans D. E., DuPont H. L., Pickering L. K., Olarte J. Humoral immune response to the heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli in naturally acquired diarrhea and antitoxin determination by passive immune hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):781–788. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.781-788.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geary S. J., Marchlewicz B. A., Finkelstein R. A. Comparison of heat-labile enterotoxins from porcine and human strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):215–220. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.215-220.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilligan P. H., Brown J. C., Robertson D. C. Immunological relationships between cholera toxin and Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):683–691. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.683-691.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Levine M. M., Merson M. H., Sack R. B., Sack D. A., Valdesuso J. R., Nalin D., Hoover D., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Solid-phase microtiter radioimmunoassay blocking test for detection of antibodies to Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):60–64. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.60-64.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L. Immunological study of the heat-labile enterotoxins of Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):564–570. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.564-570.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J. Comparison of the tissue receptors for Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli enterotoxins by means of gangliosides and natural cholera toxoid. Infect Immun. 1973 Dec;8(6):851–859. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.6.851-859.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Isolation of special antibodies which react only with homologous enterotoxins from Vibrio cholerae and Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):333–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.333-336.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Tsuji T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Immunological nonidentity of heat-labile enterotoxins from human and porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):337–340. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.337-340.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. M., Rouse J. D., Barada F. A., Guerrant R. L. Etiology of summer diarrhea among the Navajo. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1980 Jul;29(4):613–619. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1980.29.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Bergquist E. J., Nalin D. R., Waterman D. H., Hornick R. B., Young C. R., Sotman S. Escherichia coli strains that cause diarrhoea but do not produce heat-labile or heat-stable enterotoxins and are non-invasive. Lancet. 1978 May 27;1(8074):1119–1122. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90299-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Caplan E. S., Waterman D., Cash R. A., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J. Diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli that produce only heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):78–82. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.78-82.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Nalin D. R., Hoover D. L., Bergquist E. J., Hornick R. B., Young C. R. Immunity to enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):729–736. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.729-736.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Young C. R., Hughes T. P., O'Donnell S., Black R. E., Clements M. L., Robins-Browne R., Lim Y. L. Duration of serum antitoxin response following Vibrio cholerae infection in North Americans: relevance for seroepidemiology. Am J Epidemiol. 1981 Sep;114(3):348–354. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchlewicz B. A., Finkelstein R. A. Immunological differences among the cholera/coli family of enterotoxins. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1983 Jun;1(2):129–138. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(83)90042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merson M. H., Morris G. K., Sack D. A., Wells J. G., Feeley J. C., Sack R. B., Creech W. B., Kapikian A. Z., Gangarosa E. J. Travelers' diarrhea in Mexico. A prospective study of physicians and family members attending a congress. N Engl J Med. 1976 Jun 10;294(24):1299–1305. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197606102942401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M., Young C. R., Levine M. M., Craig J. P. Microtiter enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for immunoglobulin g cholera antitoxin in humans: sensitivity and specificity. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):497–500. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.497-500.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M. L., Koplan J. P., Wachsmuth I. K., Wells J. G., Gangarosa E. J., Guerrant R. L., Sack D. A. Epidemic diarrhea at Crater Lake from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. A large waterborne outbreak. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Jun;86(6):714–718. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-6-714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Hirschborn N., Woodward W. E., Sack D. A., Cash R. A. Antibodies to heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin in Apaches in Whiteriver, Arizona. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1475–1477. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1475-1477.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Jacobs B., Mitra R. Antitoxin responses to infections with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1974 Mar;129(3):330–335. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.3.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm A. M., Bäck E., Holmgren J. Enterotoxin antibodies in relation to diarrhoea in Swedish soldiers in Cyprus. Bull World Health Organ. 1977;55(6):663–668. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm A. M., Holmgren J., Black R., Levine M., Merson M. Serologic differentiation between antitoxin responses to infection with Vibrio cholerae and enterotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1983 Mar;147(3):514–522. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.3.514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Honda T., Sima H., Tsuji T., Miwatani T. Analysis of antigenic determinants in cholera enterotoxin and heat-labile enterotoxins from human and porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):50–53. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.50-53.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Honda T., Taga S., Miwatani T. In vitro formation of hybrid toxins between subunits of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin and those of cholera enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):341–346. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.341-346.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsmuth I. K., Wells J. G., Ryder R. W. Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin: comparison of antitoxin assays and serum antitoxin levels. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):348–351. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.348-351.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young C. R., Levine M. M., Craig J. P., Robins-Browne R. Microtiter enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for immunoglobulin G cholera antitoxin in humans: method and correlation with rabbit skin vascular permeability factor technique. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):492–496. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.492-496.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



