Abstract
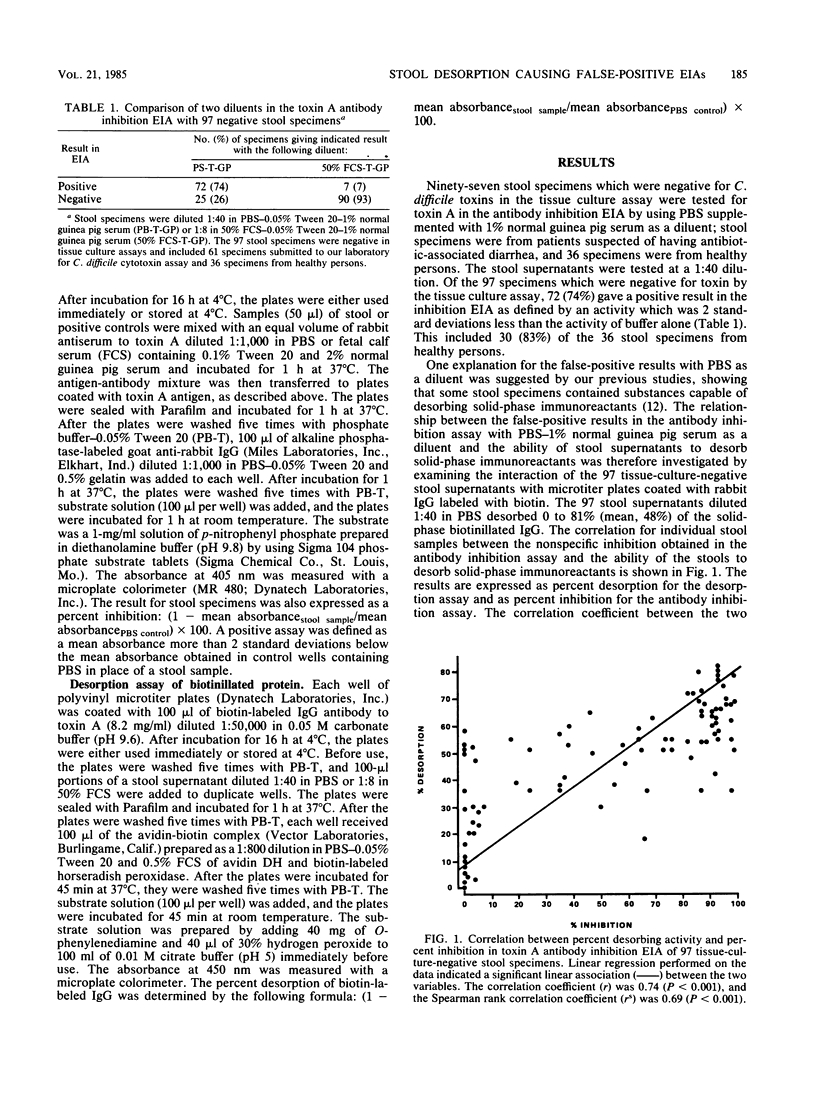
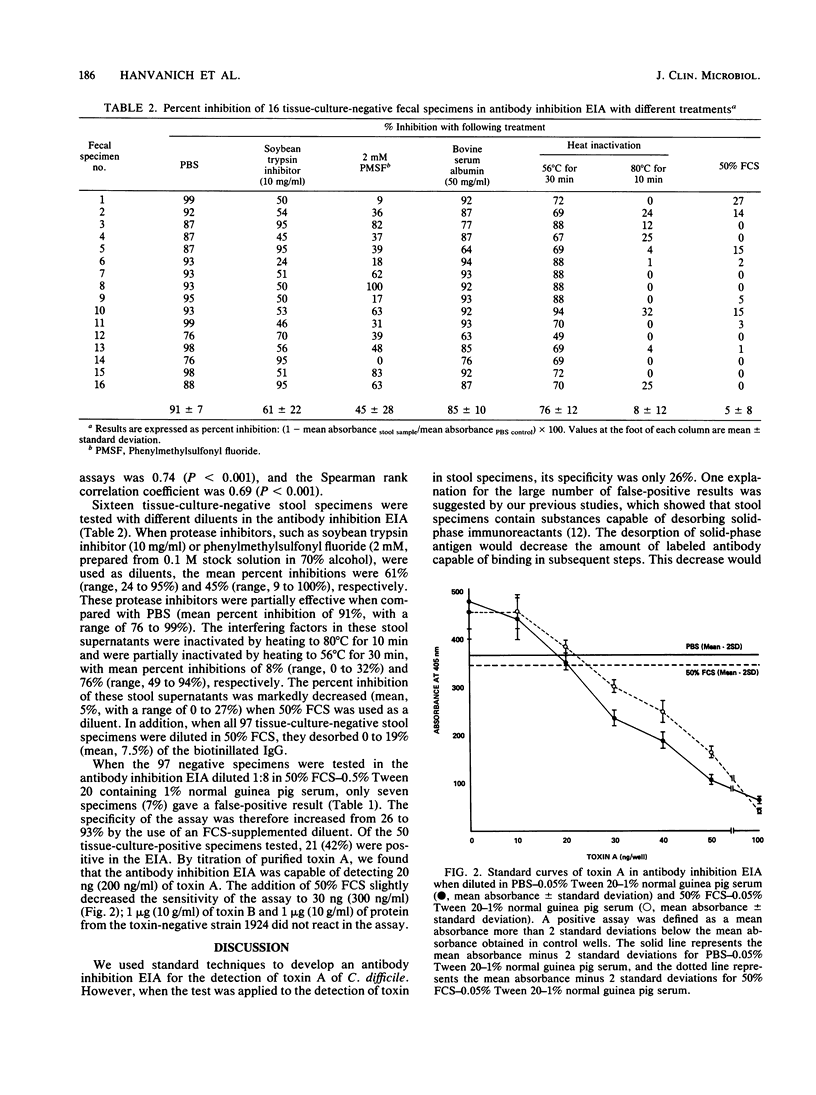
We have developed a competitive enzyme immunoassay for the measurement of purified toxin A of Clostridium difficile. However, when we applied this assay to the detection of C. difficile toxin in stool specimens, we noted a high rate of nonspecific activity in fecal specimens which did not contain toxin. We found that the low specificity (26%) of the assay was due to the presence in stool specimens of interfering factors which desorbed the antigen coated on the solid-phase surface. These factors could be detected by measurement of the desorption of biotin-labeled proteins attached to the solid-phase surface. In addition, these interfering factors were partially inactivated by heating at 56 degrees C for 10 min and partially inhibited by phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (2 mM) or soybean trypsin inhibitor (10 mg/ml). These data suggested that the desorbing activity was due to proteolytic activity in the fecal specimens. Fetal calf serum (50%) was found to be the most effective measure in preventing the interfering effect. By using 50% fetal calf serum as a diluent, we increased the specificity of the antibody inhibition enzyme immunoassay to 93%. Interfering factors in stool specimens could be a cause of false-positive results in other competitive immunoassay systems. The use of diluents which neutralize protease activity can result in a marked improvement in the specificity of competitive immunoassay systems.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayer E. A., Wilchek M. The use of the avidin-biotin complex as a tool in molecular biology. Methods Biochem Anal. 1980;26:1–45. doi: 10.1002/9780470110461.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg R. A., Yolken R. H., Rennard S. I., Dolin R., Murphy B. R., Straus S. E. New enzyme immunoassays for measurement of influenza A/Victoria/3/75 virus in nasal washes. Lancet. 1980 Apr 19;1(8173):851–853. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91356-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Clegg S. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli colonization factor antigen I in stool specimens by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):738–743. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.738-743.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guesdon J. L., Ternynck T., Avrameas S. The use of avidin-biotin interaction in immunoenzymatic techniques. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Aug;27(8):1131–1139. doi: 10.1177/27.8.90074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovi T., Väisänen V., Ukkonen P., von Bonsdorff C. H. Solid-phase enzyme immunoassay for rotavirus antigen: faecal protease activity as a reason for false-negative results. J Virol Methods. 1982 Sep;5(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(82)90096-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Matsuno S., Yamaguchi H. Efficient coating of the solid phase with rotavirus antigens for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of immunoglobulin A antibody in feces. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):259–263. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.259-263.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon B. E., Viscidi R. P., Gdovin S. L., Yolken R. H., Bartlett J. G. Enzyme immunoassays for detection of Clostridium difficile toxins A and B in fecal specimens. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):781–788. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notermans S., Timmermans P., Nagel J. Interaction of staphylococcal protein A in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for detecting staphylococcal antigens. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Nov 26;55(1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90074-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rissing J. P., Buxton T. B., Talledo R. A., Sprinkle T. J. Comparison of two enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for antigen quantitation: direct competition and antibody inhibition. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):405–410. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.405-410.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal E., Berg R. A., Pizzo P. A., Bennett J. E. Detection of Candida antigen in sera of patients with candidiasis by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay-inhibition technique. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jul;10(1):116–118. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.1.116-118.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viscidi R., Laughon B. E., Yolken R., Bo-Linn P., Moench T., Ryder R. W., Bartlett J. G. Serum antibody response to toxins A and B of Clostridium difficile. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jul;148(1):93–100. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H. Enzyme immunoassays for the detection of infectious antigens in body fluids: current limitations and future prospects. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Jan-Feb;4(1):35–68. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


