Abstract
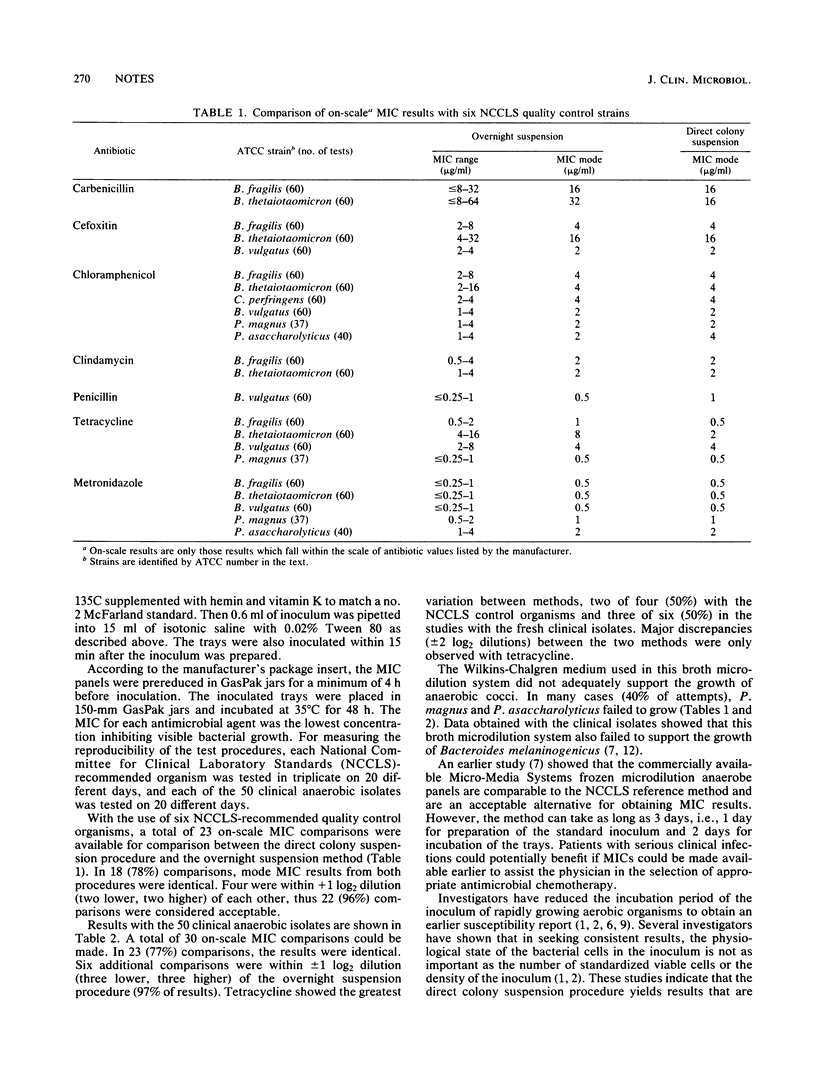
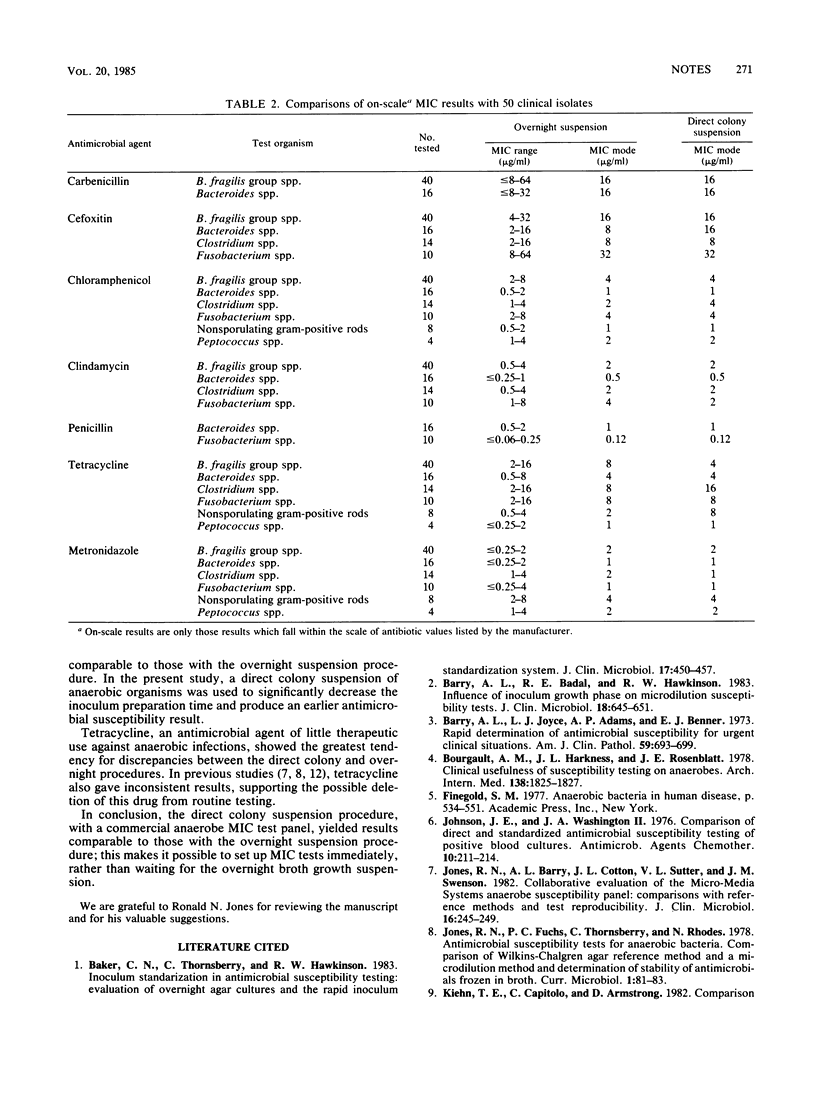
A direct colony inoculum suspension procedure was compared with the overnight suspension procedure recommended for the broth microdilution anaerobic commercial system (Micro-Media Systems, Inc., Potomac, Md.). Six National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards-recommended quality control organisms, Bacteroides fragilis ATCC 25285, Clostridium perfringens ATCC 13124, Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron ATCC 29741, Bacteroides vulgatus ATCC 29327, Peptococcus magnus ATCC 29328, Peptococcus asaccharolyticus ATCC 29743, and 50 anaerobic clinical isolates were tested against seven commonly tested antimicrobial agents. The minimum inhibitory concentration results from each suspension method (using the quality control organisms) were identical in 18 (78%) instances, and within +/- 1 log2 dilution in 96% of the comparisons. Results with the fresh clinical isolates also compared satisfactorily with the overnight procedure (97% were identical or within one dilution). The Wilkins-Chalgren test medium failed to support the growth of most anaerobic gram-positive cocci and Bacteroides melaninogenicus strains.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. N., Thornsberry C., Hawkinson R. W. Inoculum standardization in antimicrobial susceptibility testing: evaluation of overnight agar cultures and the Rapid Inoculum Standardization System. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Mar;17(3):450–457. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.3.450-457.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry A. L., Badal R. E., Hawkinson R. W. Influence of inoculum growth phase on microdilution susceptibility tests. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):645–651. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.645-651.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry A. L., Joyce L. J., Adams A. P., Benner E. J. Rapid determination of antimicrobial susceptibility for urgent clinical situations. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 May;59(5):693–699. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/59.5.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgault A. M., Harkness J. L., Rosenblatt J. E. Clinical usefulness of susceptibility testing of anaerobes. Arch Intern Med. 1978 Dec;138(12):1825–1827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. E., Washington J. A., 2nd Comparison of direct and standardized antimicrobial susceptibility testing of positive blood cultures. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Aug;10(2):211–214. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Barry A. L., Cotton J. L., Sutter V. L., Swenson J. M. Collaborative evaluation of the micro-media systems anaerobe susceptibility panel: comparisons with reference methods and test reproducibility. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Aug;16(2):245–249. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.2.245-249.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. R., Christman J. L. Susceptibility testing with anaerobic blood culture isolates. Comparison of a rapid, direct methods with standardized method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1980 Apr;73(4):558–561. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/73.4.558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt J. E., Murray P. R., Sonnenwirth A. C., Joyce J. L. Comparison of anaerobic susceptibility results obtained by different methods. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Mar;15(3):351–355. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.3.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Cuchural G. J., Jacobus N. V., Gorbach S. L., Aldridge K. E., Cleary T. J., Finegold S. M., Hill G. B., Iannini P. B., McCloskey R. V. Susceptibility of the Bacteroides fragilis group in the United States in 1981. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Apr;23(4):536–540. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.4.536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


