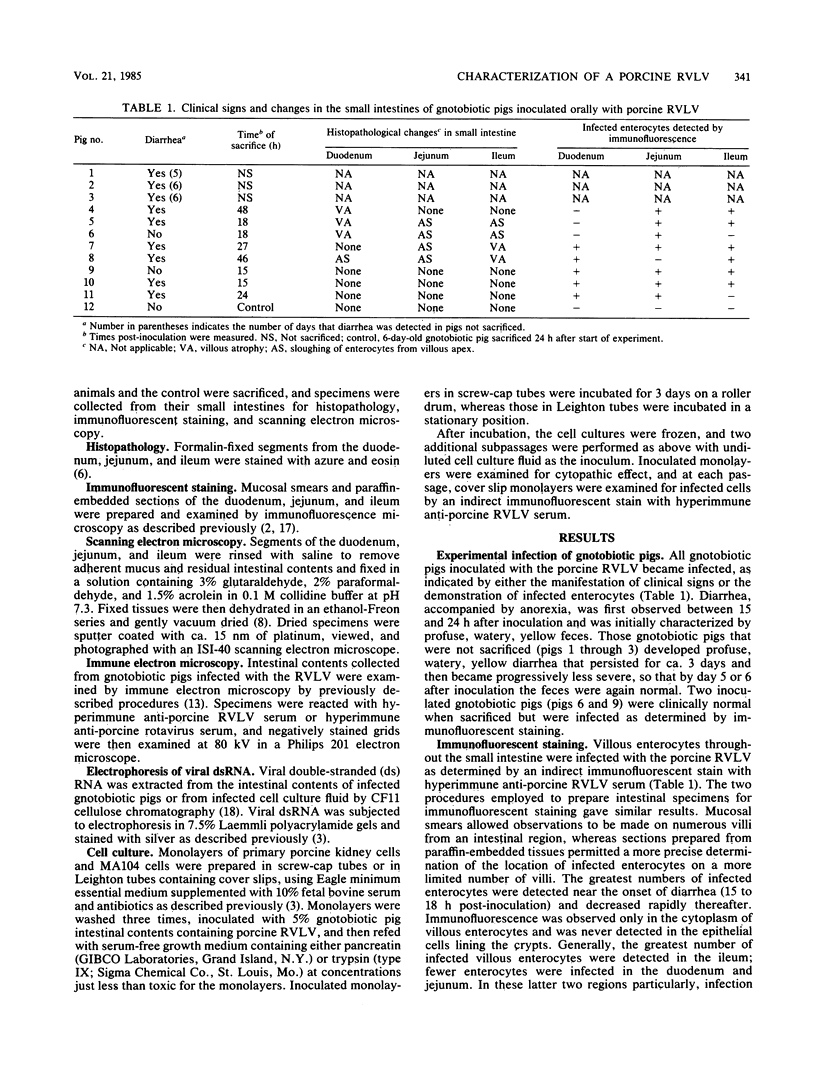
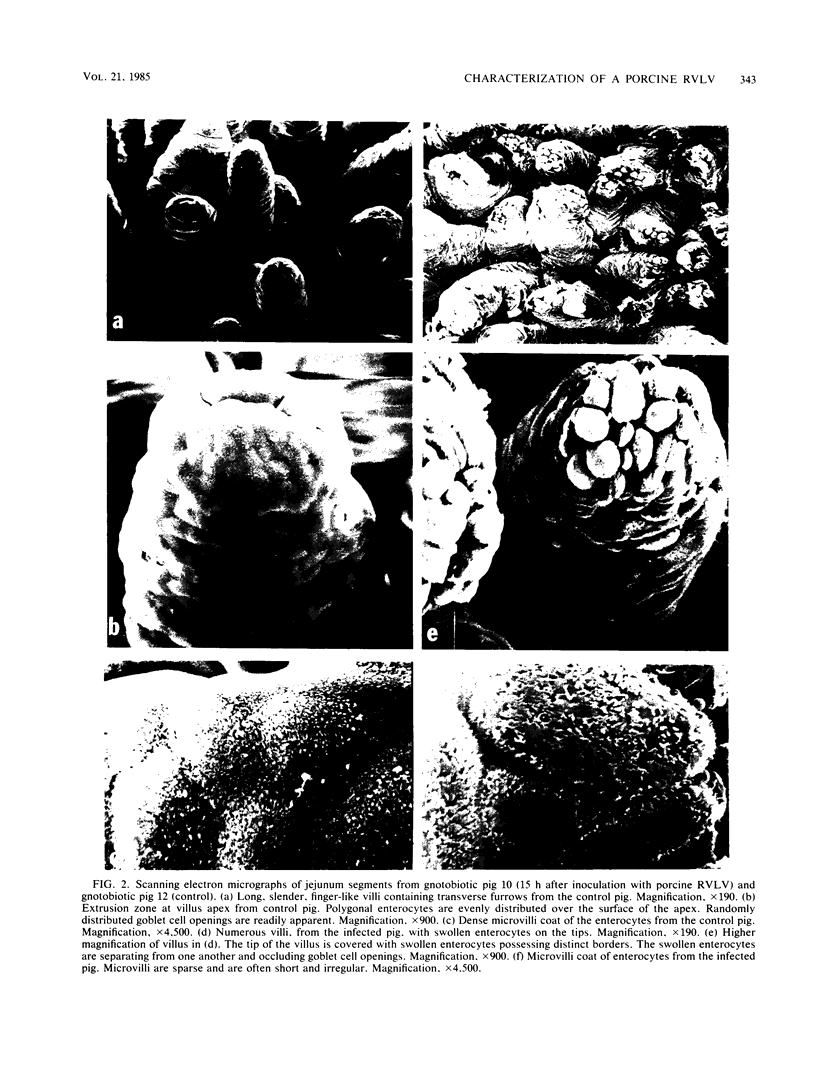
Abstract
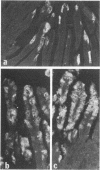
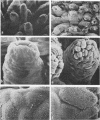
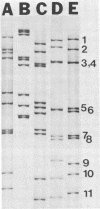
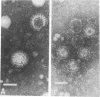
A rotavirus-like virus (RVLV) was isolated from a diarrheic pig from an Ohio swine herd. This virus infected villous enterocytes throughout the small intestine of gnotobiotic pigs and induced an acute, transitory diarrhea. Complete virions were rarely observed in the intestinal contents of infected animals; the predominant particle detected by immune electron microscopy was a corelike particle 52 nm in diameter. The genome of the porcine RVLV was composed of 11 discrete segments of double-stranded RNA that produced an electropherotype distinct from the genome electropherotypes of reovirus, rotavirus, and porcine pararotavirus. Porcine RVLV was antigenically unrelated to rotavirus, porcine pararotavirus, or reovirus but was antigenically related to a bovine RVLV.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida J. D., Bradburne A. F., Wreghitt T. G. The effect of sodium thiocyanate on virus structure. J Med Virol. 1979;4(4):269–277. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890040405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohl E. H., Saif L. J., Theil K. W., Agnes A. G., Cross R. F. Porcine pararotavirus: detection, differentiation from rotavirus, and pathogenesis in gnotobiotic pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):312–319. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.312-319.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohl E. H., Theil K. W., Saif L. J. Isolation and serotyping of porcine rotaviruses and antigenic comparison with other rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):105–111. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.105-111.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger J. C., Clarke I. N., McCrae M. A. Characterization of an antigenically distinct porcine rotavirus. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1058–1062. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1058-1062.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger J. C. Detection by electron microscopy of caliciviruses, astroviruses and rotavirus-like particles in the faeces of piglets with diarrhoea. Vet Rec. 1980 Dec 6;107(23):532–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross R. F., Moorhead P. D. An azure and eosin rapid staining technique. Can J Comp Med. 1969 Oct;33(4):317–317. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewett T. H., Woode G. N. The rotaviruses. Arch Virol. 1978;57(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01315633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung T., Chen G. M., Wang C. G., Yao H. L., Fang Z. Y., Chao T. X., Chou Z. Y., Ye W., Chang X. J., Den S. S. Waterborne outbreak of rotavirus diarrhoea in adults in China caused by a novel rotavirus. Lancet. 1984 May 26;1(8387):1139–1142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER R. C., BOHL E. H., KOHLER E. M. PROCUREMENT AND MAINTENANCE OF GERM-FREE SEINE FOR MICROBIOLOGICAL INVESTIGATIONS. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Jul;12:295–300. doi: 10.1128/am.12.4.295-300.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAdaragh J. P., Bergeland M. E., Meyer R. C., Johnshoy M. W., Stotz I. J., Benfield D. A., Hammer R. Pathogenesis of rotaviral enteritis in gnotobiotic pigs: a microscopic study. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Oct;41(10):1572–1581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley S., Bridger J. C., Brown J. F., McCrae M. A. Molecular characterization of rotaviruses with distinct group antigens. J Gen Virol. 1983 Oct;64(Pt 10):2093–2101. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-10-2093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Bohl E. H., Kohler E. M., Hughes J. H. Immune electron microscopy of transmissible gastroenteritis virus and rotavirus (reovirus-like agent) of swine. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Jan;38(1):13–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Bohl E. H., Theil K. W., Cross R. F., House J. A. Rotavirus-like, calicivirus-like, and 23-nm virus-like particles associated with diarrhea in young pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jul;12(1):105–111. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.1.105-111.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., Bohl E. H., Cross R. F., Kohler E. M., Agnes A. G. Pathogenesis of porcine rotaviral infection in experimentally inoculated gnotobiotic pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1978 Feb;39(2):213–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., McCloskey C. M., Saif L. J., Redman D. R., Bohl E. H., Hancock D. D., Kohler E. M., Moorhead P. D. Rapid, simple method of preparing rotaviral double-stranded ribonucleic acid for analysis by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):273–280. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.273-280.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thouless M. E., Bryden A. S., Flewett T. H., Woode G. N., Bridger J. C., Snodgrass D. R., Herring J. A. Serological relationships between rotaviruses from different species as studied by complement fixation and neutralization. Arch Virol. 1977;53(4):287–294. doi: 10.1007/BF01315627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Medina A., Underdahl N. R. Scanning electron microscopy of intestine of gnotobiotic piglets infected with porcine rotavirus. Can J Comp Med. 1980 Oct;44(4):403–411. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utrera V., Mazzali de Ilja R., Gorziglia M., Esparza J. Epidemiological aspects of porcine rotavirus infection in Venezuela. Res Vet Sci. 1984 May;36(3):310–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Bridger J. C., Jones J. M., Flewett T. H., Davies H. A., Davis H. A., White G. B. Morphological and antigenic relationships between viruses (rotaviruses) from acute gastroenteritis of children, calves, piglets, mice, and foals. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):804–810. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.804-810.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]