Abstract
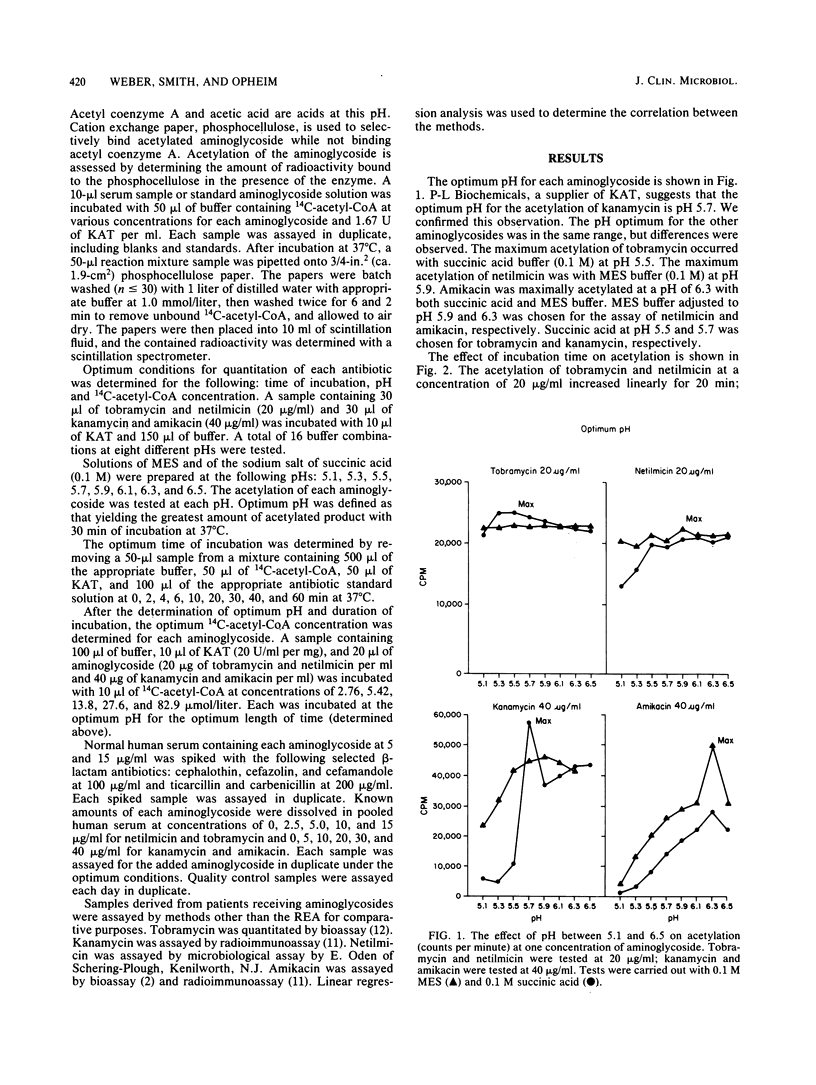
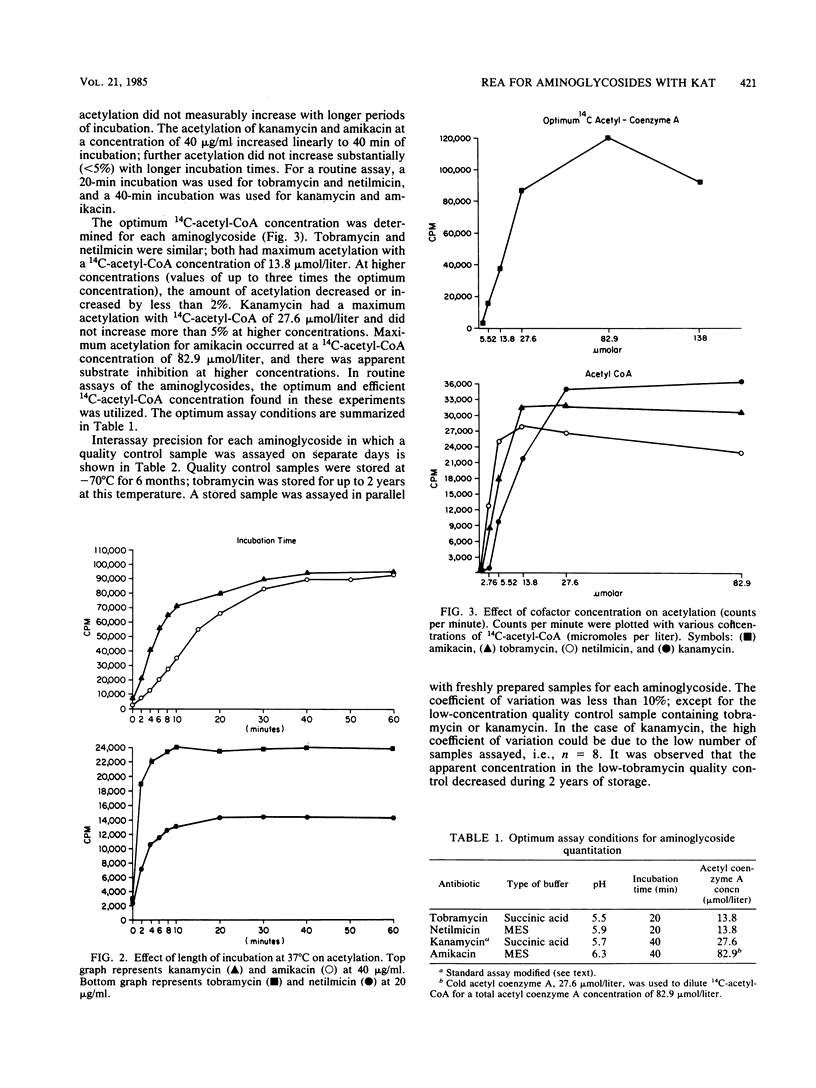
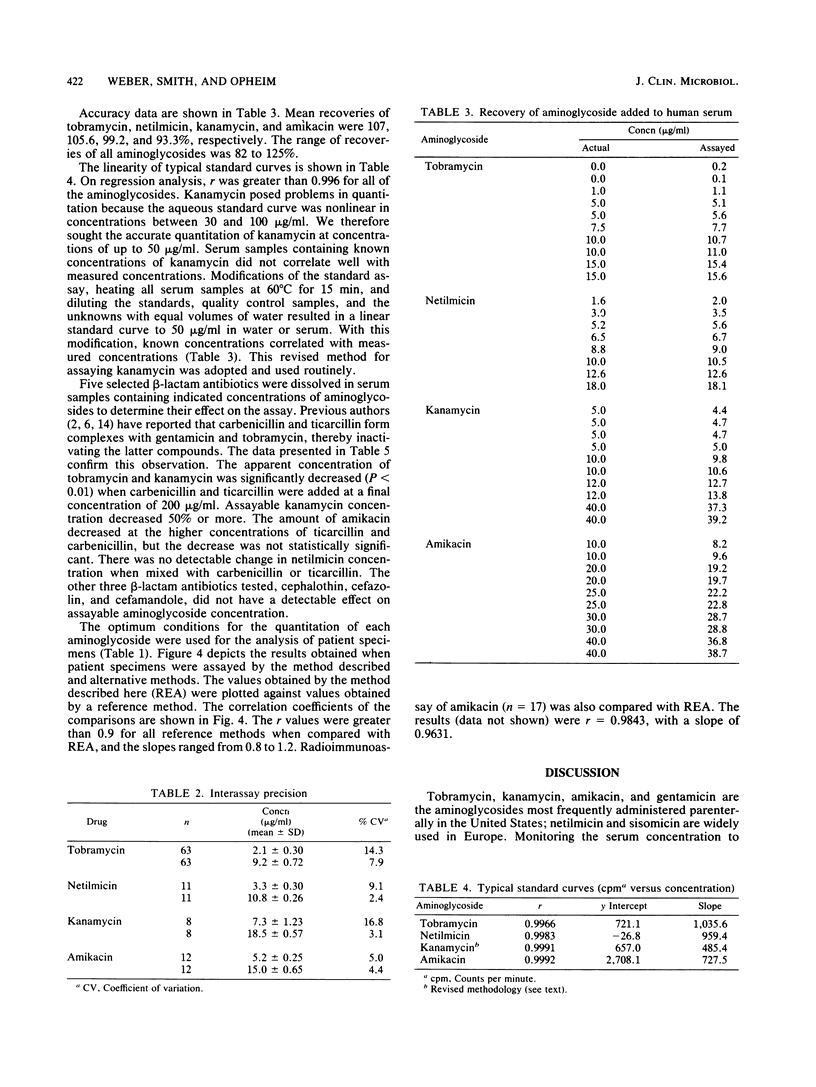
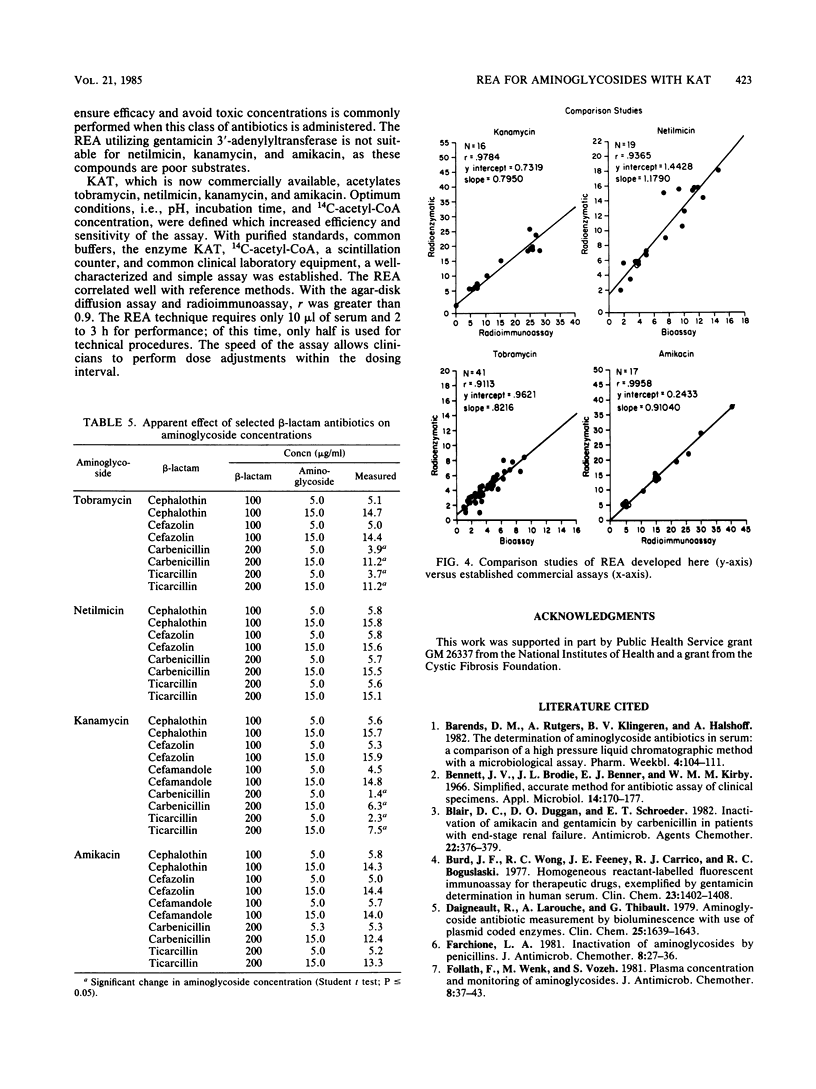
To facilitate the rapid and accurate quantitation of parenterally administered aminoglycosides, we defined the optimum conditions (pH, duration of incubation, and cofactor concentrations) to permit radioenzymatic assays with kanamycin acetyltransferase. The accuracy in quantitating tobramycin, netilmicin, kanamycin, and amikacin at concentrations in the therapeutic range was greater than 90%, with a mean recovery of 102.8%. The mean of the interassay coefficient of variation was 7.8%. Typical standard curves at six different concentrations resulted in a correlation coefficient (r value) of greater than 0.99 for each aminoglycoside. The radioenzymatic assay correlates well with the bioassay (tobramycin and netilmicin) and radioimmunoassay (amikacin and kanamycin); the correlation coefficient is greater than 0.90 for all. We conclude that the radioenzymatic assay utilizing kanamycin 6'-acetyltransferase is feasible for all commercially available parenterally administered aminoglycosides.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barends D. M., Rutgers A., Van Klingeren B., Hulshoff A. The determination of aminoglycoside antibiotics in serum: a comparison of a high performance liquid chromatographic method with a microbiological assay. Pharm Weekbl Sci. 1982 Aug 20;4(4):104–111. doi: 10.1007/BF01962630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. V., Brodie J. L., Benner E. J., Kirby W. M. Simplified, accurate method for antibiotic assay of clinical specimens. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Mar;14(2):170–177. doi: 10.1128/am.14.2.170-177.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. C., Duggan D. O., Schroeder E. T. Inactivation of amikacin and gentamicin by carbenicillin in patients with end-stage renal failure. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Sep;22(3):376–379. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.3.376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burd J. F., Wong R. C., Feeney J. E., Carrico R. J., Boguslaski R. C. Homogeneous reactant-labeled fluorescent immunoassay for therapeutic drugs exemplified by gentamicin determination in human serum. Clin Chem. 1977 Aug;23(8):1402–1408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daigneault R., Larouche A., Thibault G. Aminoglycoside antibiotic measurement by bioluminescence, with use of plasmid-coded enzymes. Clin Chem. 1979 Sep;25(9):1639–1643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farchione L. A. Inactivation of aminoglycosides by penicillins. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Jul;8 (Suppl A):27–36. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_a.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follath F., Wenk M., Vozeh S. Plasma concentration monitoring of aminoglycosides. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Jul;8 (Suppl A):37–43. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_a.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke E. L., Srinivasan S., Labthavikul P., Neu H. C. Rapid, reproducible enzyme immunoassay for tobramycin. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):93–96. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.93-96.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolley M. E., Stroupe S. D., Wang C. H., Panas H. N., Keegan C. L., Schmidt R. L., Schwenzer K. S. Fluorescence polarization immunoassay. I. Monitoring aminoglycoside antibiotics in serum and plasma. Clin Chem. 1981 Jul;27(7):1190–1197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. E., Nelson J. C., Elder H. A. Amikacin: a rapid and sensitive radioimmunoassay. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jan;7(1):42–45. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund M. E., Blazevic D. J., Matsen J. M. Rapid gentamicin bioassay using a multiple-antibiotic-resistant strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Nov;4(5):569–573. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.5.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson L. Rapid bioluminescent assay of serum amikacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Aug;10(2):125–130. doi: 10.1093/jac/10.2.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riff L. J., Jackson G. G. Laboratory and clinical conditions for gentamicin inactivation by carbenicillin. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Dec;130(6):887–891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawchuk R. J., Zaske D. E., Cipolle R. J., Wargin W. A., Strate R. G. Kinetic model for gentamicin dosing with the use of individual patient parameters. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1977 Mar;21(3):362–369. doi: 10.1002/cpt1977213362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selepak S. T., Witebsky F. G., Robertson E. A., MacLowry J. D. Evaluation of five gentamicin assay procedures for clinical microbiology laboratories. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Apr;13(4):742–749. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.4.742-749.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. H., Van Otto B., Smith A. L. A rapid chemical assay for gentamicin. N Engl J Med. 1972 Mar 16;286(11):583–586. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197203162861106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens P., Young L. S., Hewitt W. L. 125I radioimmunoassay of netilmicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):768–770. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


