Abstract
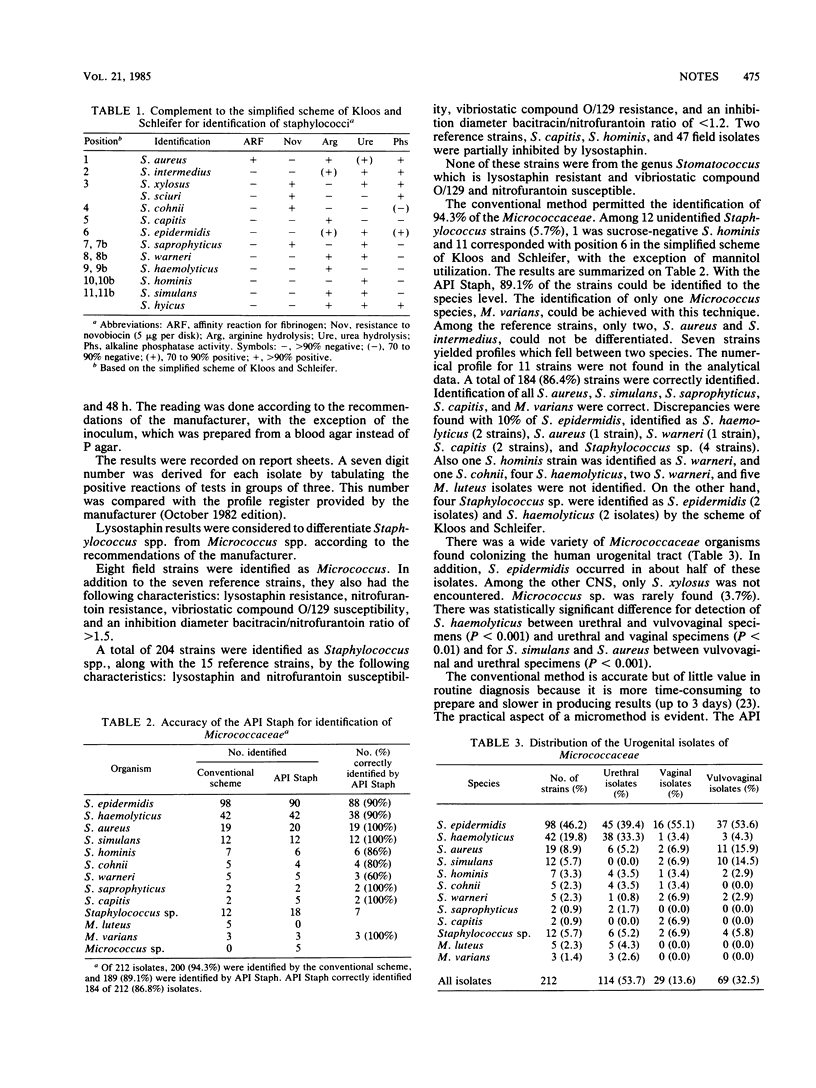
Two hundred and twelve Micrococcaceae isolates were obtained from 82 men with nongonococcal urethritis, 24 women with vaginitis, and 54 girls with vulvovaginitis. Identification and biotyping of these strains were carried out by using the simplified scheme of Kloos and Schleifer (W. E. Kloos and K. H. Schleifer, J. Clin. Microbiol. 1:82-88, 1975) and the commercially available API Staph test (DMS Staph Trac). Staphylococcus epidermidis occurred in about half of these isolates. There was no statistical difference between the urethral and vaginal specimens, except for S. haemolyticus found primarily in males and for S. simulans and S. aureus found primarily in girls between the ages of 1 and 12 years. S. saprophyticus, a major cause of urinary tract infections in young women, was never isolated from the vagina, suggesting the probability of another reservoir.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldridge K. E., Stratton C. W., Patterson L. S., Evans M. E., Hodges R. L. Comparison of the Staph-Ident system with a conventional method for species identification of urine and blood isolates of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Mar;17(3):516–520. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.3.516-520.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvet P., Chatelain R., Riou J. Y. Intérêt du composé vibriostatique O/129 pour différencier les genres Staphylococcus et Micrococcus. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1982 Nov-Dec;133(3):449–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun Y., Fleurette J., Forey F. Micromethod for biochemical identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Nov;8(5):503–508. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.5.503-508.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carret G., Bismuth R., Brun Y., Chomarat M., Coullioud D., Coupry A., Flandrois J. P., Fleurette J., Fougerat J., Freney J. Valeur de la recherche de l'affinité pour le fibrinogène pour l'identification de Staphylococcus aureus. Résultats d'une étude multicentrique. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1983 Sep;31(7):593–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Parisi J. T., Bisno A. L., Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Characterization of clinically significant strains of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):258–269. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.258-269.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox C. E. The urethra and its relationship to urinary tract infection: the flora of the normal female urethra. South Med J. 1966 May;59(5):621–626. doi: 10.1097/00007611-196605000-00027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doern G. V., Earls J. E., Jeznach P. A., Parker D. S. Species identification and biotyping of staphylococci by the API staph-ident system. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;17(2):260–263. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.2.260-263.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellner P. D., Myrick B. Speciation of coagulase-negative staphylococci in the clinical laboratory. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Apr;1(2):87–90. doi: 10.1007/BF02014197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk D., Guering S. J. Differentiation of Staphylococcus and Micrococcus spp. with the Taxo A bacitracin disk. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):719–721. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.719-721.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giger O., Charilaou C. C., Cundy K. R. Comparison of the API Staph-Ident and DMS Staph-Trac systems with conventional methods used for the identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jan;19(1):68–72. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.1.68-72.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill V. J., Selepak S. T., Williams E. C. Species identification and antibiotic susceptibilities of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Dec;18(6):1314–1319. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.6.1314-1319.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert J. P., Caillet R. Différenciation entre microcoques et staphylocoques par l'étude de la sensibilité à la nitrofurantoïne [N (5 nitro - 2 furfurylidène - 1 amino-hydantoïne)]. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1983 Mar;31(3):214–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovelius B., Mårdh P. A. Staphylococcus saprophyticus as a common cause of urinary tract infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 May-Jun;6(3):328–337. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.3.328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovelius B., Thelin I., Mårdh P. A. Staphylococcus saprophyticus in the aetiology of nongonococcal urethritis. Br J Vener Dis. 1979 Oct;55(5):369–374. doi: 10.1136/sti.55.5.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan P. A., Iravani A., Richard G. A., Baer H. Urinary tract infection caused by Staphylococcus saprophyticus. J Infect Dis. 1980 Oct;142(4):510–515. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.4.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloos W. E., Schleifer K. H. Simplified scheme for routine identification of human Staphylococcus species. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):82–88. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.82-88.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloos W. E., Wolfshohl J. F. Identification of Staphylococcus species with the API STAPH-IDENT system. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):509–516. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.509-516.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marples R. R., Richardson J. F. Evaluation of a micromethod gallery (API Staph) for the identification of staphylococci and micrococci. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Jun;35(6):650–656. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.6.650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolle L. E., Hoban S. A., Harding G. K. Characterization of coagulase-negative staphylococci from urinary tract specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;17(2):267–271. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.2.267-271.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin S. J., Lyons R. W., Murcia A. J. Endocarditis associated with cardiac catheterization due to a Gram-positive coccus designated Micrococcus mucilaginosus incertae sedis. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jun;7(6):546–549. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.6.546-549.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sewell C. M., Clarridge J. E., Young E. J., Guthrie R. K. Clinical significance of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Aug;16(2):236–239. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.2.236-239.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tselenis-Kotsowilis A. D., Koliomichalis M. P., Papavassiliou J. T. Acute pyelonephritis caused by Staphylococcus xylosus. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):593–594. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.593-594.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


