Abstract
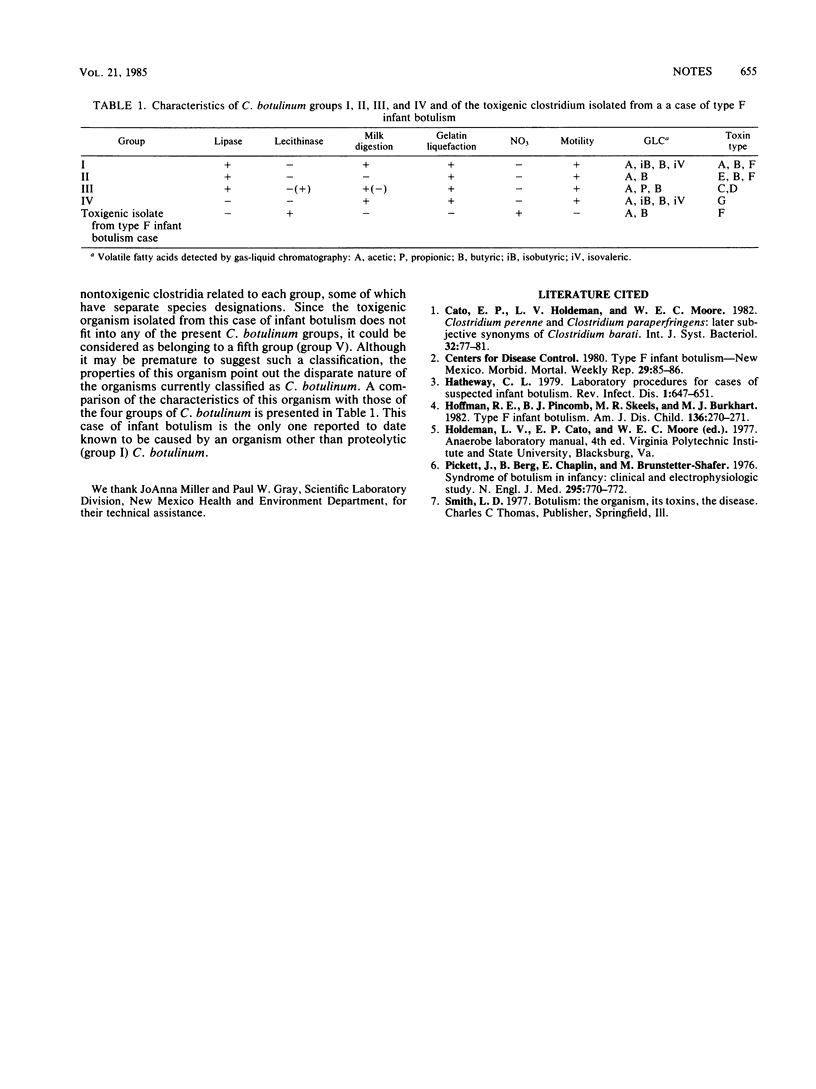
All reported cases of infant botulism except one have been caused by proteolytic strains (group I) of Clostridium botulinum, toxin types A or B. We describe the cultural and biochemical characteristics of the causative organism of this singular case of infant botulism, caused by type F botulinal toxin. Although this organism produces type F botulinal toxin, it is quite different from proteolytic (group I) C. botulinum, being more closely related to Clostridium barati.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hatheway C. L. Laboratory procedures for cases of suspected infant botulism. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 Jul-Aug;1(4):647–651. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.4.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman R. E., Pincomb B. J., Skeels M. R. Type F infant botulism. Am J Dis Child. 1982 Mar;136(3):270–271. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1982.03970390084021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett J., Berg B., Chaplin E., Brunstetter-Shafer M. A. Syndrome of botulism in infancy: clinical and electrophysiologic study. N Engl J Med. 1976 Sep 30;295(14):770–772. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197609302951407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


