Abstract
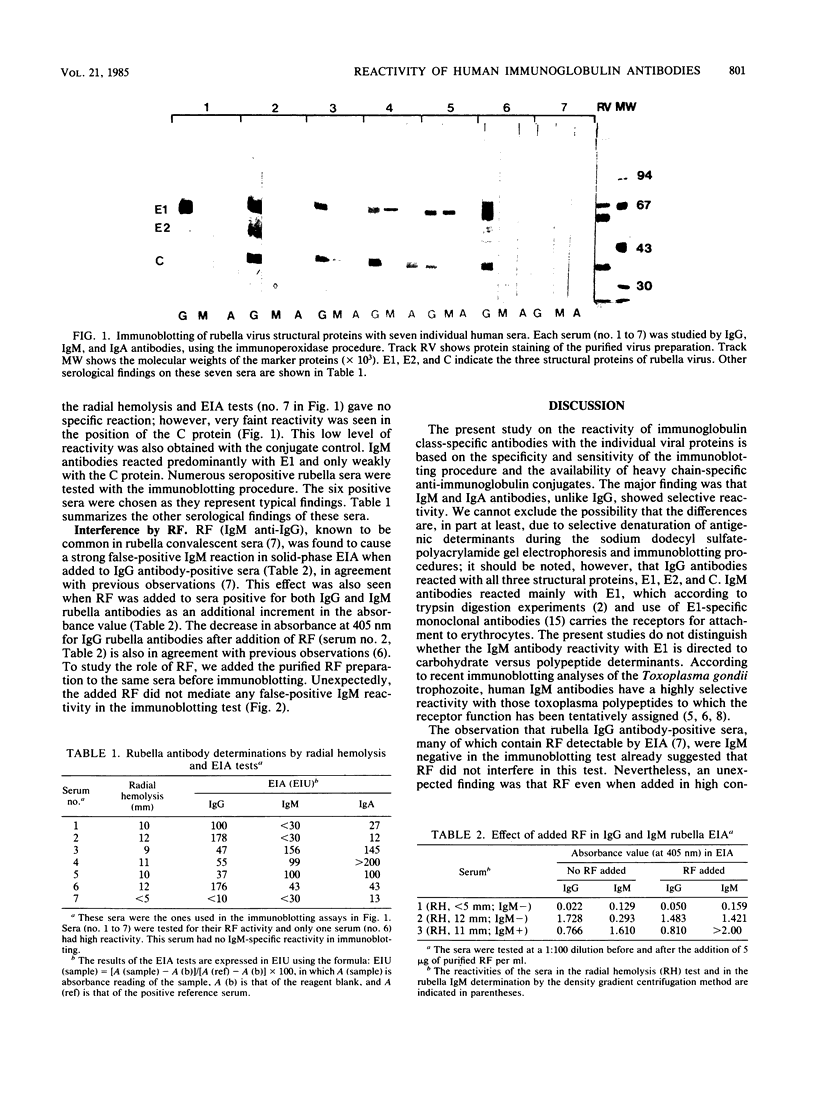
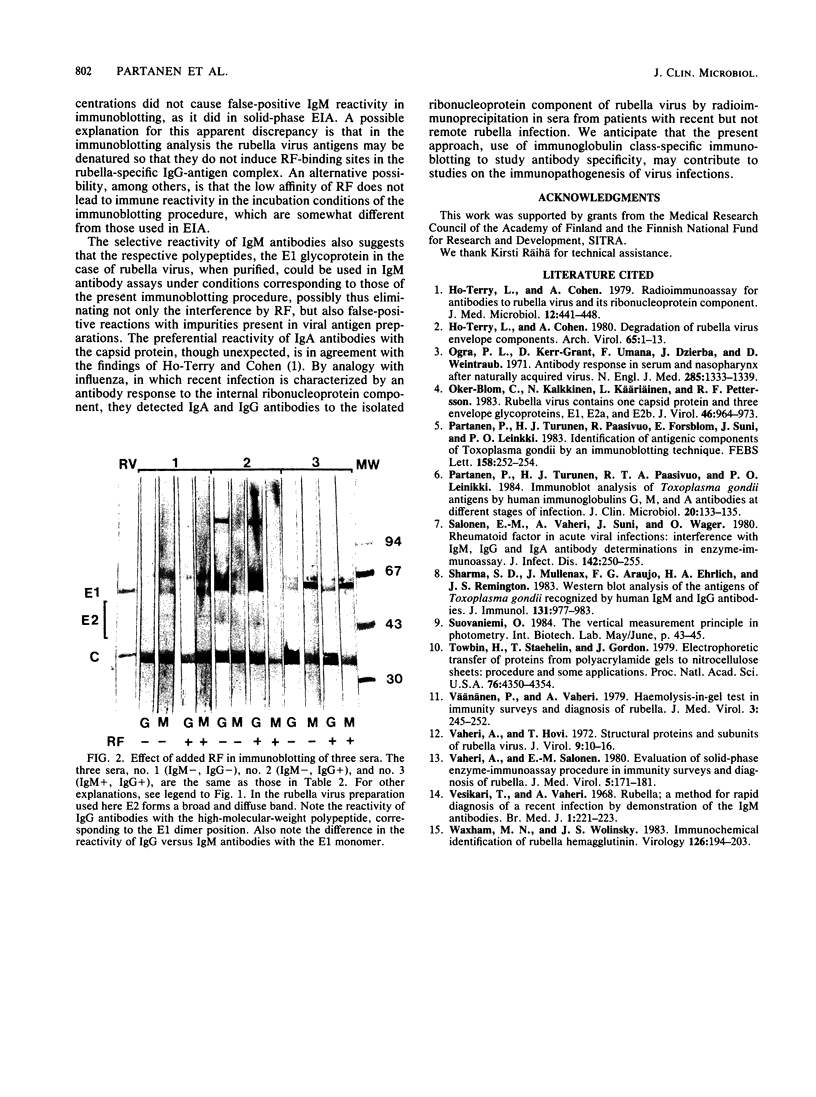
Proteins of purified rubella virus were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, transferred to nitrocellulose, and immunoblotted with human sera and immunoglobulin class heavy-chain-specific peroxidase conjugates. The levels of rubella antibodies in these sera were predetermined by the radial hemolysis test, the density gradient centrifugation method for immunoglobulin M (IgM) antibodies, and IgG-, IgM-, and IgA-specific enzyme immunoassays. In immunoblotting, rubella-specific IgG antibodies reacted with both envelope glycoproteins (E1 and E2) and the capsid protein (C). In contrast, rubella IgM antibodies reacted predominantly with E1, whereas the specific reactivity of IgA antibodies was directed mainly to the capsid protein. Purified IgM rheumatoid factor added to IgG-positive, IgM-negative serum did not give false-positive reactivity in the immunoblotting test as it did in solid-phase enzyme immunoassays. The immunoglobulin class-specific reactivities with the different viral proteins are expected to have diagnostic applications.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ho-Terry L., Cohen A. Degradation of rubella virus envelope components. Arch Virol. 1980;65(1):1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF01340535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho-Terry L., Cohen A. Radioimmunoassay for antibodies to rubella virus and its ribonucleoprotein component. J Med Microbiol. 1979 Nov;12(4):441–448. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-4-441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogra P. L., Kerr-Grant D., Umana G., Dzierba J., Weintraub D. Antibody response in serum and nasopharynx after naturally acquired and vaccine-induced infection with rubella virus. N Engl J Med. 1971 Dec 9;285(24):1333–1339. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197112092852401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oker-Blom C., Kalkkinen N., Käriäinen L., Pettersson R. F. Rubella virus contains one capsid protein and three envelope glycoproteins, E1, E2a, and E2b. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):964–973. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.964-973.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partanen P., Turunen H. J., Paasivuo R. T., Leinikki P. O. Immunoblot analysis of Toxoplasma gondii antigens by human immunoglobulins G, M, and A antibodies at different stages of infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):133–135. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.133-135.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partanen P., Turunen H. J., Paasivuo R., Forsblom E., Suni J., Leinikki P. O. Identification of antigenic components of Toxoplasma gondii by an immunoblotting technique. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jul 25;158(2):252–254. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80589-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen E. M., Vaheri A., Suni J., Wager O. Rheumatoid factor in acute viral infections: interference with determination of IgM, IgG, and IgA antibodies in an enzyme immunoassay. J Infect Dis. 1980 Aug;142(2):250–255. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.2.250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. D., Mullenax J., Araujo F. G., Erlich H. A., Remington J. S. Western Blot analysis of the antigens of Toxoplasma gondii recognized by human IgM and IgG antibodies. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):977–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaheri A., Hovi T. Structural proteins and subunits of rubella virus. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):10–16. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.10-16.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaheri A., Salonen E. M. Evaluation of solid-phase enzyme-immunoassay procedure in immunity surveys and diagnosis of rubella. J Med Virol. 1980;5(3):171–181. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890050302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Vaheri A. Rubella: a method for rapid diagnosis of a recent infection by demonstration of the IgM antibodies. Br Med J. 1968 Jan 27;1(5586):221–223. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5586.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vänänen P., Vaheri A. Hemolysis-in-gel test in immunity surveys and diagnosis of rubella. J Med Virol. 1979;3(4):245–252. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890030402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxham M. N., Wolinsky J. S. Immunochemical identification of rubella virus hemagglutinin. Virology. 1983 Apr 15;126(1):194–203. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90471-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]