Abstract
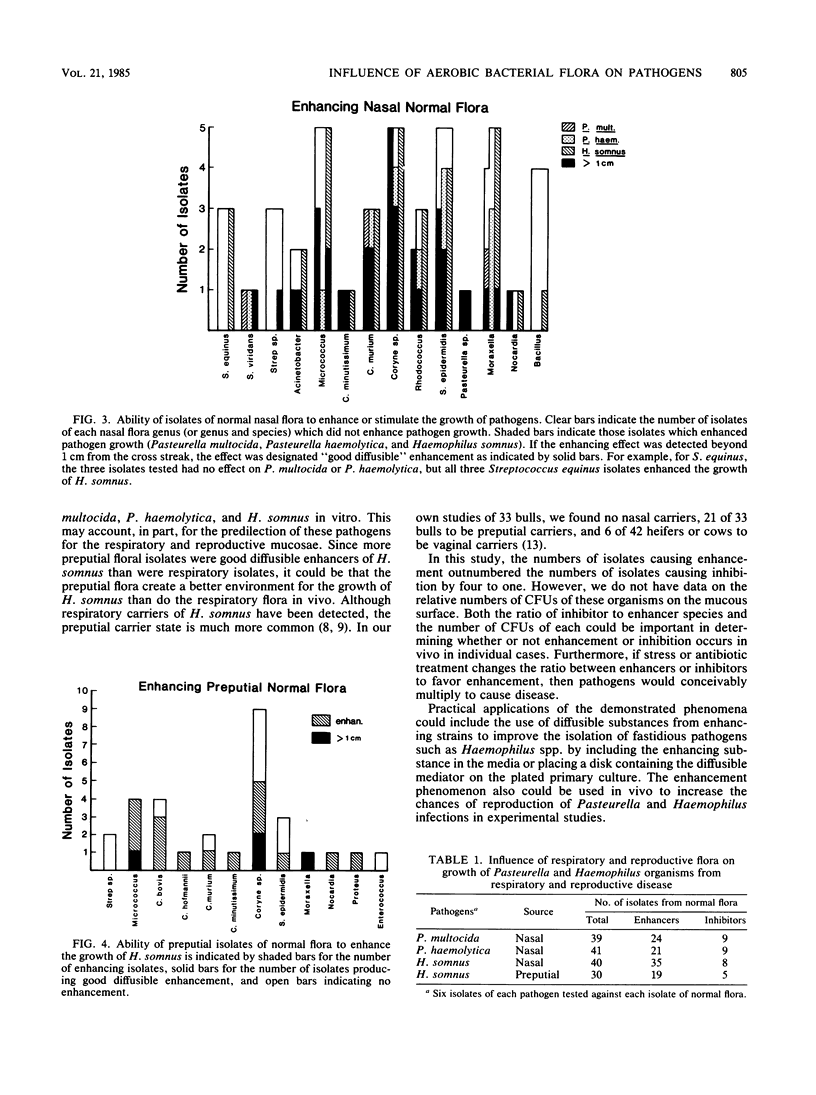
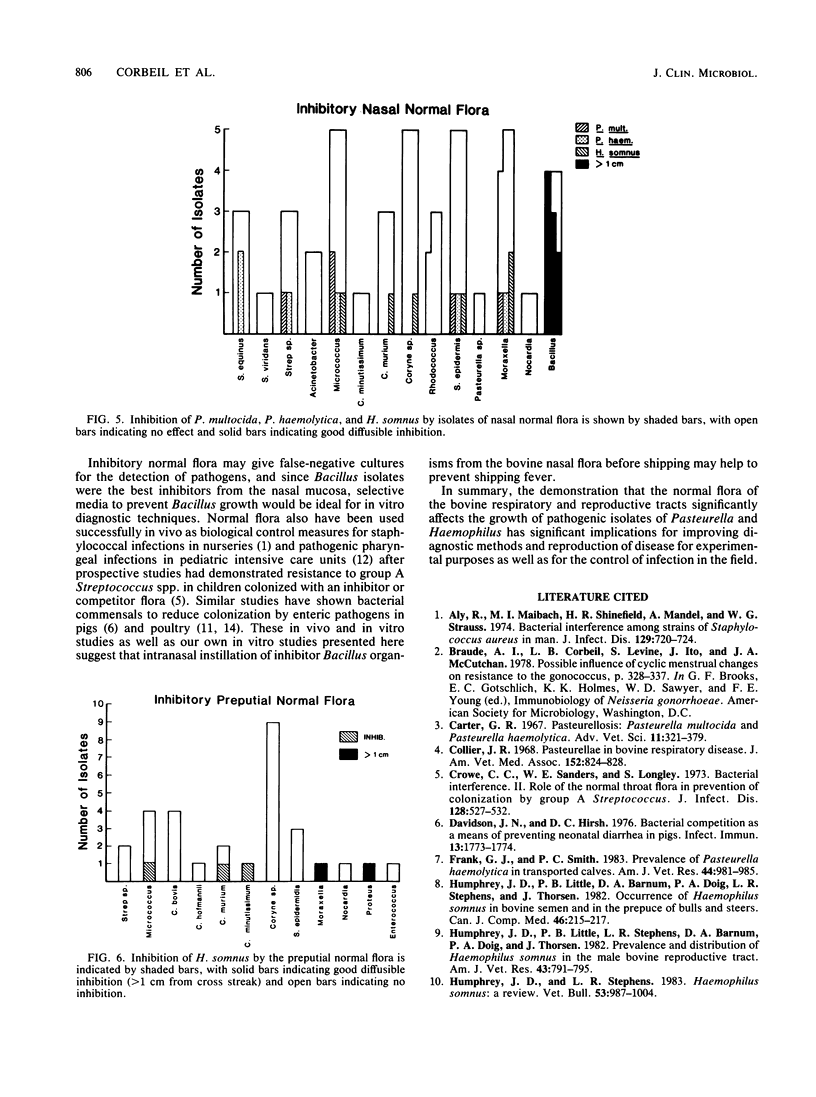
The ability of the aerobic bacterial flora from the normal bovine respiratory and reproductive tracts to enhance or inhibit the growth of Pasteurella haemolytica, P. multocida, and Haemophilus somnus was tested in vitro. Six strains of each of these pathogens were cross streaked with each isolate of bovine normal flora. Flora which enhanced the growth of these pathogenic bacteria outnumbered inhibitors four to one. An intermediate number of isolates produced no effect on pathogen growth. Most enhancers were gram positive (Micrococcus, Staphylococcus, Corynebacterium, or Rhodococcus isolates), although several isolates of Moraxella and Actinobacter were also good enhancers. For H. somnus, there were proportionally more organisms which produced marked enhancement among the preputial flora than among the nasal flora, which may account for the greater number of genital carriers than nasal carriers. Bacillus isolates were the most significant inhibitors among the nasal flora, whereas no genus or species from the reproductive tract was noted to produce appreciable inhibition. It is proposed that changes in ratios of inhibitors to enhancers may determine, in part, whether a carrier state or disease occurs. Also, suggestions are made for in vitro use of this phenomenon for diagnostic tests.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aly R., Maibach H. I., Shinefield H. R., Mandel A., Strauss W. G. Bacterial interference among strains of Staphylococcus aureus in man. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jun;129(6):720–724. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.6.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter G. R. Pasteurellosis: Pasteurella multocida and Pasteurella hemolytica. Adv Vet Sci. 1967;11:321–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr, Longley S. Bacterial interference. II. Role of the normal throat flora in prevention of colonization by group A Streptococcus. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(4):527–532. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.4.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. N., Hirsh D. C. Bacterial competition as a means of preventing neonatal diarrhea in pigs. Infect Immun. 1976 Jun;13(6):1773–1774. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.6.1773-1774.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G. H., Smith P. C. Prevalence of Pasteurella haemolytica in transported calves. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Jun;44(6):981–985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. D., Little P. B., Barnum D. A., Doig P. A., Stephens L. R., Thorsen J. Occurrence of "Haemophilus somnus" in bovine semen and in the prepuce of bulls and steers. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Apr;46(2):215–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. D., Little P. B., Stephens L. R., Barnum D. A., Doig P. A., Thorsen J. Prevalence and distribution of Haemophilus somnus in the male bovine reproductive tract. Am J Vet Res. 1982 May;43(5):791–795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soerjadi A. S., Snoeyenbos G. H., Weinack O. M. Intestinal colonization and competitive exclusion of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni in young chicks. Avian Dis. 1982 Jul-Sep;26(3):520–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprunt K., Leidy G., Redman W. Abnormal colonization of neonates in an ICU: conversion to normal colonization by pharyngeal implantation of alpha hemolytic streptococcus strain 215. Pediatr Res. 1980 Apr;14(4 Pt 1):308–313. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198004000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinack O. M., Snoeyenbos G. H., Smyser C. F., Soerjadi A. S. Reciprocal competitive exclusion of salmonella and Escherichia coli by native intestinal microflora of the chicken and turkey. Avian Dis. 1982 Jul-Sep;26(3):585–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]