Abstract
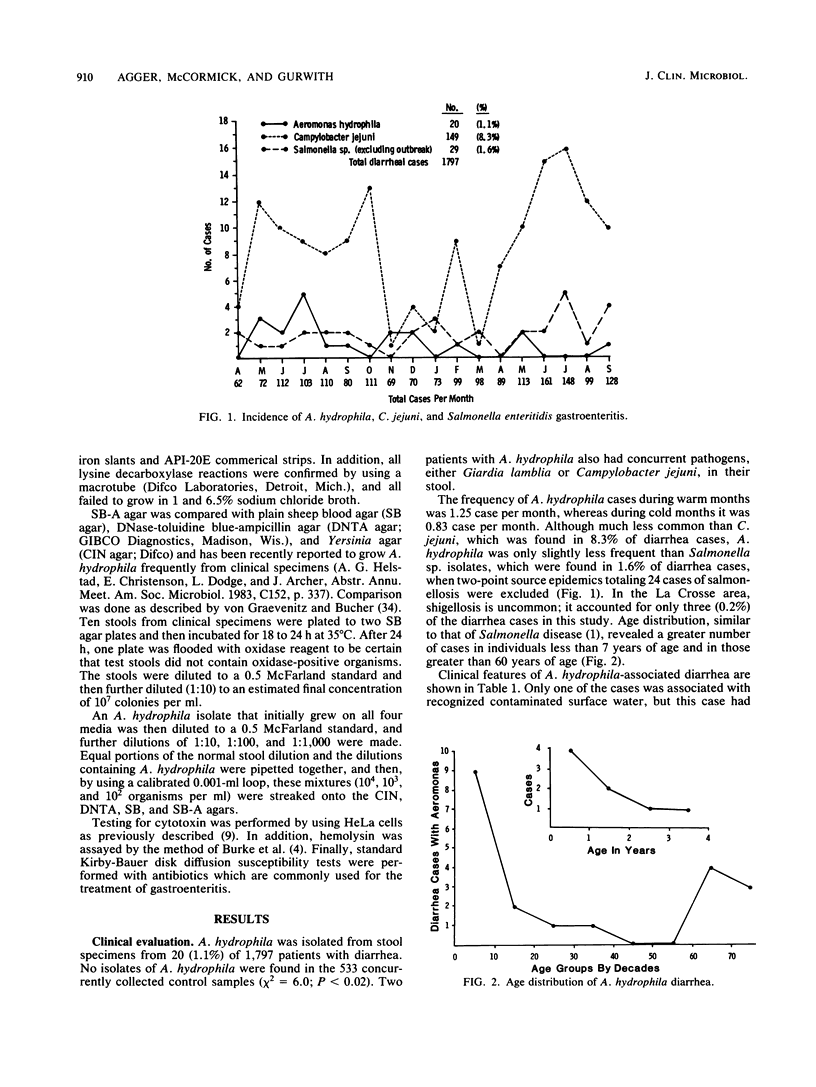
The prevalence of Aeromonas hydrophila in stool specimens from patients with diarrhea was studied during 18 months. A. hydrophila was found in 1.1% of patients with diarrhea and in none of 533 control patients (P less than 0.02). Cases were detected 1.5 times more often during the summer months than the winter months, and most occurred in children less than 2 years of age. Clinical features included fever greater than 38 degrees C (55%), abdominal cramps (35%), vomiting (25%), and duration of illness greater than 10 days (50%). Detection of A. hydrophila in stools was facilitated by the use of sheep blood agar with 15 micrograms of ampicillin per ml which was flooded with oxidase reagent after growth. A cytotoxin was produced by 62% of the isolates, and the cytotoxic strains showed positive results in a hemolysin assay and a lysine decarboxylase reaction.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhat P., Shanthakumari S., Rajan D. The characterization and significance of Plesiomonas shigelloides and Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from an epidemic of diarrhoea. Indian J Med Res. 1974 Jul;62(7):1051–1060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Feldman R. A. From the centers for disease control. Salmonella bacteremia: reports to the Centers for Disease Control, 1968-1979. J Infect Dis. 1981 May;143(5):743–746. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.5.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Cooper M., Robinson J., Gracey M., Lesmana M., Echeverria P., Janda J. M. Hemagglutination patterns of Aeromonas spp. in relation to biotype and source. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jan;19(1):39–43. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.1.39-43.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Gracey M., Robinson J., Peck D., Beaman J., Bundell C. The microbiology of childhood gastroenteritis: Aeromonas species and other infective agents. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jul;148(1):68–74. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.1.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Robinson J., Atkinson H. M., Gracey M. Biochemical characteristics of enterotoxigenic Aeromonas spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):48–52. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.48-52.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Robinson J., Beaman J., Gracey M., Lesmana M., Rockhill R., Echeverria P., Janda J. M. Correlation of enterotoxicity with biotype in Aeromonas spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1196–1200. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1196-1200.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champsaur H., Adremont A., Mathieu D., Rottman E., Auzepy P. Cholera-like illness due to Aeromonas sobria. J Infect Dis. 1982 Feb;145(2):248–254. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee B. D., Neogy K. N. Studies on Aeromonas and Plesiomonas species isolated from cases of choleraic diarrhoea. Indian J Med Res. 1972 Apr;60(4):520–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumberbatch N., Gurwith M. J., Langston C., Sack R. B., Brunton J. L. Cytotoxic enterotoxin produced by Aeromonas hydrophila: relationship of toxigenic isolates to diarrheal disease. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):829–837. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.829-837.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daily O. P., Joseph S. W., Coolbaugh J. C., Walker R. I., Merrell B. R., Rollins D. M., Seidler R. J., Colwell R. R., Lissner C. R. Association of Aeromonas sobria with human infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Apr;13(4):769–777. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.4.769-777.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. A., 2nd, Kane J. G., Garagusi V. F. Human aeromonas infections: a review of the literature and a case report of endocarditis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1978 May;57(3):267–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Murray G. F., Maddrey W. C. Aeromonas septicemia from hepatobiliary disease. Am J Dig Dis. 1973 Apr;18(4):323–331. doi: 10.1007/BF01070994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Blacklow N. R., Sanford L. B., Cukor G. G. Travelers' diarrhea among American Peace Corps volunteers in rural Thailand. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jun;143(6):767–771. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.6.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R. J., Barnishan J. In vitro susceptibilities of Aeromonas hydrophila to 32 antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Feb;19(2):357–358. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurwith M., Bourque C., Cameron E., Forrest G., Green M. Cholera-like diarrhea in Canada. Report of a case associated with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and a toxin-producing Aeromonas hydrophila. Arch Intern Med. 1977 Oct;137(10):1461–1464. doi: 10.1001/archinte.137.10.1461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson P. G., Standridge J., Jarrett F., Maki D. G. Freshwater wound infection due to Aeromonas hydrophila. JAMA. 1977 Sep 5;238(10):1053–1054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen T. C., Fliermans C. B., Hirsch R. P., Esch G. W. Prevalence and distribution of Aeromonas hydrophila in the United States. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Nov;36(5):731–738. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.5.731-738.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt L. K., Overman T. L., Otero R. B. Role of pH in oxidase variability of Aeromonas hydrophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jun;13(6):1054–1059. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.6.1054-1059.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Bottone E. J., Skinner C. V., Calcaterra D. Phenotypic markers associated with gastrointestinal Aeromonas hydrophila isolates from symptomatic children. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;17(4):588–591. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.4.588-591.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungh A., Popoff M., Wadstrom T. Aeromonas hydrophila in acute diarrheal disease: detection of enterotoxin and biotyping of strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Aug;6(2):96–100. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.2.96-100.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken A. W., Barkley R. Isolation of Aeromonas species from clinical sources. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Nov;25(11):970–975. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.11.970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohieldin M. S., Gabr M., el Hefny A., Mahmoud S. S., Abdallah H., Abdallah A. Bacteriological and clinical studies in infantile diarrhoea: II. Doubtful pathogens: Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas, Alcaligens and Aeromonas. J Trop Pediatr Afr Child Health. 1966 Mar;11(4):88–94. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.tropej.a057181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. G., Jr, Wilson R., Davis B. R., Wachsmuth I. K., Riddle C. F., Wathen H. G., Pollard R. A., Blake P. A. Non-O group 1 Vibrio cholerae gastroenteritis in the United States: clinical, epidemiologic, and laboratory characteristics of sporadic cases. Ann Intern Med. 1981 May;94(5):656–658. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-5-656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overman T. L., D'Amato R. F., Tomfohrde K. M. Incidence of "oxidase-variable" strains of Aeromonas hydrophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):244–247. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.244-247.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSNER R. AEROMONAS HYDROPHILA AS THE ETIOLOGIC AGENT IN A CASE OF SEVERE GASTROENTERITIS. Am J Clin Pathol. 1964 Oct;42:402–404. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/42.4.402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanyal S. C., Singh S. J., Sen P. C. Enteropathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila and Plesiomonas shigelloides. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Feb;8(1):195–198. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-1-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shandera W. X., Johnston J. M., Davis B. R., Blake P. A. Disease from infection with Vibrio mimicus, a newly recognized Vibrio species. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Aug;99(2):169–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotts E. B., Jr, Rimler R. Medium for the isolation of Aeromonas hydrophila. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Oct;26(4):550–553. doi: 10.1128/am.26.4.550-553.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelen P., Burke V., Gracey M. Effects of intestinal micro-organisms on fluid and electrolyte transport in the jejunum of the rat. J Med Microbiol. 1978 Nov;11(4):463–470. doi: 10.1099/00222615-11-4-463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Graevenitz A., Mensch A. H. The genus aeromonas in human bacteriology report of 30 cases and review of the literature. N Engl J Med. 1968 Feb 1;278(5):245–249. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196802012780504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T., Ljungh A., Wretlind B. Enterotoxin, haemolysin and cytotoxic protein in Aeromonas hydrophila from human infections. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1976 Apr;84(2):112–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb01911.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Graevenitz A., Bucher C. Evaluation of differential and selective media for isolation of Aeromonas and Plesiomonas spp. from human feces. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):16–21. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.16-21.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Graevenitz A., Zinterhofer L. The detection of Aeromonas hydrophila in stool specimens. Health Lab Sci. 1970 Jul;7(3):124–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]