Abstract
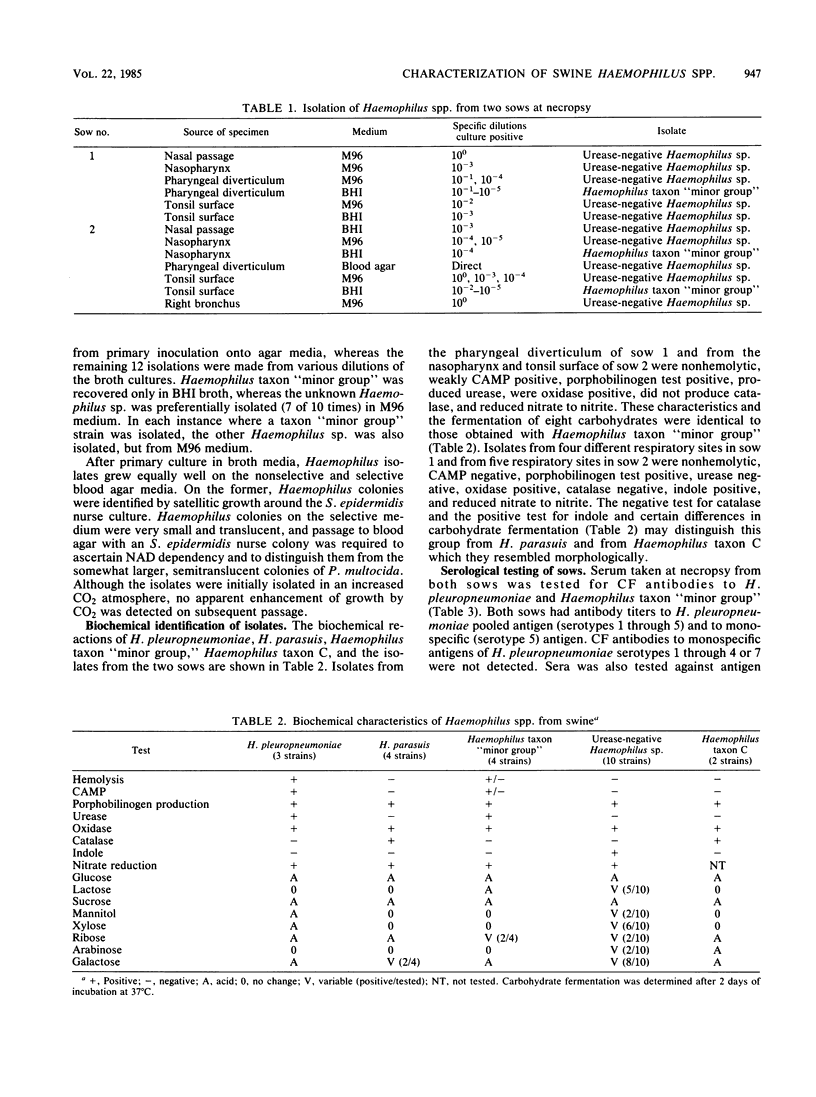
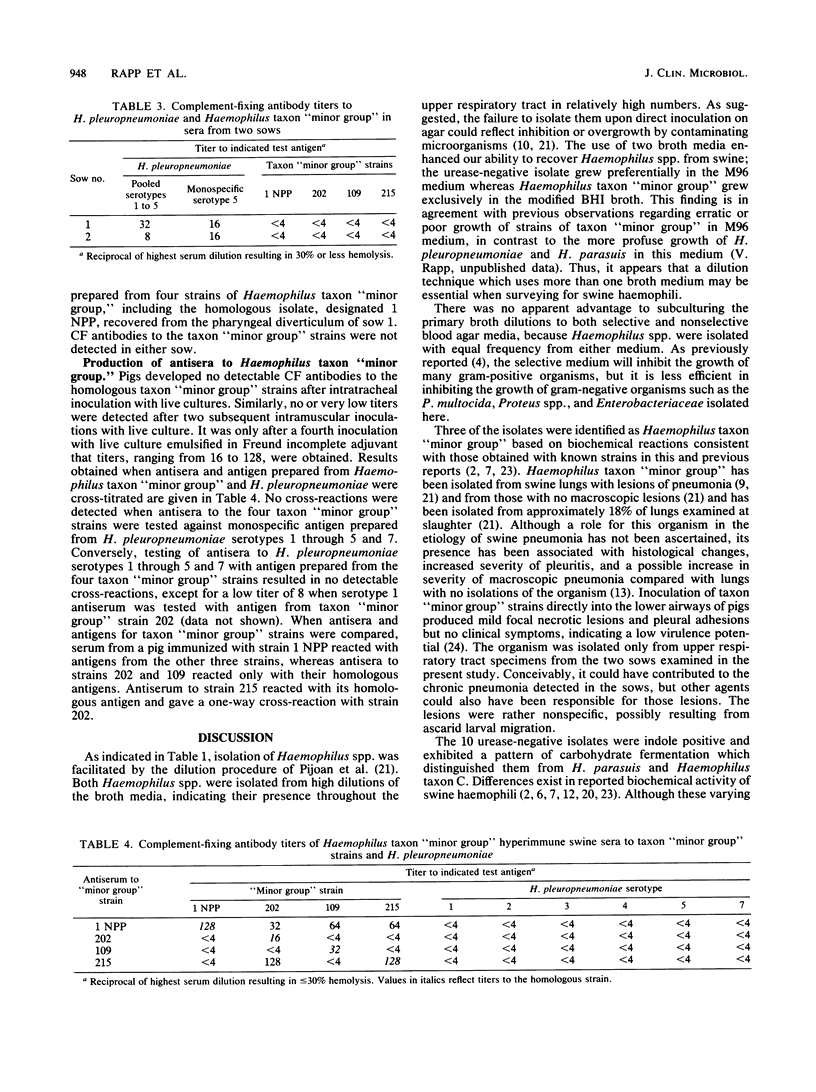
Of 30 sows from a herd believed to be free of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae infection, 2 had complement-fixing antibodies to H. pleuropneumoniae serotype 5. Necropsy and microbiological examination of the two sows revealed no evidence of H. pleuropneumoniae infection; however, Haemophilus taxon "minor group" and a urease-negative, indole-positive Haemophilus sp. were isolated from numerous respiratory tract sites in both sows. Isolation of these Haemophilus spp. was facilitated by serially diluting specimens in two broth media. Pigs from a closed, respiratory disease-free herd were inoculated with four strains of Haemophilus taxon "minor group" to determine whether the organism induces antibodies which cross-react with H. pleuropneumoniae in the complement fixation test. Antigenic heterogeneity among the taxon "minor group" strains was apparent; however, antibodies cross-reacting between these strains and H. pleuropneumoniae serotypes 1 through 5 and 7 were not detected.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bentley O. E., Farrington D. O. Evaluation of an induced Pasteurella multocida swine pneumonia model. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Nov;41(11):1870–1873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biberstein E. L., Gunnarsson A., Hurvell B. Cultural and biochemical criteria for the identification of haemophilus spp from swine. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Jan;38(1):7–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbride K. A., Rosendal S. Evaluation of a selective medium for isolation of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Can J Comp Med. 1983 Oct;47(4):445–450. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnarsson A. Evaluation of different antigens in the complement-fixation test for diagnosis of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae (parahaemolyticus) infections in swine. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Nov;40(11):1564–1567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M. A taxonomic study of the genus Haemophilus, with the proposal of a new species. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Mar;93(1):9–62. doi: 10.1099/00221287-93-1-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kume K., Nakai T., Sawata A. Isolation of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae from the nasal cavities of healthy pigs. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1984 Oct;46(5):641–647. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.46.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little T. W. Haemophilus infection in pigs. Vet Rec. 1970 Oct 3;87(14):399–402. doi: 10.1136/vr.87.14.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little T. W., Harding J. D. The interaction of Haemophilus parahaemolyticus and Pasteurella multocida in the respiratory tract of the pig. Br Vet J. 1980 Jul-Aug;136(4):371–383. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)32240-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombin L. H., Rosendal S., Mitchell W. R. Evaluation of the complement fixation test for the diagnosis of pleuropneumonia of swine caused by Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Apr;46(2):109–114. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannheim W., Pohl S., Holländer R. Zur Systematik von Actinobacillus, Haemophilus and Pasteurella: Basenzusammensetzung der DNS, Atmungschinone und kulturell-biochemische Eigenschaften repräsentativer Sammlungsstämme. Zentralbl Bakteriol A. 1980;246(4):512–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. B., Pijoan C., Hilley H. D., Rapp V. Microorganisms associated with pneumonia in slaughter weight swine. Can J Comp Med. 1985 Apr;49(2):129–137. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolet J., de Meuron P. A., Bachmann P. Sur l'hémophilose du porc. IV. L'épreuve de déviation du complément, un test de dépistage des infections à Haemophilus parahaemolyticus. Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 1971 Apr;113(4):191–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R. Haemophilus parahaemolyticus serotypes. Serological response. Nord Vet Med. 1979 Oct;31(10):401–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R., Mandrup M. Pleuropneumonia in swine caused by Haemophilus parahaemolyticus. A study of the epidemiology of the infection. Nord Vet Med. 1977 Nov;29(11):465–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R. Serological and immunological studies of pleuropneumonia of swine caused by Haemophilus parahaemolyticus. Acta Vet Scand. 1974;15(1):80–89. doi: 10.1186/BF03547495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R., Thomsen A. D., Vesterlund S. D. Pleuropneumonia caused by Haemophilus parahaemolyticus. An attempt to control the disease at two progeny testing stations by serological blood testing followed by removal of the seropositive animals and their litter mates. Nord Vet Med. 1976 Jul-Aug;28(7-8):349–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly T., Rosendal S., Niven D. F. Porcine haemophili and actinobacilli: characterization by means of API test strips and possible taxonomic implications. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Oct;30(10):1229–1238. doi: 10.1139/m84-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pijoan C., Morrison R. B., Hilley H. D. Dilution technique for isolation of Haemophilus from swine lungs collected at slaughter. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):143–145. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.143-145.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp V. J., Ross R. F., Erickson B. Z. Serotyping of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae by rapid slide agglutination and indirect fluorescent antibody tests in swine. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Jan;46(1):185–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendal S., Boyd D. A., Gilbride K. A. Comparative virulence of porcine Haemophilus bacteria. Can J Comp Med. 1985 Jan;49(1):68–74. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendal S., Mittal K. R. Serological cross-reactivity between a porcine Actinobacillus strain and Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Can J Comp Med. 1985 Apr;49(2):164–170. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz R. A., Young T. F., Ross R. F., Jeske D. R. Prevalence of antibodies to Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae in Iowa swine. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Oct;43(10):1848–1851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


