Abstract
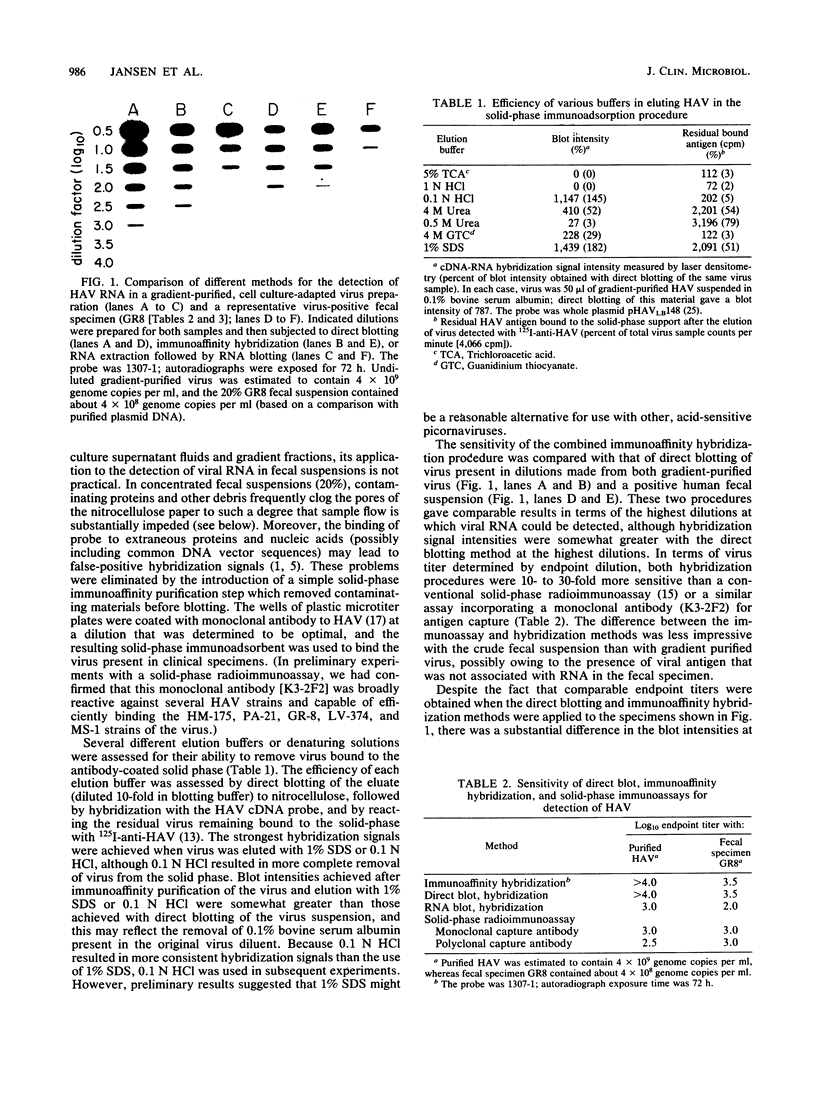
To apply cDNA-RNA hybridization methods to the detection of hepatitis A virus (HAV) in clinical materials, we developed a two-step method in which a microtiter-based, solid-phase immunoadsorption procedure incorporating a monoclonal anti-HAV capture antibody was followed by direct blotting of virus eluates to nitrocellulose and hybridization with 32P-labeled recombinant HAV cDNA. This immunoaffinity hybridization method is simple and involves few sample manipulations, yet it retains high sensitivity (10- to 30-fold more than radioimmunoassay) and is capable of detecting approximately 1 X 10(5) to 2 X 10(5) genome copies of virus. The inclusion of the immunoaffinity step removes most contaminating proteins and thus facilitates subsequent immobilization of the virus for hybridization. It also permits positive hybridization signals to be related to specific antigens and adds a level of specificity to the hybridization procedure. When the method was applied to 23 fecal specimens collected from individuals during week 1 of symptoms due to hepatitis A, 13 specimens were found to be reproducibly positive for HAV RNA by immunoaffinity hybridization, whereas only 11 contained viral antigen detectable by radioimmunoassay.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacterial contamination of human tumor samples. Science. 1984 Aug 17;225(4663):670–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baroudy B. M., Ticehurst J. R., Miele T. A., Maizel J. V., Jr, Purcell R. H., Feinstone S. M. Sequence analysis of hepatitis A virus cDNA coding for capsid proteins and RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2143–2147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binn L. N., Lemon S. M., Marchwicki R. H., Redfield R. R., Gates N. L., Bancroft W. H. Primary isolation and serial passage of hepatitis A virus strains in primate cell cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):28–33. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.28-33.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggs J. D., Melnick J. L., Conrad M. E., Felsher B. F. Viral hepatitis. Clinical and tissue culture studies. JAMA. 1970 Nov 9;214(6):1041–1046. doi: 10.1001/jama.214.6.1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov D. H., Graham D. Y., Estes M. K. Detection of rotaviruses by nucleic acid hybridization with cloned DNA of simian rotavirus SA11 genes. J Infect Dis. 1985 Aug;152(2):293–300. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.2.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duermeyer W., Wielaard F., van der Veen J. A new principle for the detection of specific IgM antibodies applied in an ELISA for hepatitis A. J Med Virol. 1979;4(1):25–32. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890040104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstone S. M., Kapikian A. Z., Purceli R. H. Hepatitis A: detection by immune electron microscopy of a viruslike antigen associated with acute illness. Science. 1973 Dec 7;182(4116):1026–1028. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4116.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyypiä T., Stålhandske P., Vainionpä R., Pettersson U. Detection of enteroviruses by spot hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Mar;19(3):436–438. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.3.436-438.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeDuc J. W., Lemon S. M., Keenan C. M., Graham R. R., Marchwicki R. H., Binn L. N. Experimental infection of the New World owl monkey (Aotus trivirgatus) with hepatitis A virus. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):766–772. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.766-772.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lednar W. M., Lemon S. M., Kirkpatrick J. W., Redfield R. R., Fields M. L., Kelley P. W. Frequency of illness associated with epidemic hepatitis A virus infections in adults. Am J Epidemiol. 1985 Aug;122(2):226–233. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon S. M., Binn L. N., Marchwicki R. H. Radioimmunofocus assay for quantitation of hepatitis A virus in cell cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):834–839. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.834-839.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon S. M., Brown C. D., Brooks D. S., Simms T. E., Bancroft W. H. Specific immunoglobulin M response to hepatitis A virus determined by solid-phase radioimmunoassay. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):927–936. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.927-936.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon S. M., Jansen R. W., Newbold J. E. Infectious hepatitis A virus particles produced in cell culture consist of three distinct types with different buoyant densities in CsCl. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):78–85. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.78-85.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon S. M., LeDuc J. W., Binn L. N., Escajadillo A., Ishak K. G. Transmission of hepatitis A virus among recently captured Panamanian owl monkeys. J Med Virol. 1982;10(1):25–36. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890100105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linemeyer D. L., Menke J. G., Martin-Gallardo A., Hughes J. V., Young A., Mitra S. W. Molecular cloning and partial sequencing of hepatitis A viral cDNA. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):247–255. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.247-255.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor A., Kornitschuk M., Hurrell J. G., Lehmann N. I., Coulepis A. G., Locarnini S. A., Gust I. D. Monoclonal antibodies against hepatitis A virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1237–1243. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1237-1243.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Najarian R., Caput D., Gee W., Potter S. J., Renard A., Merryweather J., Van Nest G., Dina D. Primary structure and gene organization of human hepatitis A virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2627–2631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provost P. J., Hilleman M. R. Propagation of human hepatitis A virus in cell culture in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Feb;160(2):213–221. doi: 10.3181/00379727-160-40422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Wong D. C., Moritsugu Y., Dienstag J. L., Routenberg J. A., Boggs J. D. A microtiter solid-phase radioimmunoassay for hepatitis A antigen and antibody. J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):349–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotbart H. A., Levin M. J., Villarreal L. P. Use of subgenomic poliovirus DNA hybridization probes to detect the major subgroups of enteroviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1105–1108. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1105-1108.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J. Physical map of polyoma viral DNA fragments produced by cleavage with a restriction enzyme from Haemophilus aegyptius, endonuclease R-HaeIII. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):946–953. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.946-953.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ticehurst J. R., Racaniello V. R., Baroudy B. M., Baltimore D., Purcell R. H., Feinstone S. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of hepatitis A virus cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5885–5889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]