Abstract
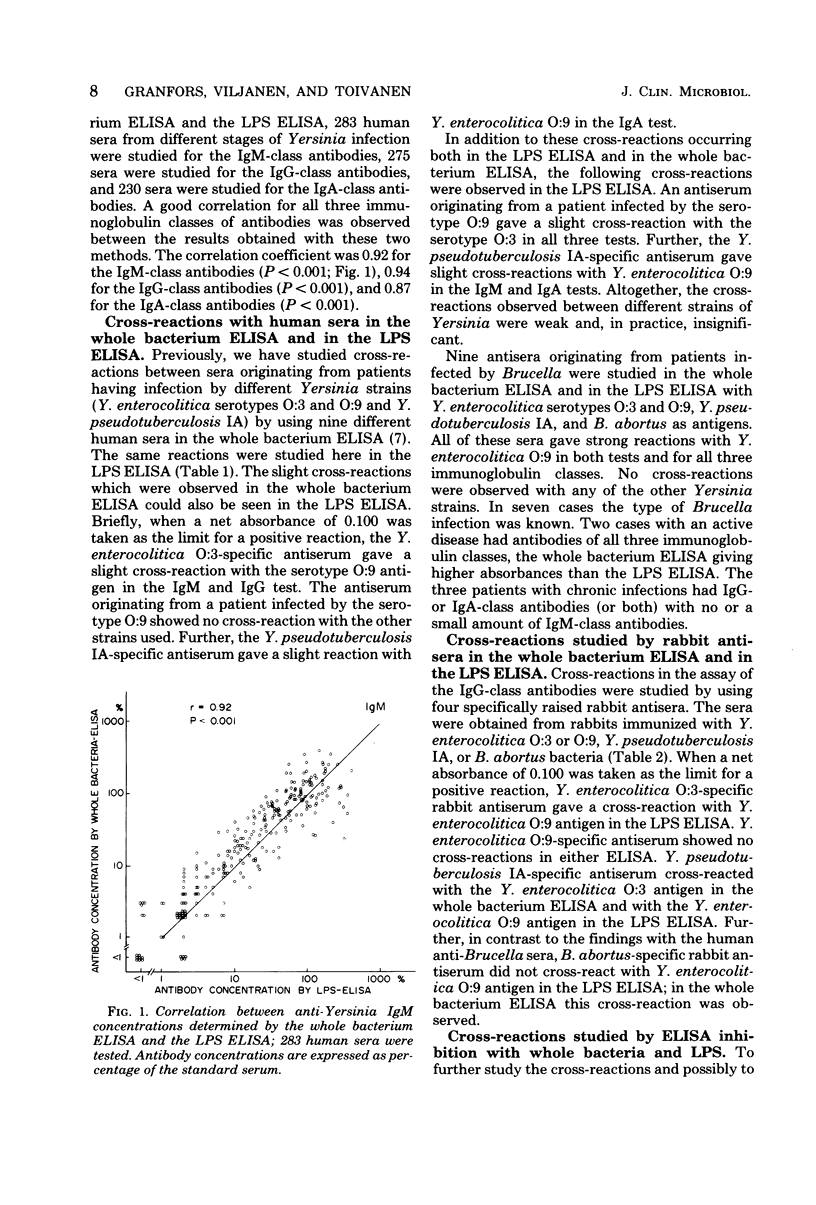
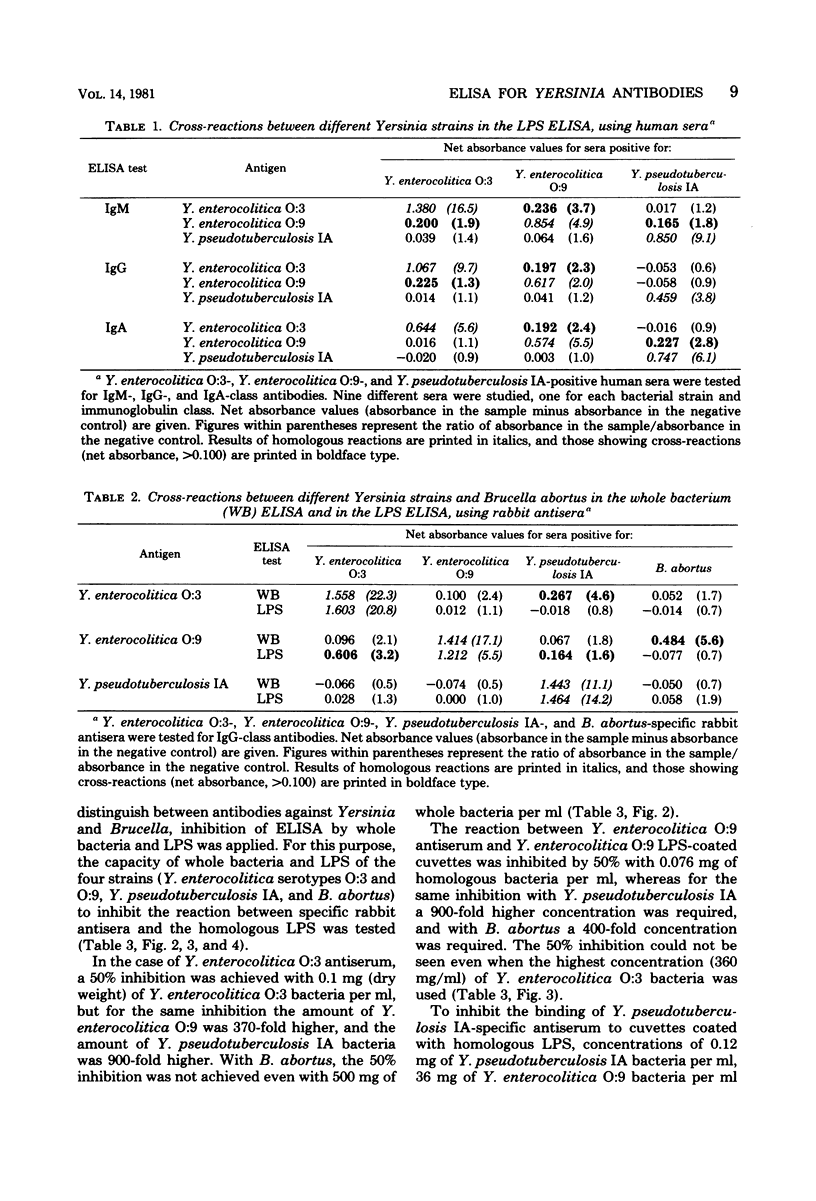
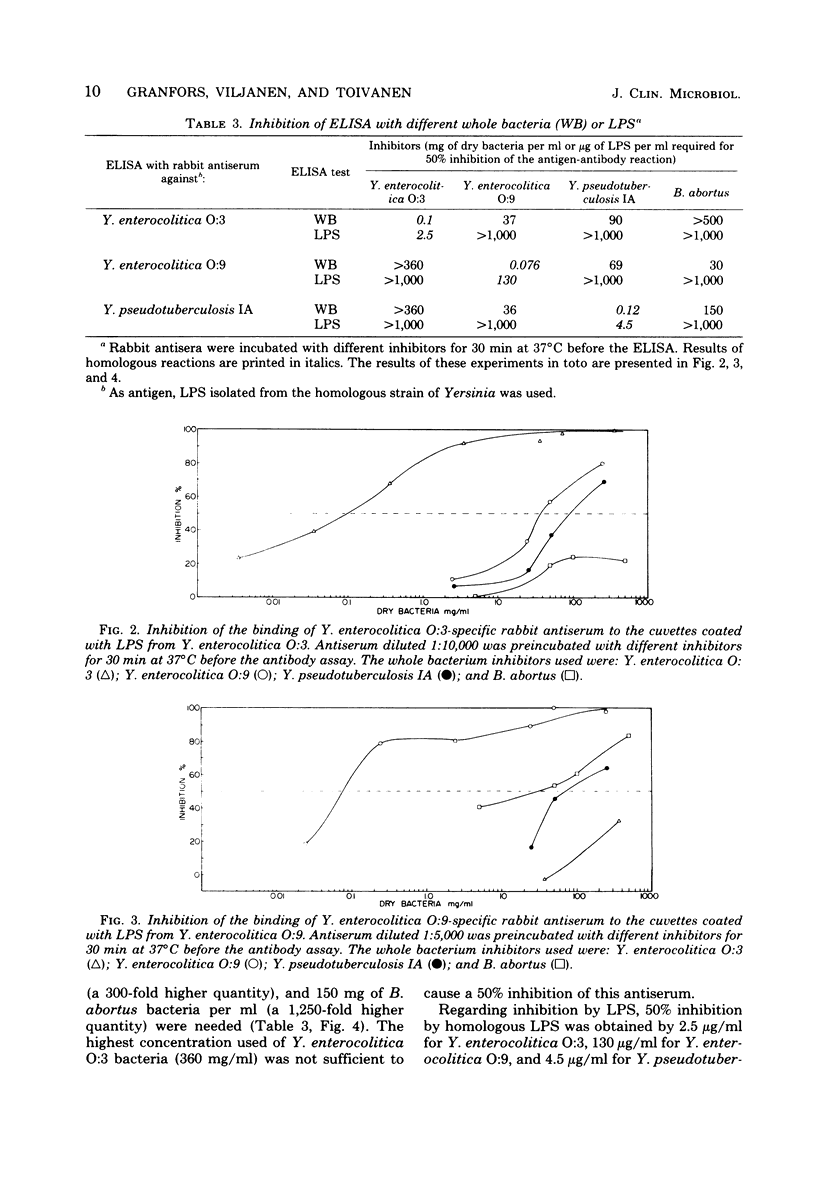
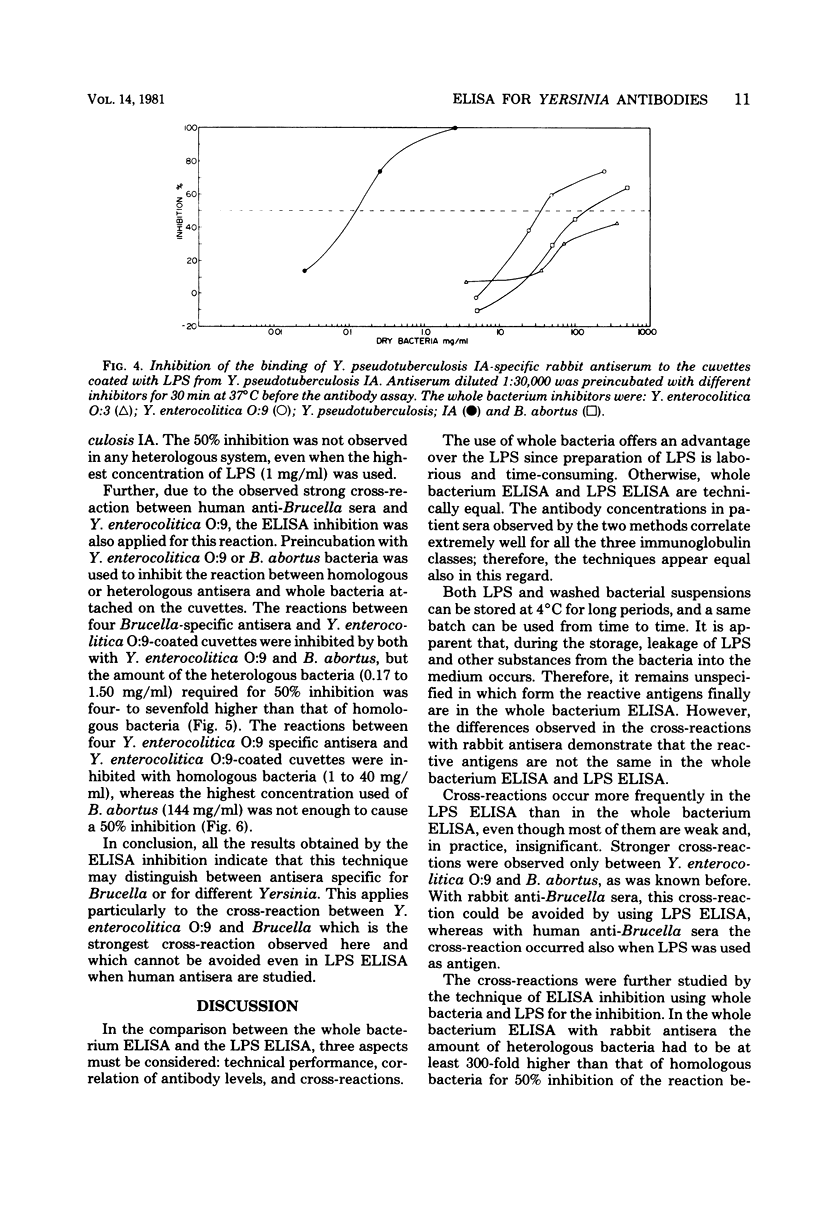
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the detection and quantitation of human immunoglobulin M (IgM), IgG, and IgA antibodies against Yersinia enterocolitica by using lipopolysaccharides as antigens is described. The results obtained with the lipopolysaccharide ELISA were compared with the results of the whole bacterium ELISA. The correlations observed were good for each immunoglobulin class. Cross-reactions between Y. enterocolitica serotypes O:3 and O:9, Yersinia pseudotuberculosis IA, and Brucella abortus were studied by human and rabbit antisera in the whole bacterium and lipopolysaccharide ELISAs and by rabbit antisera using ELISA inhibition. The greatest cross-reactivity observed was that of the anti-Brucella serum with Y. enterocolitica O:9 in the whole bacterium ELISA. In the lipopolysaccharide ELISA this cross-reaction was not demonstrable with the rabbit antiserum, but it was strong with the human antiserum. However, differential diagnosis was possible with ELISA inhibition. On the basis of our experience, we are now routinely using whole bacterium ELISA for the determination of class-specific Yersinia antibodies, and potential cross-reactions are controlled by the ELISA inhibition.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahvonen P. Human yersiniosis in Finland. I. Bacteriology and serology. Ann Clin Res. 1972 Feb;4(1):30–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahvonen P., Jansson E., Aho K. Marked cross-agglutination between Brucellae and a subtype of Yersinia enterocolitica. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1969;75(2):291–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahvonen P., Sievers K., Aho K. Arthritis associated with Yersinia enterocolitica infection. Acta Rheumatol Scand. 1969;15(3):232–253. doi: 10.3109/rhe1.1969.15.issue-1-4.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson H. E., Hurvell B., Lindberg A. A. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for titration of antibodies against Brucella abortus and Yersinia enterocolitica. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1976 Jun;84(3):168–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb00016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbel M. J. The relationship between the protective and cross-reacting antigens of Brucella spp., Yersinia enterocolitica 0:9 and Salmonella serotypes of Kauffmann-White group N. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1979;5:50–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbell M. J. The serological relationship between Brucella spp., Yersinia enterocolitica serotype IX and Salmonella serotypes of Kauffmann-White group N. J Hyg (Lond) 1975 Aug;75(1):151–171. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400047173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granfors K. Measurement of immunoglobulin M (IgM), IgG, and IgA antibodies against Yersinia enterocolitica by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: persistence of serum antibodies during disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Mar;9(3):336–341. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.3.336-341.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granfors K., Viljanen M., Tiilikainen A., Toivanen A. Persistence of IgM, IgG, and IgA antibodies to Yersinia in yersinia arthritis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Apr;141(4):424–429. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.4.424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gripenberg M., Nissinen A., Väisänen E., Linder E. Demonstration of antibodies against Yersinia enterocolitica lipopolysaccharide in human sera by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Sep;10(3):279–284. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.3.279-284.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurvell B., Ahvonen P., Thal E. Serological cross-reactions between different Brucella species and Yersinia enterocolitica. Agglutination and complement fixation. Acta Vet Scand. 1971;12(1):86–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurvell B., Lindberg A. A., Carlsson H. E. Differentiation of antibodies against Brucella abortus and Yersinia enterocolitica by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1979;5:73–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurvell B., Lindberg A. A. Serological cross-reactions between different Brucella species and Yersinia enterocolitica. Immunochemical studies on phenol-water extracted lipopolysaccharides from Brucella abortus and Yersinia enterocolitica type IX. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Feb;81(1):113–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurvell B. Serological cross-reactions between different Brucella species and Yersinia enterocolitica. Biological and chemical investigations of lipopolysaccharides from Brucella abortus and Yersinia enterocolitica type IX. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Feb;81(1):105–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02193.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurvell B. Serological cross-reactions between different Brucella species and Yersinia enterocolitica. Immunodiffusion and immunoelectrophoresis. Acta Vet Scand. 1972;13(4):472–483. doi: 10.1186/BF03547153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laitenen O., Tuuhea J., Ahvonen P. Polyarthritis associated with Yersinia enterocolitica infection. Clinical features and laboratory findings in nine cases with severe joint symptoms. Ann Rheum Dis. 1972 Jan;31(1):34–39. doi: 10.1136/ard.31.1.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx A., Sandulache R., Pop A., Cerbu A. Biochemical basis of the serological cross-reactions between Brucella abortus and Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:9. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1975 Dec;126(4):435–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx A., Sändulache R., Pop A., Cerbu A. Serological cross-reactions between Brucella abortus and Yersinia enterocolitica IX. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1974;18(4):429–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. R., Ricciardi I. D., Tizard I. R. Indirect hemagglutination employing enterobacterial common antigen and Yersinia somatic antigen: a technique to differentiate brucellosis from infections involving cross-reacting Yersinia enterocolitica. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Feb;11(2):149–152. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.2.149-152.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. R., Tizard I. R. A simple technique to differentiate between animals infected with Yersinia enterocolitica IX and those infected with Brucella abortus. Res Vet Sci. 1979 Mar;26(2):248–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandulache R., Marx A. Immunochemical studies on a Yersinia enterocolitica O:9 lipopolysaccharide cross-reacting with Brucella abortus and Vibrio cholerae extracts. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1978 Oct;129 B(3):425–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winblad S., Niléhn B., Sternby N. H. Yersinia enterocolitica (Pasteurella x) in human enteric infections. Br Med J. 1966 Dec 3;2(5526):1363–1366. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5526.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


