Abstract
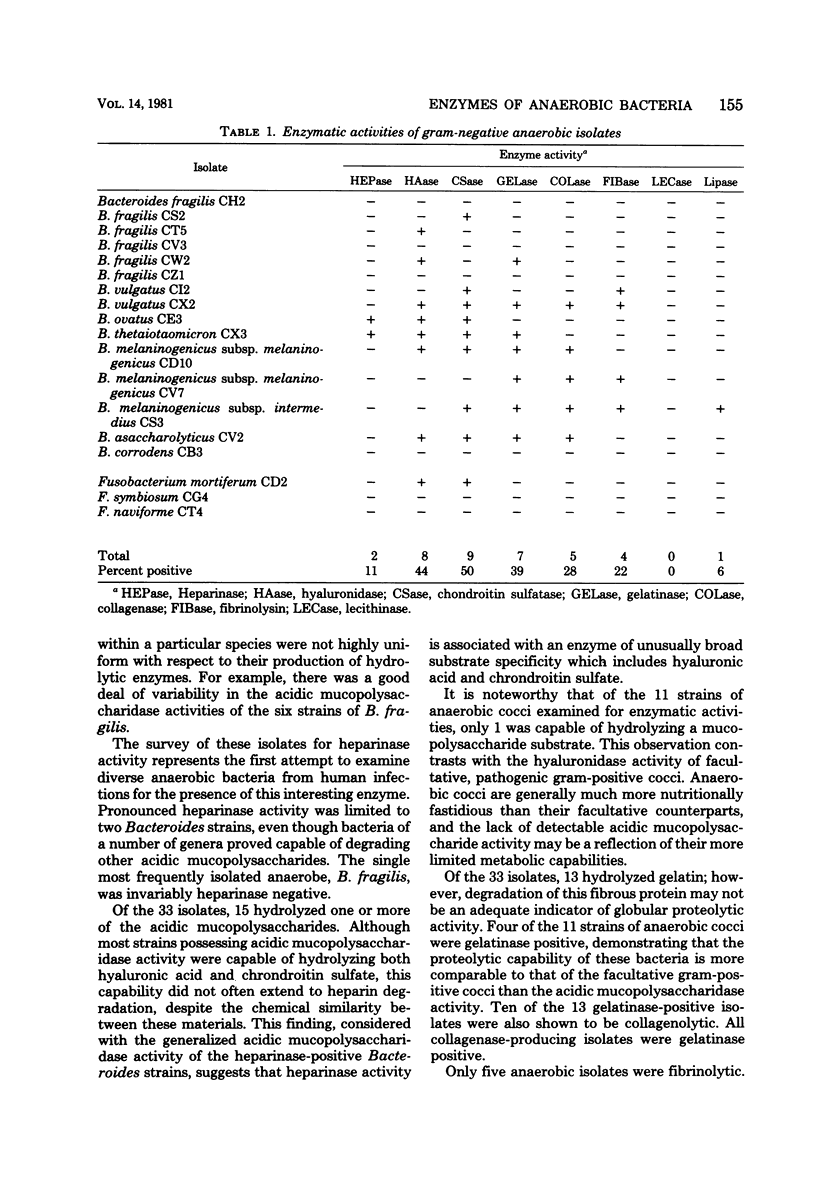
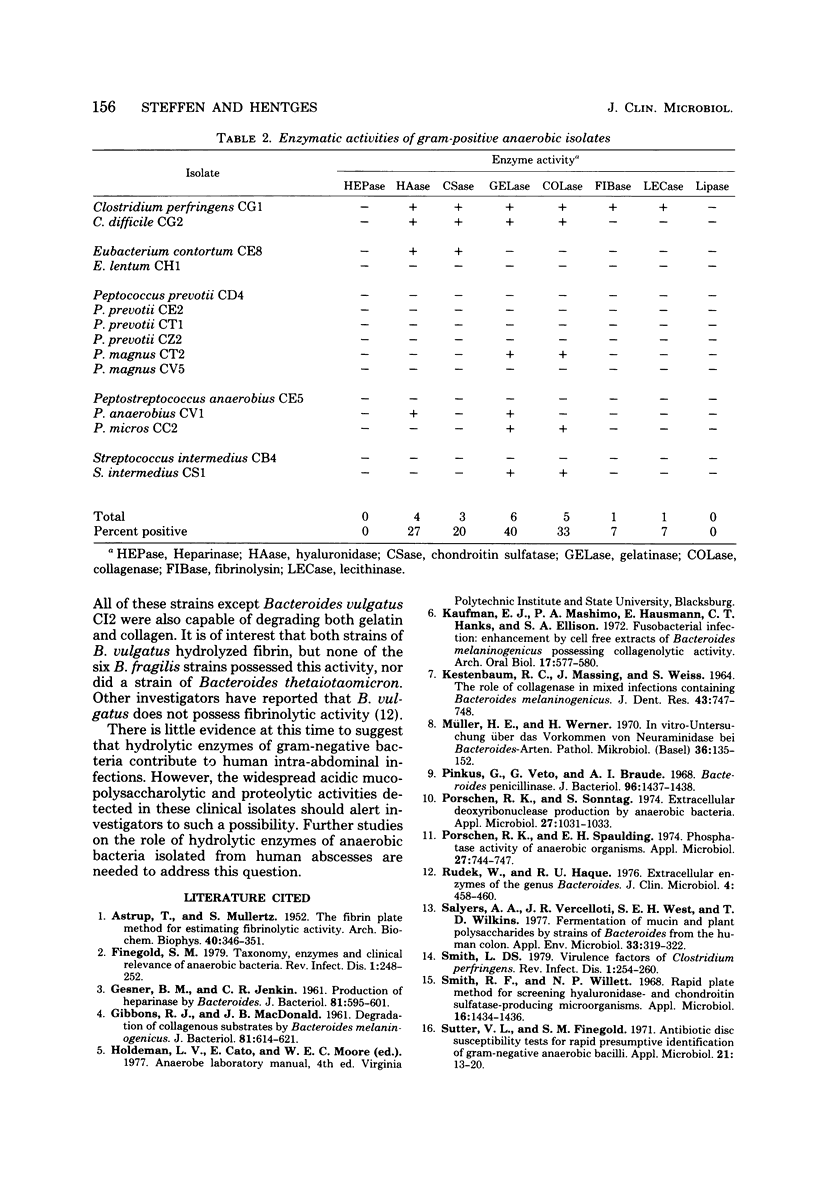
Thirty-three strains of anaerobic bacteria isolated from human clinical specimens were examined for the presence of heparinase, hyaluronidase, chondroitin sulfatase, gelatinase, collagenase, fibrinolysin, lecithinase, and lipase activities. Pronounced heparinase activity was limited to species of the genus Bacteroides. A number of species of the genera Bacteroides and Clostridium produced hyaluronidase and chondroitin sulfatase. Gelatinase, collagenase, and fibrinolysin activities were encountered in isolates of the genera Bacteroides, Clostridium, and Peptostreptococcus. All strains capable of degrading collagen also hydrolyzed other protein substrates. Lipolytic activity was minimal among these anaerobic bacteria. No specific hydrolytic activity was consistently associated with the isolates.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASTRUP T., MULLERTZ S. The fibrin plate method for estimating fibrinolytic activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Oct;40(2):346–351. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold S. M. Taxonomy, enzymes, and clinical relevance of anaerobic bacteria. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 Mar-Apr;1(2):248–253. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.2.248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GESNER B. M., JENKIN C. R. Production of heparinase by Bacteroides. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:595–604. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.595-604.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBONS R. J., MACDONALD J. B. Degradation of collagenous substrates by Bacteroides melaninogenicus. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:614–621. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.614-621.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman E. J., Mashimo P. A., Hausmann E., Hanks C. T., Ellison S. A. Fusobacterial infection: enhancement by cell free extracts of Bacteroides melaninogenicus possessing collagenolytic activity. Arch Oral Biol. 1972 Mar;17(3):577–580. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(72)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller H. E., Werner H. In vitro-Untersuchungen über das Vorommen von Neuraminidase bei Bacteroides-Arten. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1970;36(3):135–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkus G., Veo G., Braude A. I. Bacteroides penicillinase. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1437–1438. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1437-1438.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porschen R. K., Sonntag S. Extracellular deoxyribonuclease production by anaerobic bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jun;27(6):1031–1033. doi: 10.1128/am.27.6.1031-1033.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porschen R. K., Spaulding E. H. Phosphatase activity of anaerobic organisms. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Apr;27(4):744–747. doi: 10.1128/am.27.4.744-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudek W., Haque R. U. Extracellular enzymes of the genus Bacteroides. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Nov;4(5):458–460. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.5.458-460.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A., Vercellotti J. R., West S. E., Wilkins T. D. Fermentation of mucin and plant polysaccharides by strains of Bacteroides from the human colon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):319–322. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.319-322.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. F., Willett N. P. Rapid plate method for screening hyaluronidase and chondroitin sulfatase-producing microorganisms. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Sep;16(9):1434–1436. doi: 10.1128/am.16.9.1434-1436.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Antibiotic disc susceptibility tests for rapid presumptive identification of Gram-negative anaerobic bacilli. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Jan;21(1):13–20. doi: 10.1128/am.21.1.13-20.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



