Abstract
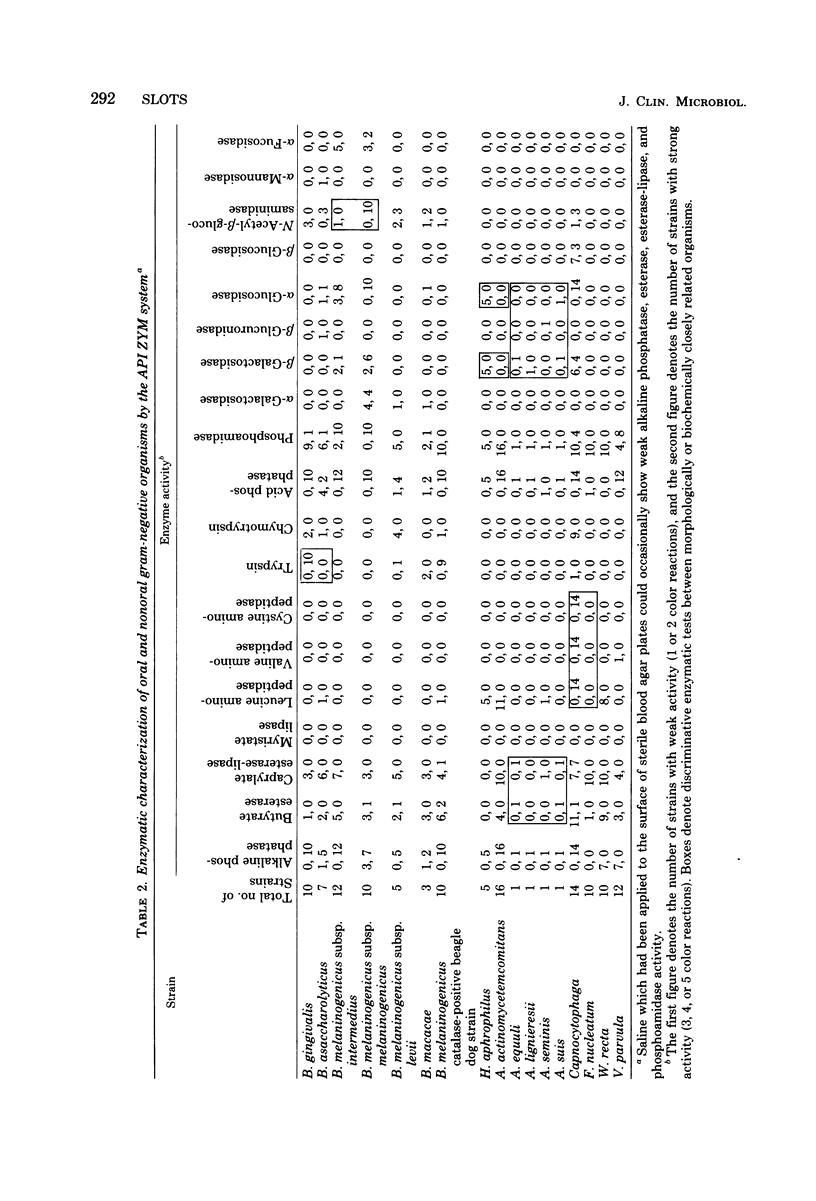
The API ZYM system (Analytab Products, Plainview, N.Y.), containing 19 chromogenic substrates, was utilized semiquantitatively to detect extracellular acid and alkaline phosphatases, aminopeptidases, proteases, esterase-lipase, phosphoamidase, and glycosidases in 128 oral and nonoral isolates of black-pigmented Bacteroides, Actinobacillus, Haemophilus aphrophilus, Capnocytophaga, Fusobacterium nucleatum, Wolinella recta, and Veillonella parvula. In the black-pigmented Bacteroides group of organisms, a strong trypsin reaction was present in Bacteroides gingivalis (oral species) but not in Bacteroides asaccharolyticus (nonoral species). Bacteroides melaninogenicus subsp. melaninogenicus, in contrast to Bacteroides melaninogenicus subsp. intermedius, exhibited strong N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase activity. H. aphrophilus produced beta-galactosidase and alpha-glucosidase, but the closely related Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans did not. Capnocytophaga was distinct with respect to strong aminopeptidase reactions. This study showed that a wide range of enzymes which have the potential of causing tissue injury and inflammation can be elaborated from major oral gram-negative species. Also, the API ZYM system appears to be a valuable adjunct to traditional biochemical testing in identifying oral gram-negative species.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hofstad T. Evaluation of the API ZYM system for identification of Bacteroides and Fusobacterium species. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1980;168(3):173–177. doi: 10.1007/BF02122851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humble M. W., King A., Phillips I. API ZYM: a simple rapid system for the detection of bacterial enzymes. J Clin Pathol. 1977 Mar;30(3):275–277. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.3.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. O., TATUM H. W. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and Hemophilus aphrophilus. J Infect Dis. 1962 Sep-Oct;111:85–94. doi: 10.1093/infdis/111.2.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek F. S., Coykendall A. L. Production of phenylacetic acid by strains of Bacteroides asaccharolyticus and Bacteroides gingivalis (sp. nov.). J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Aug;12(2):288–290. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.2.288-290.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M. Rapid identification of Actinomycetaceae and related bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Aug;8(2):127–133. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.2.127-133.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed M. J., Slots J., Mouton C., Genco R. J. Antigenic studies of oral and nonoral black-pigmented Bacteroides strains. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):564–574. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.564-574.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Genco R. J. Direct hemagglutination technique for differentiating Bacteroides asaccharolyticus oral strains from nonoral strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Sep;10(3):371–373. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.3.371-373.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Reynolds H. S., Genco R. J. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in human periodontal disease: a cross-sectional microbiological investigation. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1013–1020. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1013-1020.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J. Subgingival microflora and periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol. 1979 Oct;6(5):351–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1979.tb01935.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tharagonnet D., Sisson P. R., Roxby C. M., Ingham H. R., Selkon J. B. The API ZYM system in the identification of Gram-negative anaerobes. J Clin Pathol. 1977 Jun;30(6):505–509. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.6.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


