Abstract
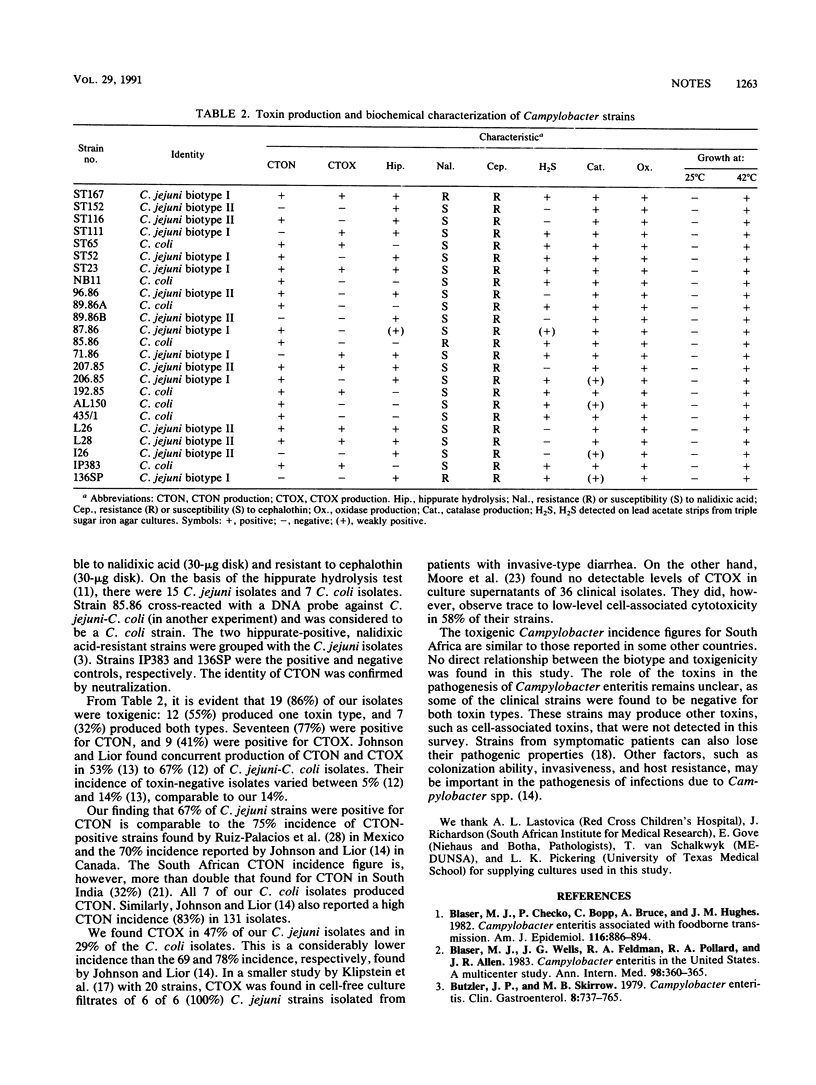
Campylobacter strains can produce a heat-labile cytotonic toxin (CTON) and various cytotoxins (CTOX). Of 22 South African Campylobacter strains tested, 86% were toxigenic (77% produced CTON, 41% produced CTOX, and 32% produced both types) and 14% were toxin negative. Campylobacter jejuni strains were 67% CTON positive and 47% CTOX positive, whereas Campylobacter coli strains were 100 and 29% positive, respectively.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaser M. J., Checko P., Bopp C., Bruce A., Hughes J. M. Campylobacter enteritis associated with foodborne transmission. Am J Epidemiol. 1982 Dec;116(6):886–894. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Wells J. G., Feldman R. A., Pollard R. A., Allen J. R. Campylobacter enteritis in the United States. A multicenter study. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Mar;98(3):360–365. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-3-360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis. Clin Gastroenterol. 1979 Sep;8(3):737–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou S. P., Dular R., Kasatiya S. Effect of ferrous sulfate, sodium metabisulfite, and sodium pyruvate on survival of Campylobacter jejuni. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Oct;18(4):986–987. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.4.986-987.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds P., Patton C. M., Barrett T. J., Morris G. K., Steigerwalt A. G., Brenner D. J. Biochemical and genetic characteristics of atypical Campylobacter fetus subsp. fetus strains isolated from humans in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;21(6):936–940. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.6.936-940.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. G., Maxwell K. O., Taylor N. S., Runsick C. D., Edmonds P., Brenner D. J. "Campylobacter upsaliensis" isolated from cats as identified by DNA relatedness and biochemical features. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Oct;27(10):2376–2378. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.10.2376-2378.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry M. K., Dalrymple J. M. Quantitative microtiter cytotoxicity assay for Shigella toxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):361–366. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.361-366.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Wanke C. A., Pennie R. A., Barrett L. J., Lima A. A., O'Brien A. D. Production of a unique cytotoxin by Campylobacter jejuni. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2526–2530. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2526-2530.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang M. N., Ederer G. M. Rapid hippurate hydrolysis method for presumptive identification of group B streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):114–115. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.114-115.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert G. A., Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E., Lambert M. A., Blaser M. J., Moss C. W. 30 years of campylobacters: biochemical characteristics and a biotyping proposal for Campylobacter jejuni. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1065–1073. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1065-1073.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. M., Lior H. Cytotoxic and cytotonic factors produced by Campylobacter jejuni, Campylobacter coli, and Campylobacter laridis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Aug;24(2):275–281. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.2.275-281.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. M., Lior H. Toxins produced by Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Lancet. 1984 Jan 28;1(8370):229–230. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92155-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keusch G. T., Donta S. T. Classification of enterotoxins on the basis of activity in cell culture. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jan;131(1):58–63. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Properties of crude Campylobacter jejuni heat-labile enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):314–319. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.314-319.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F., Short H. B. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for virulence properties of Campylobacter jejuni clinical isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jun;23(6):1039–1043. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.6.1039-1043.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F., Short H., Schenk E. A. Pathogenic properties of Campylobacter jejuni: assay and correlation with clinical manifestations. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):43–49. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.43-49.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindblom G. B., Kaijser B., Sjögren E. Enterotoxin production and serogroups of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli from patients with diarrhea and from healthy laying hens. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1272–1276. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1272-1276.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathan V. I., Rajan D. P., Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Enterotoxigenic Campylobacter jejuni among children in South India. Lancet. 1984 Oct 27;2(8409):981–981. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91193-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCardell B. A., Madden J. M., Stanfield J. T. Effect of iron concentration on toxin production in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Can J Microbiol. 1986 May;32(5):395–401. doi: 10.1139/m86-075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. A., Blaser M. J., Perez-Perez G. I., O'Brien A. D. Production of a Shiga-like cytotoxin by Campylobacter. Microb Pathog. 1988 Jun;4(6):455–462. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90030-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olusanya O., Adebayo J. O., Williams B. Campylobacter jejuni as a bacterial cause of diarrhoea in Ile-Ife, NIgeria. J Hyg (Lond) 1983 Aug;91(1):77–80. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400060058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., Sorger S., Lackman L., Sinai R. E., Marks M. I. Campylobacter gastroenteritis in children. J Pediatr. 1979 Apr;94(4):589–591. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins D. M., Coolbaugh J. C., Walker R. I., Weiss E. Biphasic culture system for rapid Campylobacter cultivation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):284–289. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.284-289.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Palacios G. M., Torres J., Torres N. I., Escamilla E., Ruiz-Palacios B. R., Tamayo J. Cholera-like enterotoxin produced by Campylobacter jejuni. Characterisation and clinical significance. Lancet. 1983 Jul 30;2(8344):250–253. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90234-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svedhem A., Kaijser B. Campylobacter fetus subspecies jejuni: a common cause of diarrhea in Sweden. J Infect Dis. 1980 Sep;142(3):353–359. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.3.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walder M. Epidemiology of campylobacter enteritis. Scand J Infect Dis. 1982;14(1):27–33. doi: 10.3109/inf.1982.14.issue-1.06. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


