Abstract
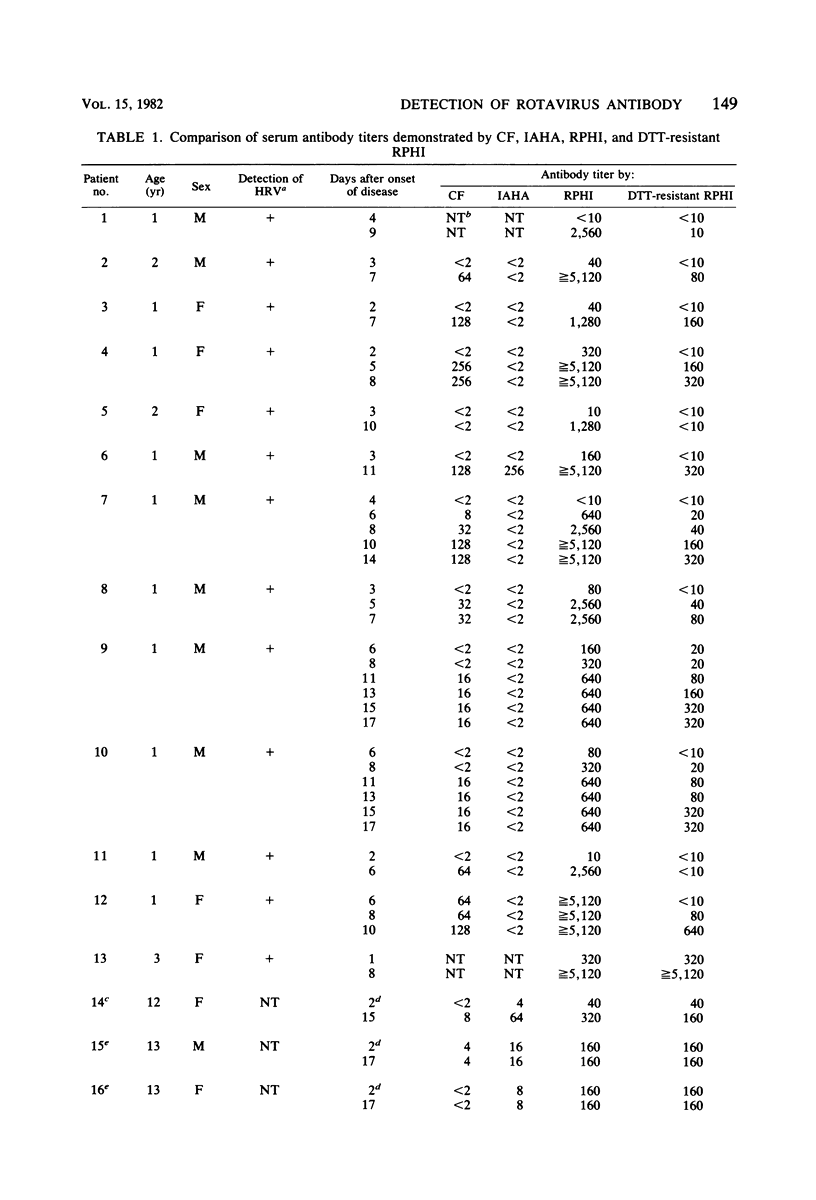
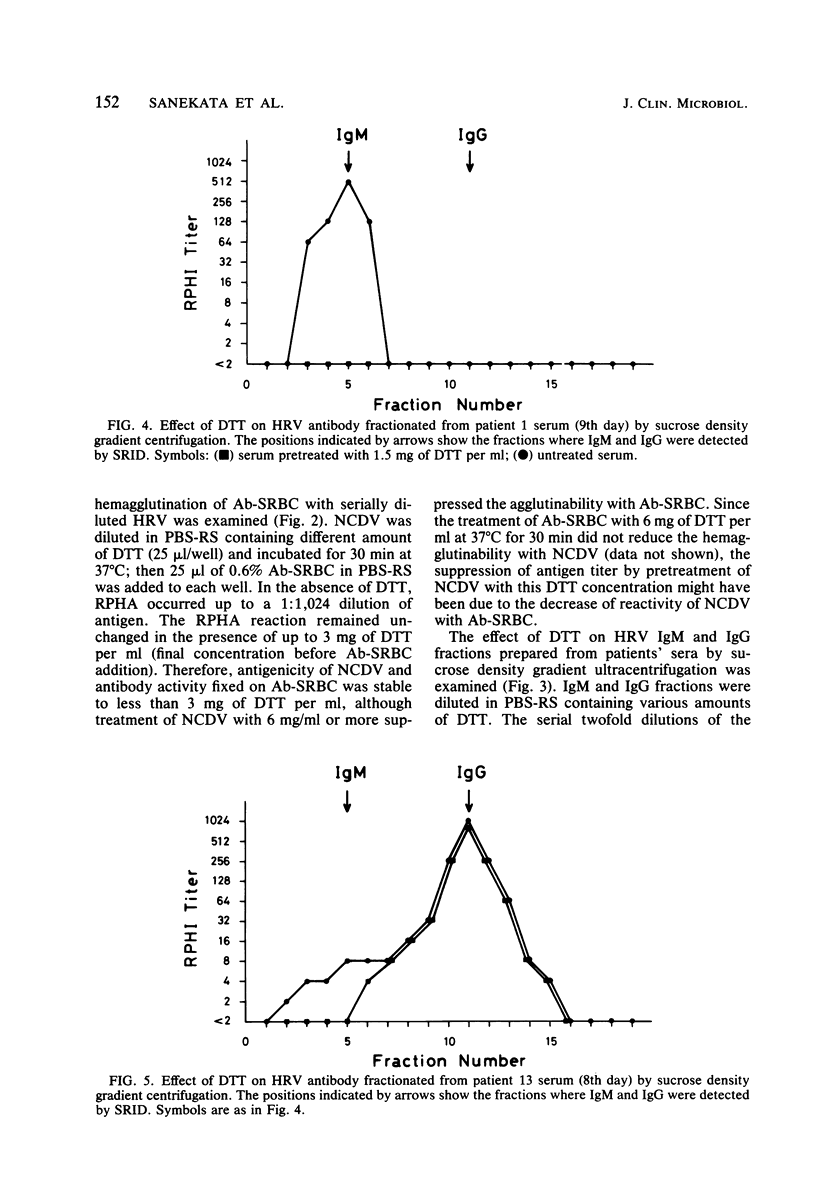
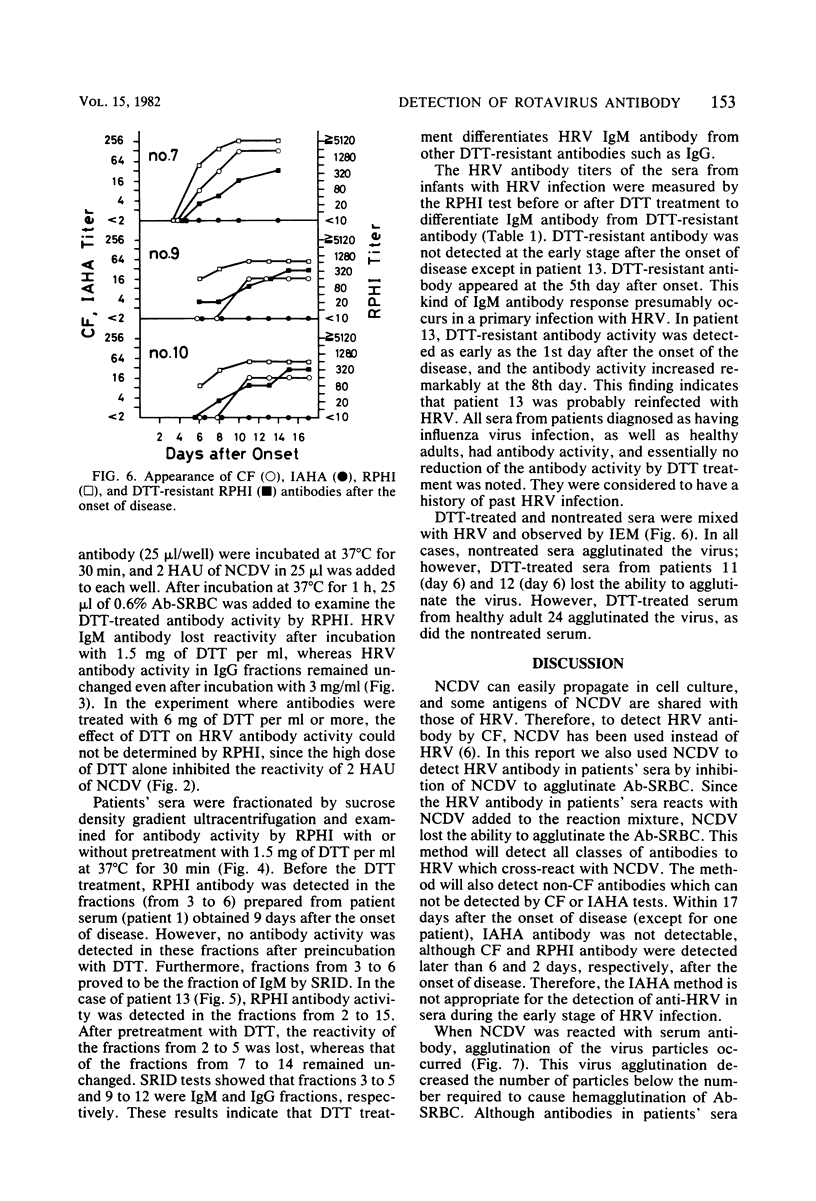
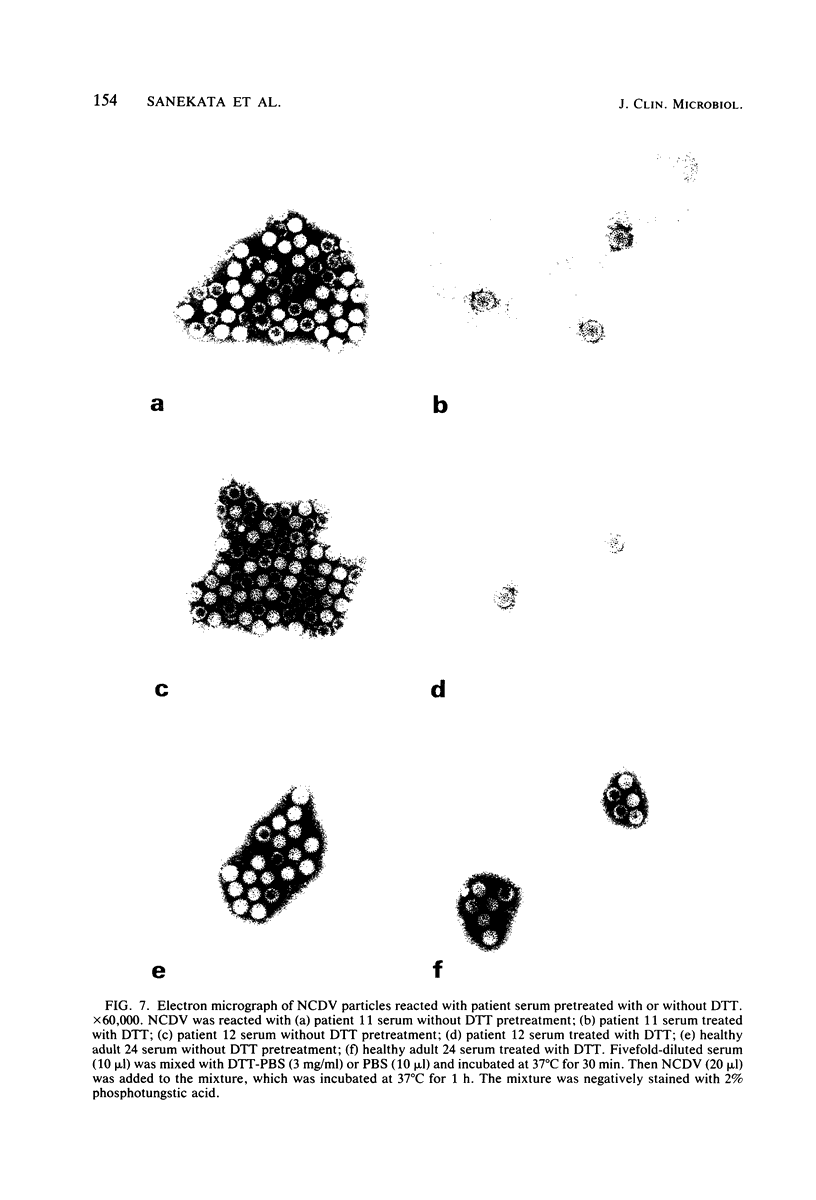
A reverse passive hemagglutination inhibition (RPHI) test was developed for detecting rotavirus antibody in patients' sera. Sheep erythrocytes coated with guinea pig antibody against Nebraska calf diarrhea virus (NCDV) were readily hemagglutinated by NCDV in a reaction called reverse passive hemagglutination (RPHA). Inhibition of this RPHA reaction was used to detect the presence of rotavirus antibody in patients' sera which cross-reacted with NCDV. The sensitivity of RPHI was consistently at least 10 times greater than that of the complement fixation test for detection of rotavirus antibody in patients' sera. Since immunoglobulin M (IgM) antibody activity detected by RPHI was destroyed by pretreatment of serum with dithiothreitol (DDT), whereas DTT-resistant antibodies such as IgG remained unchanged, the titer of IgM antibody could be distinguished from that of DTT-resistant antibody by comparing the results of two RPHI tests performed with and without DTT pretreatment. From the IgM antibody response pattern, primary and secondary rotavirus infections could be distinguished.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe Y., Inouye S. Complement-fixing immunoglobulin M antibody response in patients with infantile gastroenteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):284–287. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.284-287.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop R. F., Davidson G. P., Holmes I. H., Ruck B. J. Detection of a new virus by electron microscopy of faecal extracts from children with acute gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1974 Feb 2;1(7849):149–151. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92440-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blacklow N. R., Echeverria P., Smith D. H. Serological studies with reovirus-like enteritis agent. Infect Immun. 1976 Jun;13(6):1563–1566. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.6.1563-1566.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cukor G., Blacklow N. R., Capozza F. E., Panjvani Z. F., Bednarek F. Persistence of antibodies to rotavirus in human milk. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):93–96. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.93-96.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gust I. D., Pringle R. C., Barnes G. L., Davidson G. P., Bishop R. F. Complement-fixing antibody response to rotavirus infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Feb;5(2):125–130. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.2.125-130.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Cline W. L., Mebus C. A., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., James H. D., Jr, VanKirk D., Chanock R. M. New complement-fixation test for the human reovirus-like agent of infantile gastroenteritis. Nebraska calf diarrhea virus used as antigen. Lancet. 1975 May 10;1(7915):1056–1061. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91827-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Kim H. W., Wyatt R. G., Cline W. L., Arrobio J. O., Brandt C. D., Rodriguez W. J., Sack D. A., Chanock R. M., Parrott R. H. Human reovirus-like agent as the major pathogen associated with "winter" gastroenteritis in hospitalized infants and young children. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 29;294(18):965–972. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604292941801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Kim H. W., Wyatt R. G., Rodriguez W. J., Ross S., Cline W. L., Parrott R. H., Chanock R. M. Reoviruslike agent in stools: association with infantile diarrhea and development of serologic tests. Science. 1974 Sep 20;185(4156):1049–1053. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4156.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konno T., Imai A., Suzuki H., Ishida N. Letter: Mercaptoethanol-sensitive antibody to reovirus-like agents in acute epidemic gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1975 Dec 27;2(7948):1312–1312. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90654-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konno T., Suzuki H., Imai A., Ishida N. Reovirus-like agent in acute epidemic gastroenteritis in Japanese infants: fecal shedding and serologic response. J Infect Dis. 1977 Feb;135(2):259–266. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. L., Gary G. W., Jr, Palmer E. L. Comparison of hemagglutination-inhibition, complement-fixation and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for quantitation of human rotavirus antibodies. Arch Virol. 1979;62(2):131–136. doi: 10.1007/BF01318065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayumi M., Okochi K., Nishioka K. Detection of Australia antigen by means of immune adherence haemagglutination test. Vox Sang. 1971 Feb;20(2):178–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1971.tb00549.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishima T., Ichikawa T., Yamaguchi H., Miyazu M., Nagayoshi S., Ozaki T., Isomura S., Suzuki S. Acute infantile gastroenteritis caused by rotavirus in Japan. Eur J Pediatr. 1978 Dec 1;129(4):259–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00441356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orstavik I., Haug K. W. Virus-specific IgM antibodies in acute gastroenteritis due to a reovirus-like agent (rotavirus). Scand J Infect Dis. 1976;8(4):237–240. doi: 10.3109/inf.1976.8.issue-4.03. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanekata T., Yoshida Y., Oda K. Detection of rotavirus from faeces by reversed passive haemagglutination method. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Sep;32(9):963–963. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.9.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanekata T., Yoshida Y., Okada H. Detection of rotavirus in faeces by latex agglutination. J Immunol Methods. 1981;41(3):377–385. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90199-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkkinen H. K., Meurman O. H., Halonen P. E. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay of IgA, IgG, and IgM antibodies to human rotavirus. J Med Virol. 1979;3(4):281–289. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890030406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., Gill V. W., Sereno M. M., Kalica A. R., VanKirk D. H., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Letter: Probable in-vitro cultivation of human reovirus-like agent of infantile diarroea. Lancet. 1976 Jan 10;1(7950):98–99. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Wyatt R. G., Kim H. W., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Immunological response to infection with human reovirus-like agent: measurement of anti-human reovirus-like agent immunoglobulin G and M levels by the method of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):540–546. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.540-546.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zissis G., Lambert J. P., De Kegel D. Routine diagnosis of human rotaviruses in stools. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Feb;31(2):175–178. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.2.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



