Abstract
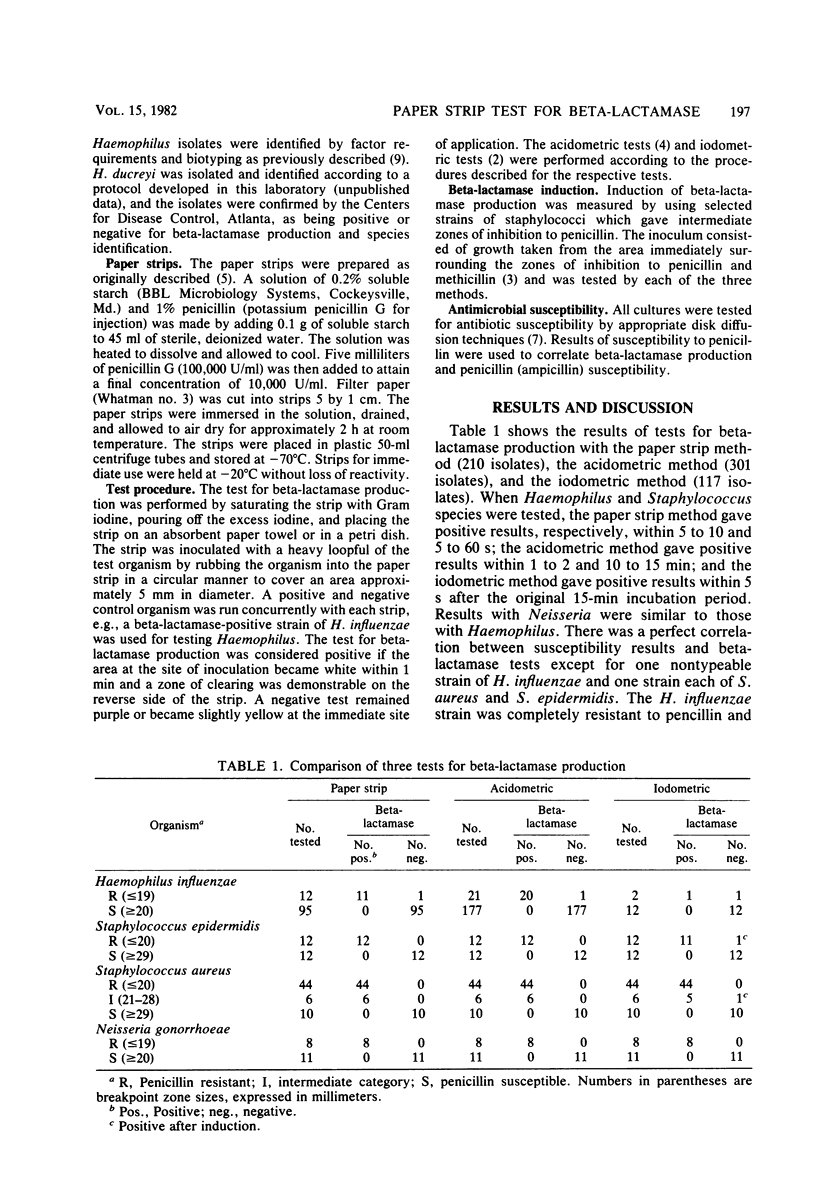
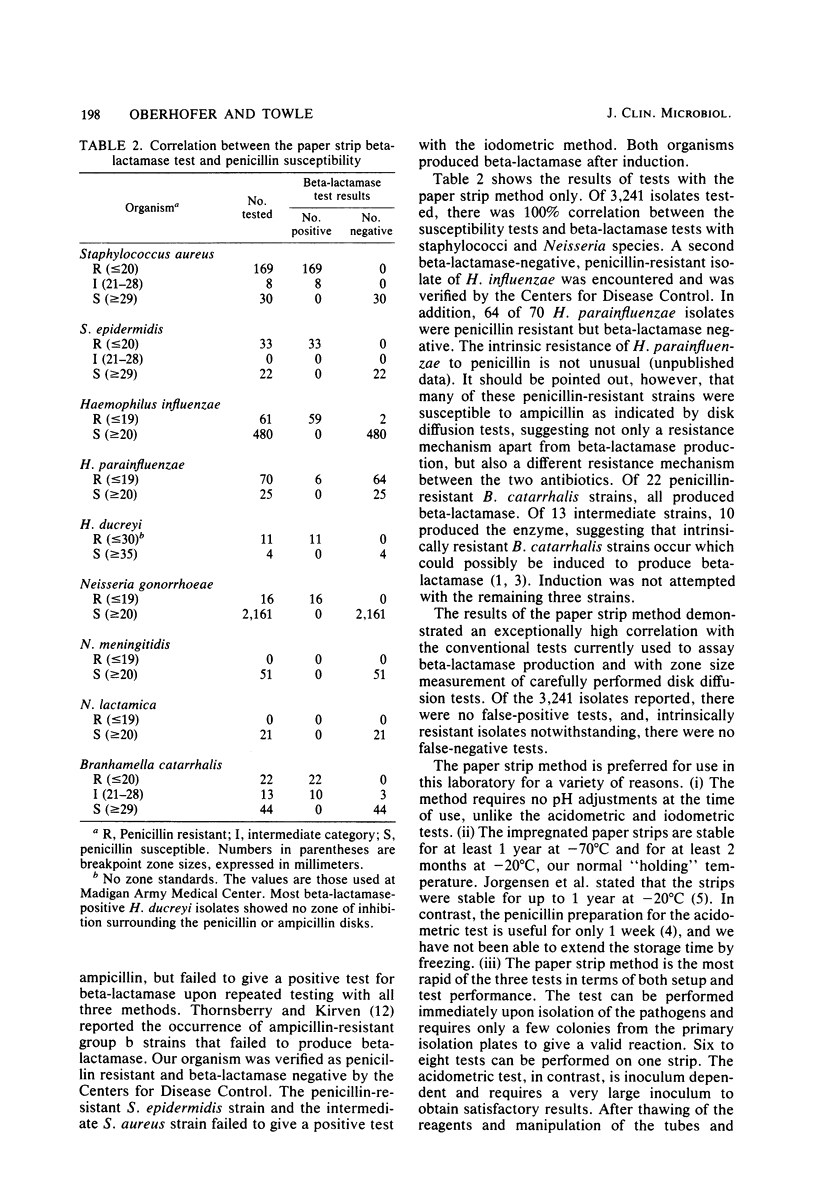
The penicillin-starch paper strip method was compared with the acidometric and iodometric methods for assaying beta-lactamase production, using fresh isolates of clinically important bacteria. Results obtained by the three methods were compared for rapidity, accuracy, and stability of reagents. Of the 210 isolates tested by the paper strip method, 301 isolates tested by the acidometric method, and 117 isolates tested by the iodometric method, all were in perfect agreement with the disk diffusion susceptibility test except one strain each of Haemophilus influenzae, Staphylococcus aureus, and Staphylococcus epidermidis. The H. influenzae isolate was penicillin resistant and failed to give a positive test for beta-lactamase in all three tests. The staphylococci (intermediate and resistant in susceptibility, respectively) failed to give a positive test for beta-lactamase with the iodometric method. The results of the paper strip method, in which 3,241 strains representing nine species of bacteria were used, correlated completely with disk susceptibility tests except for 2 and 69 strains, respectively, of penicillin-resistant, beta-lactamase-negative H. influenzae and H. parainfluenzae. The results of this study indicate that the paper strip method is accurate, simple to perform, extremely economical, and uses materials that are stable when stored frozen. It is eminently suitable for routine laboratory use.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams A. P., Barry A. L., Benner E. J. A simple, rapid test to differentiate penicillin-susceptible from penicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1970 Dec;122(6):544–546. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.6.544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin B. W. Iodometric detection of Haemophilus influenzae beta-lactamase: rapid presumptive test for ampicillin resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Mar;7(3):265–270. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.3.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duma R. J., Kunz L. J. Penicillinase production in the evaluation of disk sensitivity testing of staphylococci to penicillin. Am J Clin Pathol. 1970 Jun;53(6):865–870. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/53.6.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escamilla J. Susceptibility of Haemophilus influenza to ampicillin as determined by use of a modified, one-minute beta-lactamase test. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jan;9(1):196–198. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.1.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H., Lee J. C., Alexander G. A. Rapid penicillinase paper strip test for detection of beta-lactamase-producing Haemophilus influenzae and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jun;11(6):1087–1088. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.6.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery K., Raymundo L., Jr, Drew W. L. Chromogenic cephalosporin spot test to detect beta-lactamase in clinically significant bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):205–207. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.205-207.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVICK R. P., RICHMOND M. H. NATURE AND INTERACTIONS OF THE GENETIC ELEMENTS GOVERNING PENICILLINASE SYNTHESIS IN STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:467–480. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.467-480.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhofer T. R., Back A. E. Biotypes of Haemophilus encountered in clinical laboratories. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Aug;10(2):168–174. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.2.168-174.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen I. G., Jacobson J., Rudderman R. Rapid capillary tube method for detecting penicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Mar;23(3):649–650. doi: 10.1128/am.23.3.649-650.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., Kirven L. A. Ampicillin resistance in Haemophilus influenzae as determined by a rapid test for beta-lactamase production. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Nov;6(5):653–654. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.5.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


