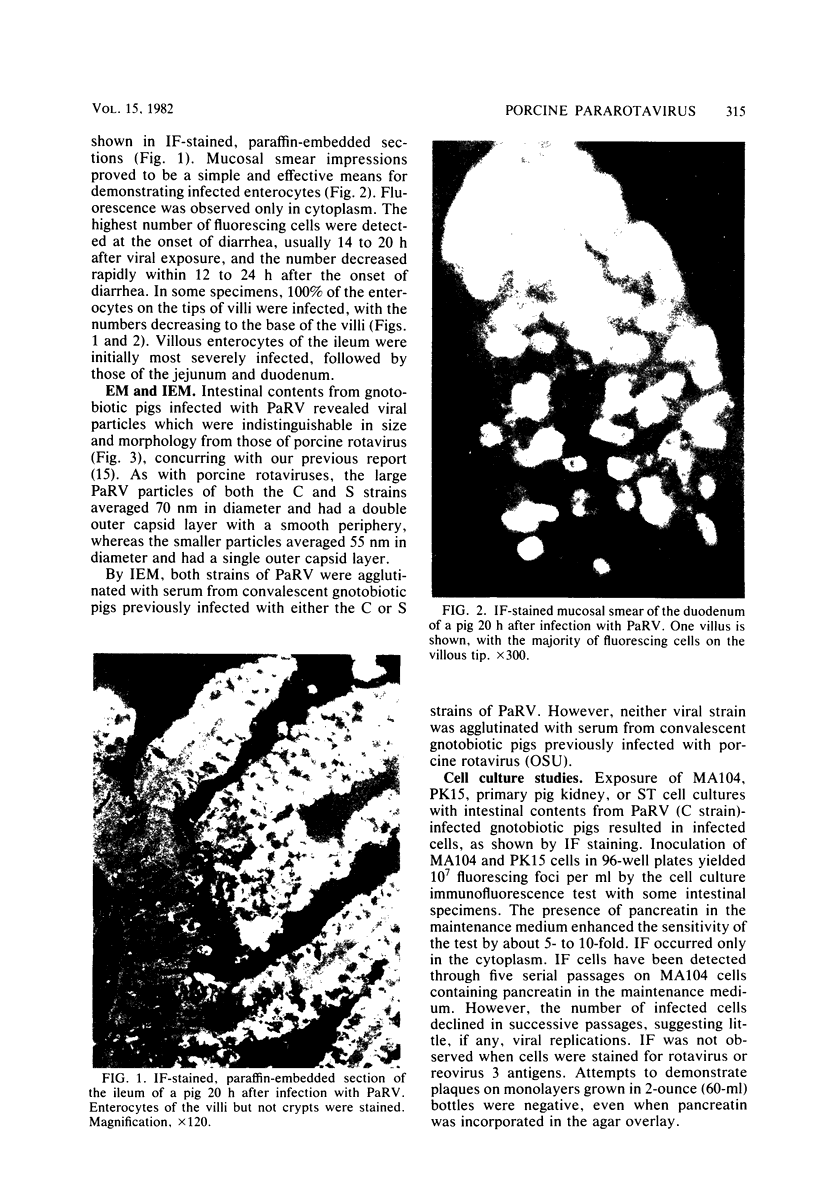
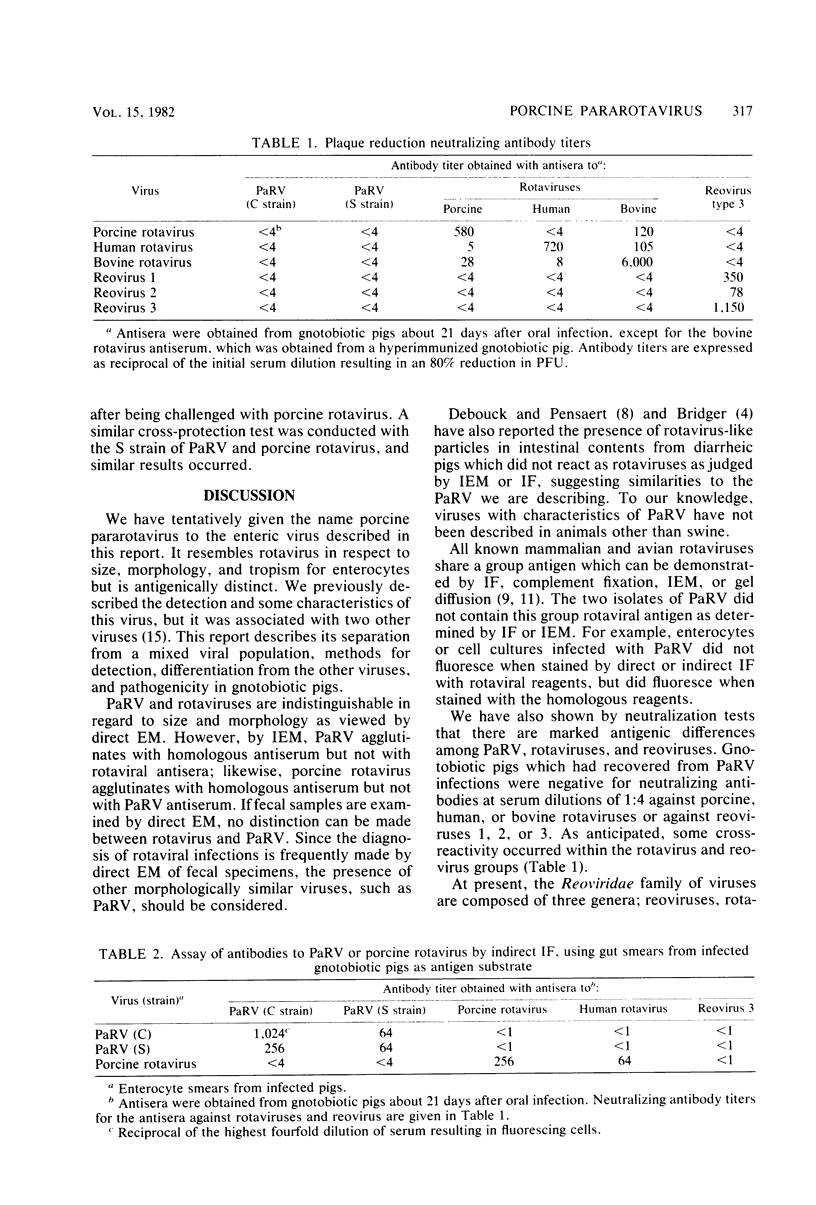
Abstract
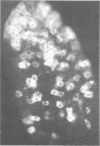
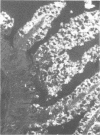
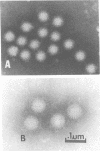
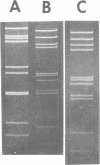
Some characteristics of a newly recognized porcine enteric virus are described. Tentatively, the virus was referred to as porcine pararotavirus (PaRV) because it resembled rotaviruses in respect to size, morphology, and tropism for villous enterocytes of the small intestine. However, it was antigenically distinct from porcine, human, and bovine rotaviruses and reoviruses 1, 2, and 3, and the electrophoretic migration pattern of PaRV double-stranded RNA was distinct from the electrophoretic migration patterns of the rotaviral and reoviral genomes. By passage in gnotobiotic pigs, PaRV was isolated from two suckling diarrheic pigs originating from two herds. After oral exposure of gnotobiotic pigs, villous enterocytes of the small intestines became infected as judged by immunofluorescence, resulting in villous atrophy and diarrhea. Mortality was high when gnotobiotic pigs less than 5 days old were infected. The C strain of this virus was serially passed 10 times in gnotobiotic pigs, and electron microscopy, immunofluorescence, and serological tests indicated no extraneous agents. The virus was serially passed five times in cell cultures which contained pancreatin in the medium, but replication was negligible or absent, as the number of immunofluorescent cells decreased with each passage. Since rotaviral infections are frequently diagnosed by direct electron microscopy of fecal specimens, the presence of other morphologically similar viruses, such as PaRV, should be considered. The use of immune electron microscopy is suggested as a means of helping recognize this situation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babiuk L. A., Mohammed K., Spence L., Fauvel M., Petro R. Rotavirus isolation and cultivation in the presence of trypsin. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Dec;6(6):610–617. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.6.610-617.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banatvala J. E., Totterdell B., Chrystie I. L., Woode G. N. In-vitro detection of human rotaviruses. Lancet. 1975 Oct 25;2(7939):821–821. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)80057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohl E. H., Kohler E. M., Saif L. J., Cross R. F., Agnes A. G., Theil K. W. Rotavirus as a cause of diarrhea in pigs. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Feb 15;172(4):458–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger J. C. Detection by electron microscopy of caliciviruses, astroviruses and rotavirus-like particles in the faeces of piglets with diarrhoea. Vet Rec. 1980 Dec 6;107(23):532–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryden A. S., Davies H. A., Thouless M. E., Flewitt T. H. Diagnosis of rotavirus infection by cell culture. J Med Microbiol. 1977 Feb;10(1):121–125. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-1-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross R. F., Moorhead P. D. An azure and eosin rapid staining technique. Can J Comp Med. 1969 Oct;33(4):317–317. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debouck P., Pensaert M. Experimental infection of pigs with Belgian isolates of the porcine rotavirus. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1979 Sep;26(7):517–526. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1979.tb00845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewett T. H., Woode G. N. The rotaviruses. Arch Virol. 1978;57(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01315633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER R. C., BOHL E. H., KOHLER E. M. PROCUREMENT AND MAINTENANCE OF GERM-FREE SEINE FOR MICROBIOLOGICAL INVESTIGATIONS. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Jul;12:295–300. doi: 10.1128/am.12.4.295-300.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno S., Inouye S., Kono R. Plaque assay of neonatal calf diarrhea virus and the neutralizing antibody in human sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jan;5(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.1.1-4.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty M. S., Allan G. M., Todd D., McFerran J. B. Isolation and cell culture propagation of rotaviruses from turkeys and chickens. Arch Virol. 1979;61(1-2):13–21. doi: 10.1007/BF01320587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pursell A. R., Cole J. R., Jr Procedure for fluorescent-antibody staining of virus-infected cell cultures in plastic plates. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 May;3(5):537–540. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.5.537-540.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Bohl E. H., Kohler E. M., Hughes J. H. Immune electron microscopy of transmissible gastroenteritis virus and rotavirus (reovirus-like agent) of swine. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Jan;38(1):13–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Bohl E. H., Theil K. W., Cross R. F., House J. A. Rotavirus-like, calicivirus-like, and 23-nm virus-like particles associated with diarrhea in young pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jul;12(1):105–111. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.1.105-111.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., Bohl E. H., Agnes A. G. Cell culture propagation of porcine rotavirus (reovirus-like agent). Am J Vet Res. 1977 Nov;38(11):1765–1768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., Bohl E. H., Cross R. F., Kohler E. M., Agnes A. G. Pathogenesis of porcine rotaviral infection in experimentally inoculated gnotobiotic pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1978 Feb;39(2):213–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., McCloskey C. M., Saif L. J., Redman D. R., Bohl E. H., Hancock D. D., Kohler E. M., Moorhead P. D. Rapid, simple method of preparing rotaviral double-stranded ribonucleic acid for analysis by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):273–280. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.273-280.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., James W. D., Bohl E. H., Theil K. W., Saif L. J., Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Human rotavirus type 2: cultivation in vitro. Science. 1980 Jan 11;207(4427):189–191. doi: 10.1126/science.6243190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]