Abstract
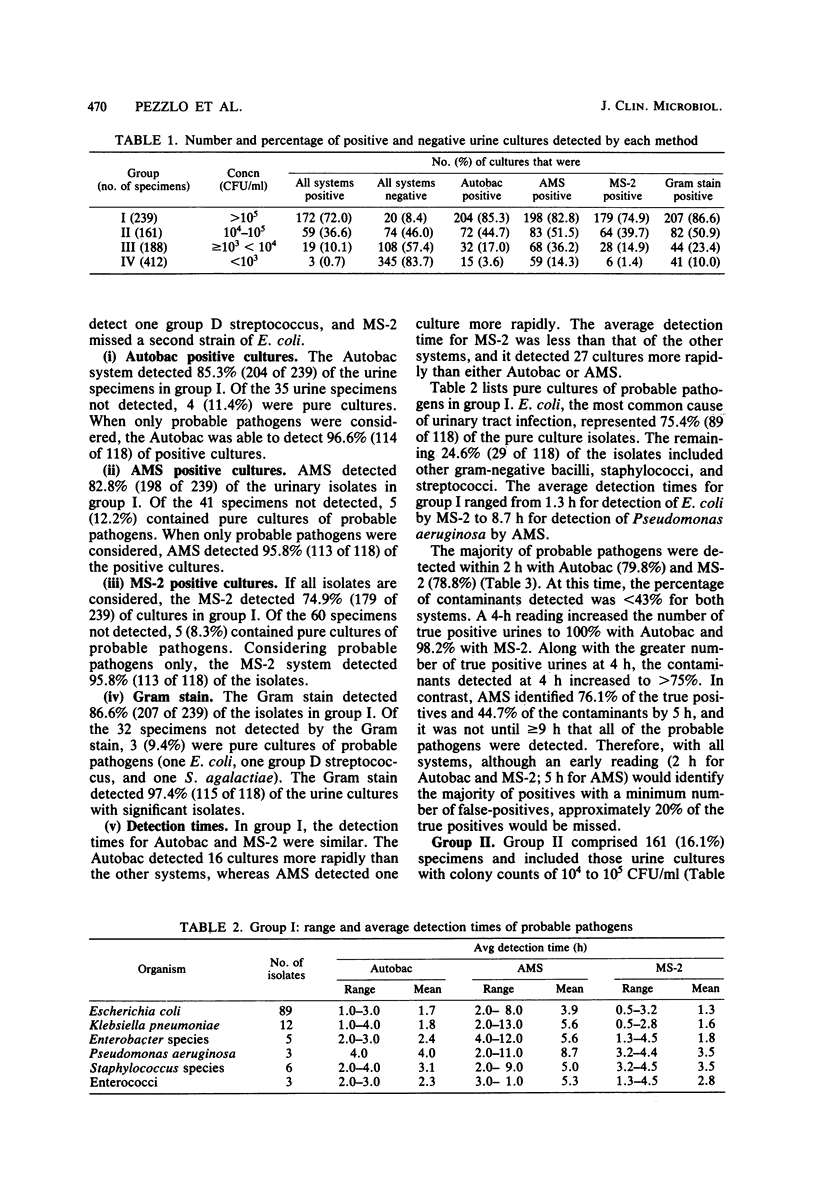
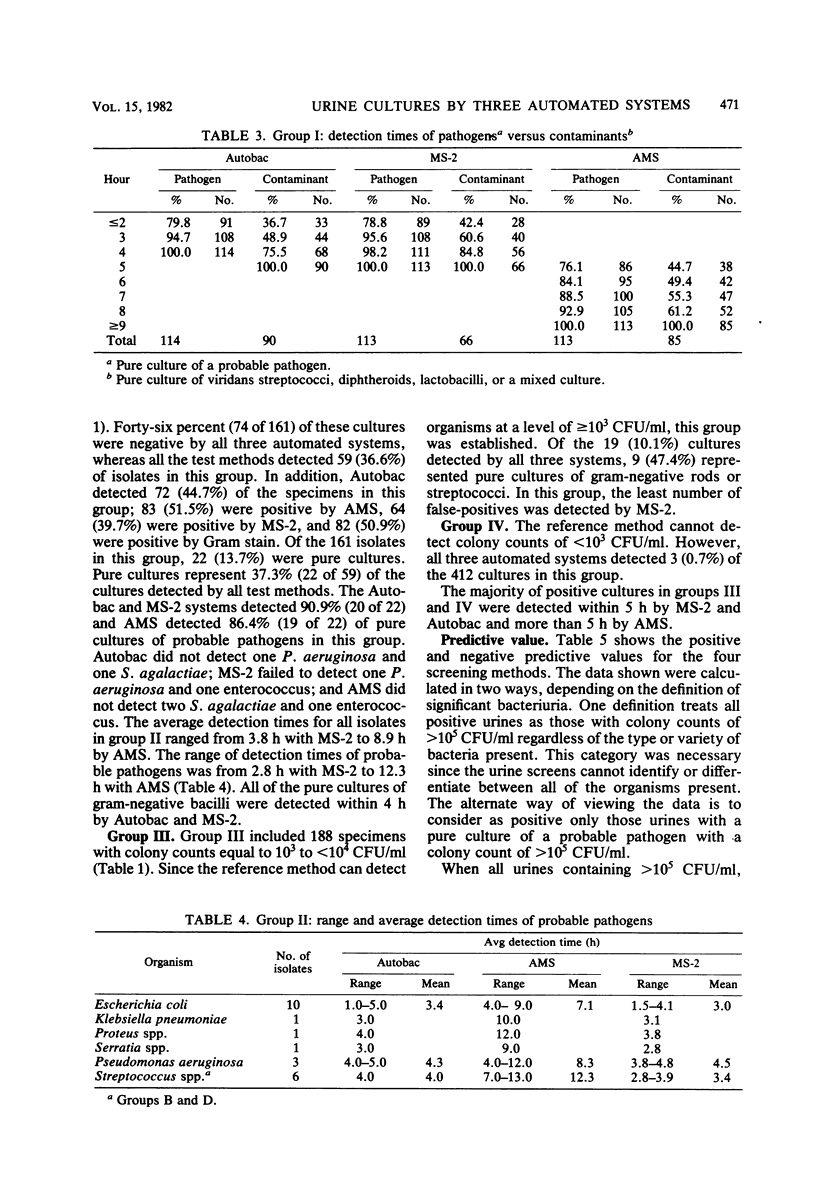
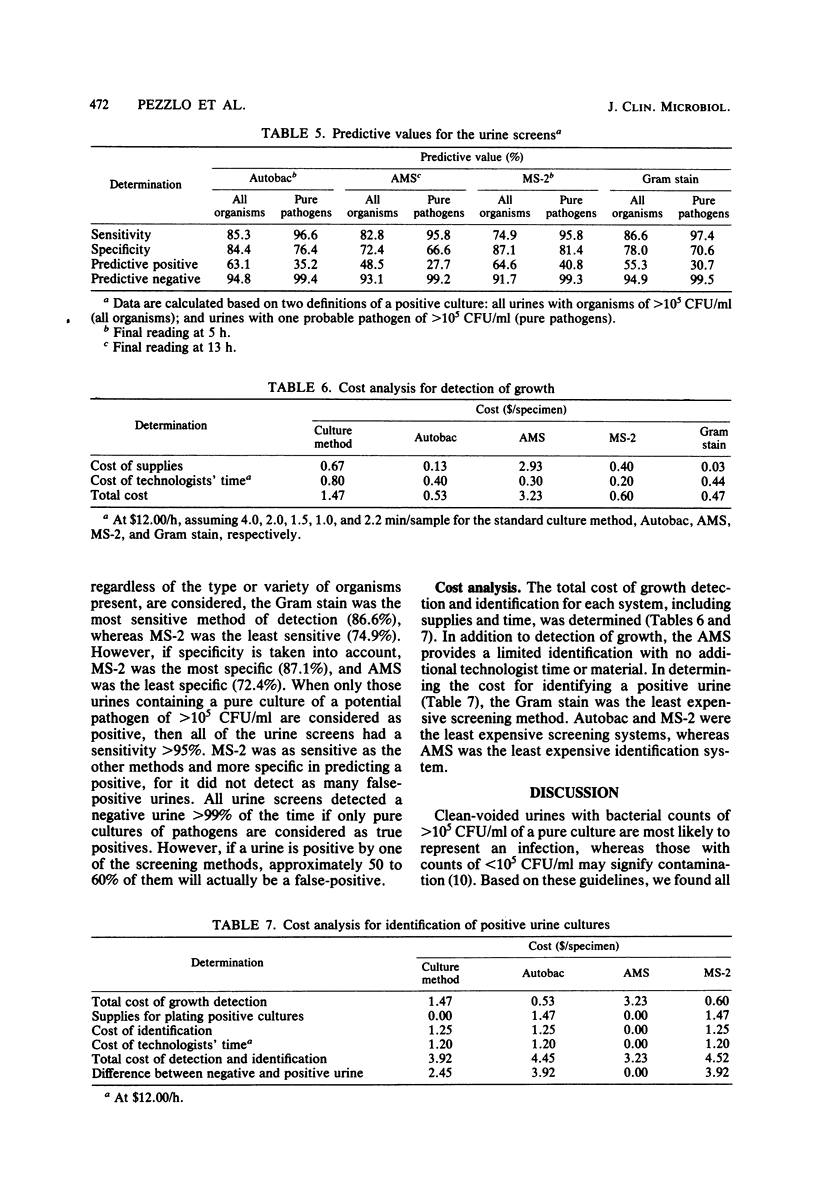
A study was conducted to compare three automated systems and the Gram stain for their ability to detect significant bacteriuria. A total of 1,000 urine specimens were evaluated by Autobac MTS (General Diagnostics), Auto Microbic system (AMS; Vitek Systems, Inc.), and MS-2 (Abbott Laboratories) and compared with a semiquantitative culture plate method. Two hundred thirty-nine (23.9%) specimens had colony counts of >105 colony-forming units (CFU)/ml by the culture plate method (group I). Of these, 204 (85.3%) were positive by Autobac, 198 (82.8%) were positive by AMS, and 179 (74.9%) were positive by MS-2. When pure cultures of diphtheroids, lactobacilli, and viridans streptococci not group D were considered contaminants and therefore excluded, there were 118 specimens containing pure cultures of probable pathogens. The percentage of significant isolates detected was 97.4% (115 of 118) by the Gram stain, 96.6% (114 of 118) by Autobac, and 95.8% (113 of 118) by AMS and MS-2. The average detection time for all organisms was 2.2 h by Autobac, 6.1 h by AMS, and 1.8 h by MS-2; therefore, all three methods were more rapid than the 18- to 24-h standard plate culture method. One hundred sixty-one (16.1%) specimens had colony counts of 104 to 105 CFU/ml (group II). The probable pathogens not detected in this group were two (1.2%) by Autobac and MS-2 and three by AMS (1.9%). The average detection time for group II was 4.2 h by Autobac, 8.9 h by AMS, and 3.8 h by MS-2. Six hundred specimens had colony counts of <104 CFU/ml. Of these, 188 had colony counts equal to 103 and <104 CFU/ml (group III), and 412 cultures were below detectable limits by the standard plate method (group IV). Less than 37 and 15% of groups III and IV, respectively, were detected by instrumentation. Average detection times for groups III and IV were 4.6 and 4.8 h by Autobac, 10 and 11 h by AMS, and 4.2 and 4.4 h by MS-2. The cost of supplies and technical time with Gram stain, Autobac, and MS-2, when used as screening methods, were comparable and considerably less expensive than for the reference method. The AMS was the least expensive system when the cost for identifying probable pathogens was included.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldridge C., Jones P. W., Gibson S., Lanham J., Meyer M., Vannest R., Charles R. Automated microbiological detection/identification system. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Oct;6(4):406–413. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.4.406-413.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander D. N., Ederer G. M., Matsen J. M. Evaluation of an adenosine 5'-triphosphate assay as a screening method to detect significant bacteriuria. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jan;3(1):42–46. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.1.42-46.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cady P., Dufour S. W., Lawless P., Nunke B., Kraeger S. J. Impedimetric screening for bacteriuria. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Mar;7(3):273–278. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.3.273-278.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale D. C., Wright D. N., McKie J. E., Isenberg H. D., Jenkins R. D., Matsen J. M. Rapid screening for bacteriuria by light scatter photometry (Autobac): a collaborative study. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):147–150. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.147-150.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg H. D., Gavan T. L., Sonnenwirth A., Taylor W. I., Washington J. A., 2nd Clinical laboratory evaluation of automated microbial detection/identification system in analysis of clinical urine specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Aug;10(2):226–230. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.2.226-230.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins R. D., Hale D. C., Matsen J. M. Rapid semiautomated screening and processing of urine specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Mar;11(3):220–225. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.3.220-225.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H., Jones P. M. Comparative evaluation of the Limulus assay and the direct Gram stain for detection of significant bacteriuria. Am J Clin Pathol. 1975 Jan;63(1):142–148. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/63.3.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KASS E. H. Asymptomatic infections of the urinary tract. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1956;69:56–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. T., Balfour L. C. Evaluation and optimization of urine screening by Autobac. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Apr;13(4):677–680. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.4.677-680.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb V. A., Dalton H. P., Wilkins J. R. Electrochemical method for the early detection of urinary-tract infections. Am J Clin Pathol. 1976 Jul;66(1):91–95. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/66.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. F., Alexander J. Microscopy of stained urine smears to determine the need for quantitative culture. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Oct;4(4):372–374. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.4.372-374.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson D. P., Koepke J. A. The Automicrobic System for urines. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Dec;10(6):823–833. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.6.823-833.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransohoff D. F., Feinstein A. R. Problems of spectrum and bias in evaluating the efficacy of diagnostic tests. N Engl J Med. 1978 Oct 26;299(17):926–930. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197810262991705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


