Abstract
AIM: To examine the human hepatic parenchymal and stromal components in rat liver and the phenotypic changes of human cells in liver of human-rat chimera (HRC) generated by in utero transplantation of human cells during partial hepatectomy (PHx)-induced liver regeneration.
METHODS: Human hepatic parenchymal and stromal components and phenotypic changes of human cells during liver regeneration were examined by flow cytometry, in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry.
RESULTS: ISH analysis demonstrated human Alu-positive cells in hepatic parenchyma and stroma of recipient liver. Functional human hepatocytes generated in this model potentially constituted human hepatic functional units with the presence of donor-derived human endothelial and biliary duct cells in host liver. Alpha fetoprotein (AFP)+, CD34+ and CD45+ cells were observed in the chimeric liver on day 10 after PHx-induced liver regeneration and then disappeared in PHx group, but not in non-PHx group, suggesting that dynamic phenotypic changes of human cells expressing AFP, CD34 and CD45 cells may occur during the chimeric liver regeneration. Additionally, immunostaining for human proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) showed that the number of PCNA-positive cells in the chimeric liver of PHx group was markedly increased, as compared to that of control group, indicating that donor-derived human cells are actively proliferated during PHx-induced regeneration of HRC liver.
CONCLUSION: HRC liver provides a tool for investigating human liver regeneration in a humanized animal model.
Keywords: Human-rat chimera, Humanized liver, Human hepatocyte-like cells, Humanized hepatic functional unit, Partial hepatectomy model, Liver regeneration
INTRODUCTION
The complexity of a biologic network can only be reproduced using an in vivo system, and complex biological and pathological processes often require an in vivo analysis. However, biomedical researches in humans are largely performed in in vitro models lacking of the components and complexity of a living organism because of scientific, technical and ethical considerations. Since there is a certain level of similarity between animals and humans, various laboratory animals including small (e.g. mice and rats) and large animals (e.g. pigs, dogs and non-human primates) are instrumental in increasing the understanding of human biology and disease. However, laboratory animals cannot fully replicate human physiology and disease because animal models are enormously limited by the practical considerations, physiological and genetic diversity, etc.
Since these findings derived from mice and in vitro human models cannot always be extrapolated to precisely reflect the true situations in humans, a preclinically and/or clinically relevant human-animal chimera (HAC) carrying various humanized organs, such as liver, brain, heart, kidney, etc, constituted by a wide variety of transplanted donor-derived human cells with different cell phenotypes engrafted into the recipient organs, has been developed by performing in utero transplantation or blastocyst transplantation of various human stem cells (hSCs) during the preimmune development stage, which can imitate the in vivo situations in humans, thus greatly facilitating related researches based on HAC harboring humanized organs within the xenogeneic competitive settings[1–24].
In utero transplantation of hSCs, such as human hematopoietic stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells, into fetal sheep[2,6], goats[24], rats[19,20], and mice[18,22] or blastocyst transplantation of hSCs into mice[22], has led to the establishment of non-injury human-animal xenograft models carrying humanized liver, in which a significant number of functional donor-derived human mature hepatocyte-like cells (HLCs) stained positively for human albumin (Alb), alpha fetoprotein (AFP) and hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 can be found. Moreover, such a “HAC liver” can also produce and secrete human Alb, alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartic acid aminotransferase (AST) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) in the circulation of host mice[18] and sheep[2,6] that have undergone transplantation.
Compared with the general laboratory animals including mice, rats, pigs, dogs, non-human primates, and immune-deficient mice (in vivo injury model) carrying humanized liver reconstructed with human hepatocytes[5,25–28] or hSCs[29,30], such a HAC harboring humanized liver with a relatively large number of donor-derived human liver cells clustered to form functional human liver units in host animal liver is an in vivo non-injury human-animal xenograft animal model with normal physiological conditions, and will become an ideal in vivo system for studies of the mechanisms underlying human liver development, repair and regeneration; the pathogenesis of human liver-related diseases including viral hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), etc; and drug discovery and preclinical assessment of ADME-Tox[17,19,20,25,31].
From a scientific perspective, human-rat chimera (HRC) and human-mouse chimera (HMC) carrying humanized organs are the suitable models for mechanistic research. Thus, attention has been paid to the new generation of non-injury models, such as HRC and HMC (data not shown) carrying humanized liver, and their potential applications[19,20].
Our previous data demonstrate that donor-derived human liver cells with different cellular phenotypes are formed in chimeric liver of some animals after in utero transplantation of hSCs, including human liver cells stained positively for CD34 (markers for hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells and oval cells), CD45 (markers for oval cells and nucleated cells of hematopoietic lineage), AFP (embryonic hepatocyte marker), CK8 and CK18 (hepatocyte markers), CK19 (markers for cholangiocyte and bile duct cells), and Alb (hepatocyte marker), suggesting that donor-derived human hepatocyte and cholangiocyte lineages exist in host liver[19,20]. Moreover, human hepatic cell differentiation in rat liver appears to partially follow the process of hepatic ontogeny[20].
Furthermore, donor-derived functional human mature HLCs in parenchyma of human-sheep chimeric liver constitute the “humanized hepatic functional units” with the presence of donor-derived human hepatic stromal cells (endothelial and biliary duct cells) integrated into the chimeric liver stroma[2], which remains to be confirmed in HRC liver[19,20].
Based on the HRC carrying newly developed humanized liver after in utero transplantation of hSCs[19,20], this study was to further identify the donor-derived human stromal components of HRC liver by in situ hybridization (ISH) for detecting donor-derived human cells in HRC liver, and to examine the changes in cellular phenotypes of donor-derived human cells during partial hepatectomy (PHx)-induced liver regeneration in the xenogeneic competitive environment, which helps to establish a solid foundation for the further research and potential applications based on such a “humanized liver”.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
HRC generation
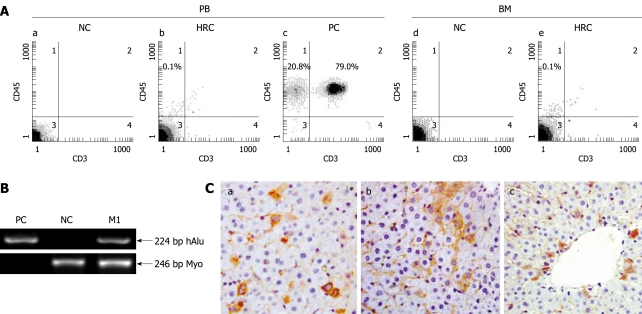
Human-rat hybrid animals were produced by in utero transplanting low-density mononuclear cells (MNCs) from human umbilical cord blood (hUCB) into fetal rats at the gestation of 9-11 d. The engraftment and long-term survival of donor-derived human cells in the HRC liver were determined by human gene-specific PCR (Figure 1B) for human Alu repetitive sequence (hAlu) on genomic DNA prepared from the liver of MNC-transplanted rats (MTRs) which were positive for human CD45 cells in peripheral blood (PB). PCR-positive organs were subjected to ISH for human Alu sequences and immunohistochemistry (IHC) using antibodies specific for human β2-microglobulin (β2-M), CK18 and CK19. Chimerism was accepted if the liver samples were positive for β2-M, CK18, CK19 and ISH. Protocols for producing and identifying HRC have been described elsewhere[19]. All time points referred to the time length after birth. Animal care and experiment were performed according to the Ethical Guidelines for Animal Care, Handling and Termination established by the Subcommittee of Sun Yat-Sen University. The study was approved by the Ethics Review Committee of Sun Yat-Sen University. hUCB samples were obtained from normal full-term deliveries and informed consent was given by the participants.
Figure 1.
Screening for human-rat chimera (HRC) derived from in utero transplantation of hUCB-MNCs. Human-rat hybrid animals were produced by in utero transplantation of low-density mononuclear cells (MNCs) from human umbilical cord blood (hUCB) into fetal rats at the gestation of 9-11 d. A: Representative flow cytometric analysis of human CD45-positive cell engraftment in PB and BM of HRC. After birth, peripheral blood (PB) was collected at the indicated time points. The collected blood cells were stained with anti-human CD45 and CD3 antibodies and analyzed by flow cytometry. MNC-transplanted rat (MTR) was killed at end of each experiment, with bone morrow (BM) obtained and assessed for human CD45+ cell engraftment by 2-color flow cytometry. Human PB from healthy volunteers was used as a positive control (PC) and normal rat PB was used a negative control (NC); B: Identification of human genes in liver of MTR by human gene-specific PCR. To determine the human donor contribution in the liver of MTR, PCR was carried out on genomic DNA with primers specific for hAlu gene[19]. The PCR products were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis from positive-control human blood genomic DNA (lane PC), normal/non-transplanted rat genomic DNA (lane NC) and genomic DNA prepared from liver of one MTR was shown. Rat myogenin (Myo)-specific PCR was carried out for quality and quantity controls of genomic DNA with primers specific for rat Myo gene[19]. Data are representative of three independent PCRs yielding similar results. Arrow indicates the position of PCR products amplified by the primers for hAlu[19]. M1: Molecular weight DNA marker (DL2000, TaKaRa); C: Immunohistochemical analysis of various human antigens in liver of MTR. In the receipt liver, donor-derived human cells with different cellular phenotypes were detected by IHC for different human markers, such as β2-microglobulin [β2-M (a), CK18 (b) and CK19 (c)]. Brown staining shows positive human cells in various tissues from MTR and human samples (data not shown), whereas no positive human cells were found in normal control (NC) rats (data not shown).
ISH for detecting donor-derived human cells in HRC liver
After evaluation of the donor-derived human cell distribution in HRC liver by human gene-specific PCR on genomic DNA, human donor contribution in the formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded liver tissues (from HRC) proved by PCR for hAlu gene prior to immunohistochemical assessment[19], was further determined by ISH for human DNA Alu sequences. Digoxigenin (DIG)-labeled Alu probes (DNA probes) were obtained from PanPath B.V. (Amsterdam, Netherlands). Hybridization was performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions. DIG-labeled hybrids were detected with an anti-DIG-alkaline phosphatase conjugate and a BCIP/NBT substrate giving a light-blue precipitate, and counterstained (pink) with nuclear fast red.
Experimental design
Seventy percent of PHx rat liver model provides an effective medium for study of the transition and regulation of hepatocytes from quiescent to proliferating phase. Ten selected rats, at the age of 2 mo, with CK18-positive and/or CK19-positve hHLC engraftment in the HRC liver were randomly divided into 70% PHx group (PHx group) and control group (non-PHx group) (n = 5). Before (day 0) and after 10 and 20 d of PHx, minimal liver tissues were dissected from each rat of PHx group and control group, and used to detect donor-derived human cells stained positively for CK18, CK19, CD34, CD45 and AFP with IHC.
Immunohistochemical detection of donor-derived human cells
The minimal chimeric liver samples were immediately harvested from HRC containing donor-derived human cells in rat liver at the indicated time points after birth, fixed in 10% formalin, and paraffin embedded. The sections (4-μm) were heated in a 10 mmol/L Na-citrate buffer (pH 6.0) at 95°C for 20 min and cooled at room temperature for antigen detection. An envision system was used for immunohistochemical analysis. Human cells with different cell phenotypes in chimeric liver were detected with antibodies to CD45, CD34, CK18, CK19 and AFP (DAKO), respectively. The complex was visualized with diaminobenzidinetetrahydrochloride (DAB) and counterstained with hematoxylin. Anti-human CD45, CK18 and AFP antibodies used as primary antibodies could specifically react with human CD45, CK18 and AFP antigens, respectively. Data from the Antibody Company indicate that anti-human CD34 and CK19 antibodies could cross-react very mildly with rat CD34 and CK19 antigens, respectively. However, our previous study strongly indicated that CD34 and CK19 antibodies do not cross-react with their corresponding antigens, CD34 and CK19, in IHC[20]. Since anti-human CD45, CK18, AFP, CD34 and CK19 antibodies have been confirmed to specifically react with human CD45, CK18, AFP, CD34 and CK19 antigens, but not with rat CD45, CK18, AFP, CD34 and CK19 antigens, thus MNC-derived human CD45+, CK18+, AFP+, CD34+ and CK19+ cells engrafted into rat liver can be easily distinguished from rat CD45+, CK18+, AFP+, CD34+ and CK19+ cells, respectively, by IHC performed on chimeric liver sections of HRC. For each staining, tissue sections were prepared from a normal rat as a negative control (NC). To identify donor-derived human cells in rat liver sections, we performed IHC on six different sections from each rat that underwent transplantation. The variability in percentage of donor-derived human cells was not significant between sections, but significant between animals which is consistent with the reported findings[19,20].
IHC for proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)
To perform immunostaining for PCNA, liver tissue sections were autoclaved in a 10 mmol/L citrate buffer at 121°C for 5 min and cooled to room temperature. After washed in PBS with 0.05% Tween 20 (PBS-T), the sections were primarily incubated with anti-PCNA antibody (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) overnight at 4°C. After washed three times in PBS-T, the sections were incubated with secondary HRP-conjugated anti-mouse antibody (Chemicon, Temecula, CA) for 1 h at room temperature following its manufacturer’s instructions. The complex was visualized with DAB and counterstained with hematoxylin.
RESULTS
Human donor contributions in MTR liver analyzed by ISH for human Alu sequences
Human donor contribution in recipient liver was determined by human Alu gene-specific PCR. The presence of donor-derived human cells in PCR-positive rat liver was confirmed by IHC using antibodies specific for human β2-M which is present in almost all cells of the body except for red blood cells[19] (Figure 1B and C). Moreover, 0.1%-10.7% of β2-M-positive human cells in the liver sections analyzed at the indicated time points were of human origin which is consistent with the reported data[20].
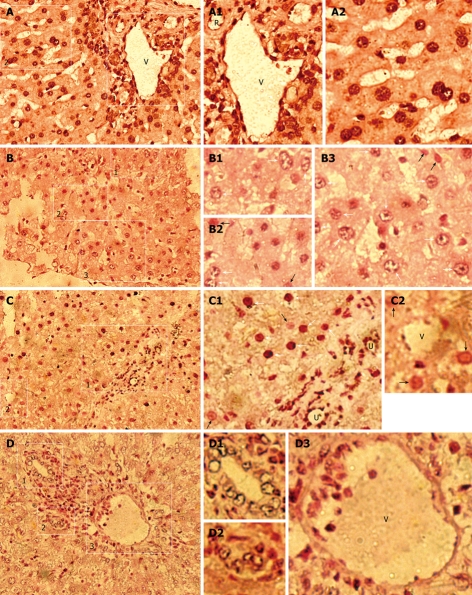
Since human Alu (hAlu) repetitive sequence constitutes 10% of human genomes, the results of this study, obtained by PCR and IHC for β2-M, were further confirmed by ISH with a human Alu-specific probe to detect donor-derived human cells containing Alu sequences in chimeric liver. ISH analysis indicated that a large number of human Alu-positive cells with black/dark brown nuclei were found in the hepatic parenchyma and stroma of receipts (Figure 2B-D), but not in normal control rats (NCR) (data not shown). Moreover, all human cells in human liver samples demonstrated black/dark brown nuclei (Figure 2A). These findings illustrate that there are donor-derived cells of human origin in the liver of host rats.
Figure 2.
Human donor contributions in HRC liver analyzed by in situ hybridization (ISH) for human Alu sequences. Black/dark brown Alu-positive human cells in nuclei (white arrow) were identified in receipt liver using a probe specific for human DNA Alu sequences, and counterstained (pink) with nuclear fast red. Black/dark brown hybridization signals (white arrow) shows Alu-positive human cells in liver of MTR and human samples, whereas no Alu-positive human cells were found in normal control (NC) rats (data not shown). White arrow and black arrow indicate the partially demonstrated Alu-positive and negative human cells in B1-B3, C1 and C2, respectively. A: Human liver (positive control); B-D: Detection of donor-derived human cells in the chimeric liver of HRC. R: Artery; U: Bile duct; V: Vein. A: Low-power magnification of hAlu-positive human cells; A1: High-power magnification of the region (1) in the right rectangle of (A) demonstrating hAlu-positive vein (V) containing hAlu-positive human endothelial cell-like cells (hECLs), hAlu-positive artery (R) containing hAlu-positive human cells, and hAlu-positive human hepatocytes and other human cells in human liver; A2: High-power magnification of the region (2) in the left rectangle of (A), hAlu-positive human hepatocytes and other human cells in human liver; B: Low-power magnification of hAlu-positive human cells; B1: High-power magnification of hAlu-positive human cells (white arrow) of the rectangle region (1) in (B); B2: High-power magnification of hAlu-positive human cells (white arrow) and hAlu-negative cells (white arrowhead) of the rectangle region (2) in (B); B3: High-power magnification of hAlu-positive human cells (white arrow) and hAlu-negative cells (white arrowhead) of the rectangle region (3) in (B); C: Low-power magnification of hAlu-positive human cells; C1: High-power magnification of the rectangle region (1) in (C) showing hAlu-positive human hepatocyte-like cells (hHLCs) (white arrow), hAlu-positive bile duct (U) epithelial cells and other human cells (white arrow) in chimeric liver; C2: High-power magnification of the rectangle region (2) in (C) showing hAlu-positive hECLs in vein (V) of chimeric liver; D: Low-power magnification of hAlu-positive small bile ducts (U) and hAlu-positive vein (V) in chimeric liver; D1, D2: High-power magnification of hAlu-positive small bile ducts (U) in (1, 2) of (D), respectively; D3: High-power magnification of vein (V) containing hAlu-positive hECLs in (3) of (D).
Formation of humanized liver with donor-derived human hepatic parenchymal and stromal components in HRC
Mammalian liver is composed of hepatic parenchymal components, such as stem/progenitor cells including oval cells, and cells expressing AFP, CK18, CK8, Alb, etc, in hepatocyte lineage, and hepatic stromal components including endothelial and biliary duct cells, etc[31]. Our previous data fully demonstrate that donor-derived human cells positive for CD34, CD45, AFP, CK8, CK18, CK19 and Alb are formed in the chimeric liver of HRC, suggesting that donor-derived human hepatic parenchymal components are formed in rat liver[19,20].
To further evaluate the in vivo differentiation potential of transplanted human cells into hepatic stromal cells, including endothelial and biliary duct cells, etc, in host liver, we performed ISH on liver sections from rats that underwent transplantation using a probe specific for the human Alu sequence. hAlu-positive vein (V) containing hAlu-positive human endothelial cell-like cells (hECLs), hAlu-positive artery (R) containing hAlu-positive human cells, hAlu-positive human hepatocytes, and other human cells, were found in the same liver section of human liver samples (Figure 2A). Moreover, no hAlu-positive human cells with black/dark brown nuclei were observed in the sections from control group (data not shown). ISH showed that a large number of cell nuclei in vein walls containing hAlu-positive hECLs (Figure 2C, C2 and D3) and biliary ducts containing hAlu-positive human bile duct epithelial cells (Figure 2C, C1, D1 and D2) were of human origin, indicating that donor-derived human hepatic stromal components (i.e. donor-derived human endothelial and biliary duct cells) are formed in rat liver. Furthermore, hAlu-positive vein (V) and bile duct (U) were observed in hepatic stroma and hAlu-positive human cells in hepatic parenchyma of host rats (Figure 2C and D), suggesting that humanized liver with donor-derived human hepatic parenchymal and stromal components is formed in xenogeneic competitive settings.
Changes in cellular phenotypes of donor-derived human cells during PHx-induced liver regeneration in HRC
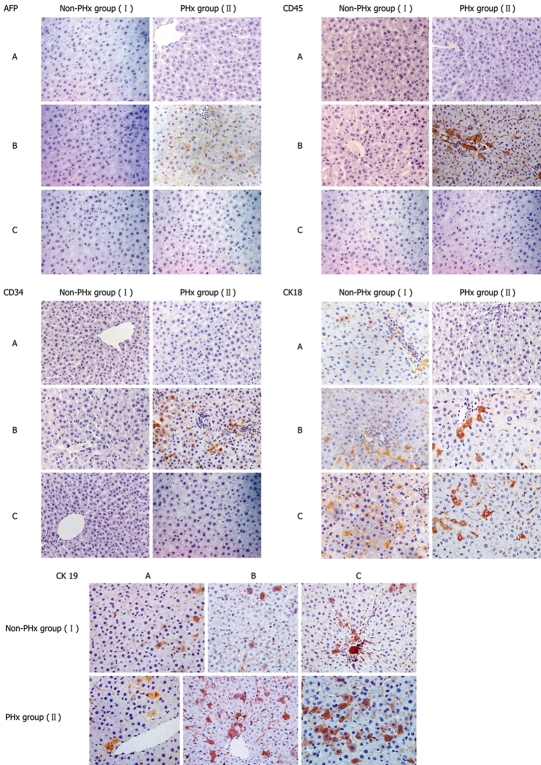
The well-characterized PHx model of rat liver regeneration was used to explore the evolvement rules in cellular phenotypes of donor-derived human cells participating in PHx-induced chimeric liver regeneration, and IHC was used detect the expression of cell markers, such as AFP, CD34, CD45, CK18 and CK19. IHC analysis showed phenotypic changes of donor-derived human cells during PHx-induced liver regeneration in HRC (Figure 3). The changes in the cellular phenotypes of donor-derived human cells during PHx-induced liver regeneration in five HRCs after PHx are summarized in Table 1. Donor-derived AFP+, CD34+ and CD45+ human cells in the portal area were found in the chimeric liver of HRC after 10 d of PHx in PHx group but not in control group (Figure 3 and Table 1), suggesting that dynamic changes of donor-derived human cells expressing AFP, CD34 and CD45 may occur during liver regeneration.
Figure 3.
Representative immunohistochemistric analysis of phenotypic changes of donor-derived human cells in HRC liver during PHx-induced liver regeneration. Seventy percent partial hepatectomy (PHx), a procedure that removes 70% of the liver, is regarded as the preferred in vivo method to study liver growth due to its synchronized growth response. In the representative chimeric livers of animals 5 and 6 (Table 1), donor-derived human cells with different cellular phenotypes were detected by IHC for different human markers (AFP, CD34, CD45, CK18 and CK19). Minimal liver tissues used for IHC were collected before PHx, and after 10 and 20 d of PHx. Additionally, the untransplanted control group was also set up when we performed this experiment (data not shown). The results demonstrate that CD45+, CK18+, AFP+, CD34+ and CK19+ cells could not be detected in liver sections from untransplanted control rats by human-specific IHC, suggesting that human-specific IHC can show human specificity of staining (data not shown). PHx: 70% partial hepatectomy, I: Non-PHx group; II: PHx group. A: before PHx; B: 10 d after PHx; C: 20 d after PHx.
Table 1.
Phenotypic changes of donor-derived human cells in HRC liver during PHx-induced liver regeneration
| Animal No. (age) |
Cell markers |
||||||||||
|
AFP |
CK19 |
CK18 |
CD34 |
CD45 |
|||||||
| I | II | I | II | I | II | I | II | I | II | ||
| 1 and 2 (2 mo) | A | - | - | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| B | - | + | + | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | |
| C | - | - | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | |
| 3 and 4 (2 mo) | A | - | - | + | + | + | - | + | - | - | - |
| B | - | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | - | + | |
| C | - | - | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | + | |
| 5 and 6 (2 mo) | A | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| B | - | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | - | + | |
| C | - | - | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | |
| 7 and 8 (2 mo) | A | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | - | - |
| B | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | |
| C | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | |
| 9 and 10 (2 mo) | A | - | - | - | - | + | + | - | - | - | - |
| B | - | - | - | - | + | + | - | - | - | + | |
| C | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | |
Animals 1-10 at the age of 2 mo with the engraftment of donor-derived hHLCs in the liver of HRC were screened by human gene-specific PCR for hAlu as previously described[19,20] and ISH for human Alu sequences confirmed by detecting human β2-M expression using IHC. Animals 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10 at the age of 2 mo underwent 70% PHx. Age-matched animals 1, 3, 5, 7 and 9 (not undergone PHx), were used as negative controls. In the human-rat chimeric liver, donor-derived human cells with different cellular phenotypes were detected by IHC for different markers (AFP, CD34, CD45, CK18 and CK19). Minimal liver tissues from PHx (II) and non-PHx (I) groups used for IHC were dissected and collected before PHx (A), and after 10 d (B) and 20 d (C) of PHx.
Proliferative activity of hHLCs during PHx-induced liver regeneration in HRC
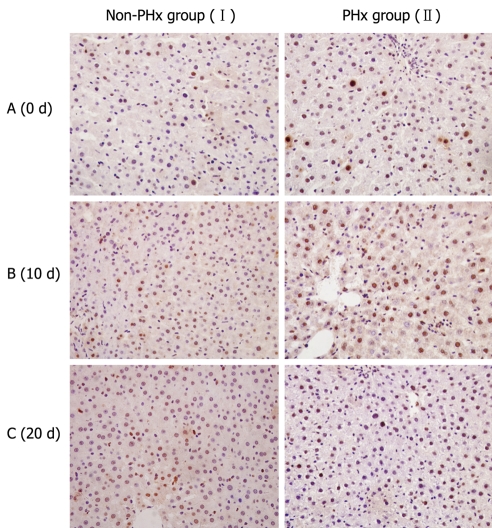
Since PCNA is present specifically in nuclei of proliferating cells, it was employed to indicate the active proliferation of donor-derived human cells during human-rat chimeric liver regeneration in this study. Immunostaining for human PCNA showed that the number of PCNA-positive cells in chimeric liver was significantly higher in PHx group than in control group after 10 d of PHx (Figure 4), indicating that donor-derived hHLCs are actively proliferated during PHx-induced HRC liver regeneration.
Figure 4.
Proliferative activities of hHLCs during PHx-induced liver regeneration in HRC. Immunostaining for PCNA, a marker for cell proliferation, was performed to evaluate the proliferation of hHLCs. An antibody against PCNA antigen was used to evaluate the percentage of hepatocytes in the regenerative process after 70% hepatectomy. Ten days after PHx, PCNA staining demonstrated the active proliferation of hHLCs in the PHx group (II) compared with the control group (I).
DISCUSSION
Adult mammalian liver contains different cell types, such as stem/progenitor cells including oval cells, hepatocytes, bile duct epithelial cells, vascular endothelial cells, stellate cells, Kupffer cells (K), fibroblasts and leukocytes, etc, which constitute the functional units of liver[31]. Hepatocytes are responsible for most liver functions and account for 90% of liver weight.
Since in vivo study of human biology is severely limited by scientific, technical and ethical constraints, livers of small and large laboratory animals are routinely used to establish human liver biology and disease models, which, however, cannot fully replicate the complex biological and pathological processes of human liver. It is, therefore, necessary to develop a preclinically and/or clinically relevant HAC harboring a “humanized liver” with a relatively large number of different human liver and bile duct epithelial cells that cluster to form functional human liver units in host animals, which can imitate the in vivo situations in humans. Such a HAC harboring a “humanized liver” can be used in study of human liver development, repair and regeneration, the pathogenesis of human hepatitis virus infection, and human liver-specific metabolic responses to drugs, etc.
Transplantation of human hepatocytes into immunodeficient mice can generate humanized mice carrying a humanized liver, and nearly 80%-90% of which can be replaced by transplanted human hepatocytes[25,27,32,33]. Furthermore, functional donor-derived human mature hepatocytes are positive for Alb, CK18 and CK8 in such a “humanized liver”. The presence of donor-derived human hepatic progenitor cells in liver parenchyma and donor-derived functional human bile canaliculi connected to mouse canaliculi can form donor-derived human hepatic functional units in animal livers, while the plasma in humanized mice carrying a humanized liver contains human Alb and additional 21 human proteins[25,26,32,33]. However, the following significant drawbacks greatly limit the widespread use of such humanized mice derived from immunodeficient mice in study of human liver development, repair and regeneration, and pathogenesis of human hepatitis virus infection. On the one hand, transplanted foreign cells migrating into host liver from host spleen may not develop into all cell types in human liver required for normal liver function. On the other hand, immunodeficient mouse recipients have no normal immune system. In other words, after birth, this model is lack of a completely normal physiological environment, but the body immune system is involved in the pathogenesis of human hepatitis, and in control of human liver development, repair and regeneration.
Naturally occurring migration patterns of stem cells, availability of extending homing and engraftment sites, tissue- and organ-specific signals from niche in early embryo of animals greatly facilitate the widespread distribution of human donor cells in the recipient body, and promote them to home and engraft into various tissues and organs, in which human donor cells are actively influenced by the signals from niches to undergo reprogram, proliferation and differentiation in specific tissues and organs of recipients[19,20,34]. In utero or blastocyst transplantation of hSCs from multiple sources can form all possible donor-derived human cell types in the recipient liver, which in turn constitute human hepatic parenchymal and stromal components[2,6,18–20,22,24]. In contrast to the immunodeficient mice harboring a humanized liver, HAC in liver humanization possess and potential human immune system can be reconstituted with donor-derived human differentiated cells (data not shown). Besides the functional donor-derived human mature HLCs positive for human Alb, AFP, HNF-4, etc, throughout the host liver parenchyma, an “ideal human-animal chimeric liver” can also synthesize and secrete human Alb, ALT, AST and ALP into the circulation of host animals[2,6,18–20,22,24]. Our findings demonstrate that donor-derived human mature hepatocytes, endothelial and biliary duct cells in human-rat chimeric liver, constitute the “humanized hepatic functional units” in animal liver[2,19,20]. In addition, other donor-derived human cell types, such as liver stem/progenitor cells, stellate and Kupffer cells (K), fibroblasts and leukocytes in human liver, remain to be further identified in HRC liver.
It has been reported that after in utero transplantation of hMNCs, the transplanted human stem/progenitor cells can engraft into the recipient liver, and are actively influenced by niche signals to participate in organogenesis of recipients in the xenogeneic competitive settings[19,20], indicating that HAC carrying humanized liver cells derived from in utero or blastocyst transplantation of hSCs is more superior to that in immunodeficient mice harboring humanized liver.
Since most of our present knowledge on liver regeneration is derived from laboratory mice and rats, but not from human beings due to the lack of an ideal in vivo model[35], HAC harboring a humanized liver will become an ideal in vivo system for investigating human liver regeneration and its mechanism.
Mature hepatocytes, liver stem cells or bone marrow (BM)-derived stem cells will be mobilized to participate in liver regeneration and repair, while various liver injury models, such as PHx, AAF/PHx, and AAF models, can induce different cell proliferative responses in liver[31]. In this study, the well-established 70% PHx model was used to induce acute chimeric liver injury and liver regeneration was induced with PHx. Donor-derived AFP+, CD34+ and CD45+ human cells were found in the chimeric liver on day 10 in PHx group but not in control group, suggesting that the donor-derived hSCs, engrafted into the BM of HAC, can be mobilized to migrate into the chimeric liver from the chimeric BM of HRC, thus participating in the regeneration and repair of injured chimeric liver during the acute liver damage. Additionally, the donor-derived human cells were engrafted in rat BM (Figure 1A). During chimeric liver regeneration, the donor-derived CD34+ and CD45+ human cells were detected in the portal area of chimeric liver, indicating that BM-derived hSCs participate in the regeneration of injured chimeric liver, which needs to be confirmed by further experiments. Generally, liver stem cells are not significantly proliferated after mild liver damage and BM-derived stem cells can directly enter liver from outside and subsequently develop into mature hepatic cells, but do not migrate into the portal area[31]. In this study, the markers of various donor-derived human cells in chimeric liver varied with time, demonstrating the changing process of surface markers of BM-derived hSCs, mature hepatocytes or liver stem cells during the regeneration of damaged chimeric liver. During liver regeneration after acute liver damage, the actively mobilized BM-derived hSCs in chimeric BM migrate into the chimeric liver, and further differentiate into hepatocytes to support the regeneration of injured chimeric liver, while donor-derived human mature hepatocytes and liver stem cells in chimeric liver participate in the regeneration and repair of injured chimeric liver[36].
Anyway, HAC liver will become a powerful in vivo system for examining human-specific biological processes of damaged liver regeneration and repair.
Remaining constraints of such a “HAC” containing humanized liver cells include non-consistent engraftment of human cells in the same organ of different individuals, and inadequate human cells engrafted in HAC liver. For example, the percentage of donor-derived human cells in the chimeric liver of HRC is 0.1%-10.7%[20].
The countermeasures for the elimination of the above constraints include definite cell components of human stem/progenitor cells used for transplantation, standard manipulation of transplantation, the need for genetic modifications to further humanize the host strain[37], and loss of host hepatocytes, etc.
In summary, humanized liver can show insights into in vivo human liver biology, and provide an in vivo powerful system for more precisely replicating the complex biological and pathological processes of human liver, and further allow us to investigate human liver-specific biological processes and diseases. However, efforts should be made to develop the optimal and pragmatic humanized animal models meeting the growing needs for animal models to carry out in vivo studies of human cells, tissues and organs.
COMMENTS
Background
Data demonstrate that donor-derived human hepatocyte-like cells with different cellular phenotypes and of functional human hepatocytes are formed in chimeric liver of human-rat chimera (HRC) after in utero transplantation of human cells. Formation of human hepatic parenchymal and stromal components in rat liver was further examined, and humanized liver harboring HRC was used to investigate the phenotypic changes of donor-derived human cells engrafted into rat liver during 70% partial hepatectomy (PHx)-induced liver regeneration.
Research frontiers
HRC carrying humanized liver generated by in utero transplantation of human cells has been developed by the authors. HRC harboring human-rat chimeric liver was used to study the human liver-specific biological processes and human liver-specific diseases.
Innovations and breakthroughs
Humanized liver was employed to investigate the process of human hepatic ontogeny and to examine the phenotypic changes of donor-derived human cells engrafted into rat liver during PHx-induced liver regeneration in this study.
Applications
Compared with the general laboratory animals including mice, rats, pigs, dogs and non-human primates, and immune-deficient mice (in vivo injury model) carrying humanized liver reconstructed with human hepatocytes or stem cells, HRC carrying growing humanized liver with a relatively large number of donor-derived human liver cells clustering to form functional human liver units in host liver, is the in vivo non-injury human-animal xenograft animal model with normal physiological conditions, and will become an ideal and suitable in vivo system for studies of the mechanisms underlying human liver development, repair and regeneration, the pathogenesis of human liver-related diseases including viral hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and drug discovery and drug preclinical assessment of ADME-Tox.
Terminology
Humanized animals generated by in utero transplantation or blastocyst transplantation of various human stem cells were defined in this study as normal animals engrafted with human cells, tissues or organs with normal physiological conditions.
Peer review
The manuscript describes the successful development of HRC carrying humanized liver generated by in utero transplantation of human cells. The findings of this study indicate that donor-derived functional human hepatocytes generated in this model constitute human hepatic functional units with donor-derived human endothelial and biliary duct cells in host liver. More importantly, HRC harboring human-rat chimeric liver was used to preliminarily examine the phenotypic changes of donor-derived human cells engrafted into rat liver during PHx-induced liver regeneration.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Professor Lu TC (Shihezi University, Xinjiang, China) for his unstinting advice and technical guidance, Qiu GG, Huang WG, Chen FY, Guo FF, Yang GZ and Zheng WW (Center of Experimental Animals, Sun Yat-sen University) for their technical assistance, Yang XH, Li Y and Zhang W (Zhongshan School of Medicine, Sun Yat-sen University) for kindly providing reagents.
Supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 30271177 and No. 39870676; the Major Science and Technology Projects of Guangdong Province, No. B602; the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. 021903; the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, No. 2009B060300008; the Science and Technology Projects of Guangzhou City, No. 2002Z2E0121; the Medical Scientific Research Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. A2007359; the Science and Technology Talented Man Foundation of Outstanding Young and Middle-aged People of Southern Medical University, the Special Fund of Scientific Instrument Collaborative Share-net in Guangzhou, No. 2006176
Peer reviewer: Dr. Guangcun Huang, Center for Cell & Developmental Biology, The Research Institute at Nationwide Children’s Hospital and The Ohio State University, 700 Childrens Drive, Columbus, OH 43205, United States
S- Editor Tian L L- Editor Wang XL E- Editor Ma WH
References
- 1.Airey JA, Almeida-Porada G, Colletti EJ, Porada CD, Chamberlain J, Movsesian M, Sutko JL, Zanjani ED. Human mesenchymal stem cells form Purkinje fibers in fetal sheep heart. Circulation. 2004;109:1401–1407. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000124222.16321.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Almeida-Porada G, Porada CD, Chamberlain J, Torabi A, Zanjani ED. Formation of human hepatocytes by human hematopoietic stem cells in sheep. Blood. 2004;104:2582–2590. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-01-0259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Almeida-Porada G, Crapnell K, Porada C, Benoit B, Nakauchi H, Quesenberry P, Zanjani ED. In vivo haematopoietic potential of human neural stem cells. Br J Haematol. 2005;130:276–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2005.05588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Almeida-Porada G, Porada C, Gupta N, Torabi A, Thain D, Zanjani ED. The human-sheep chimeras as a model for human stem cell mobilization and evaluation of hematopoietic grafts' potential. Exp Hematol. 2007;35:1594–1600. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2007.07.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Behringer RR. Human-animal chimeras in biomedical research. Cell Stem Cell. 2007;1:259–262. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2007.07.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chamberlain J, Yamagami T, Colletti E, Theise ND, Desai J, Frias A, Pixley J, Zanjani ED, Porada CD, Almeida-Porada G. Efficient generation of human hepatocytes by the intrahepatic delivery of clonal human mesenchymal stem cells in fetal sheep. Hepatology. 2007;46:1935–1945. doi: 10.1002/hep.21899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Colletti EJ, Almeida-Porada G, Chamberlain J, Zanjani ED, Airey JA. The time course of engraftment of human mesenchymal stem cells in fetal heart demonstrates that Purkinje fiber aggregates derive from a single cell and not multi-cell homing. Exp Hematol. 2006;34:926–933. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2006.04.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Durr M, Harder F, Merkel A, Bug G, Henschler R, Muller AM. Chimaerism and erythroid marker expression after microinjection of human acute myeloid leukaemia cells into murine blastocysts. Oncogene. 2003;22:9185–9191. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Fujiki Y, Fukawa K, Kameyama K, Kudo O, Onodera M, Nakamura Y, Yagami K, Shiina Y, Hamada H, Shibuya A, et al. Successful multilineage engraftment of human cord blood cells in pigs after in utero transplantation. Transplantation. 2003;75:916–922. doi: 10.1097/01.TP.0000057243.12110.7C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Harder F, Henschler R, Junghahn I, Lamers MC, Muller AM. Human hematopoiesis in murine embryos after injecting human cord blood-derived hematopoietic stem cells into murine blastocysts. Blood. 2002;99:719–721. doi: 10.1182/blood.v99.2.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Harrison MR, Slotnick RN, Crombleholme TM, Golbus MS, Tarantal AF, Zanjani ED. In-utero transplantation of fetal liver haemopoietic stem cells in monkeys. Lancet. 1989;2:1425–1427. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Koestenbauer S, Vanderzwalmen P, Hammer A, Schoonjans L, Danloy S, Zech H, Dohr G, Zech NH. Apoptosis affects integration frequency: adult stem cells injected in blastocysts show high caspase-3 activity. Cell Biol Int. 2007;31:489–493. doi: 10.1016/j.cellbi.2006.11.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Liechty KW, MacKenzie TC, Shaaban AF, Radu A, Moseley AM, Deans R, Marshak DR, Flake AW. Human mesenchymal stem cells engraft and demonstrate site-specific differentiation after in utero transplantation in sheep. Nat Med. 2000;6:1282–1286. doi: 10.1038/81395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Muotri AR, Nakashima K, Toni N, Sandler VM, Gage FH. Development of functional human embryonic stem cell-derived neurons in mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:18644–18648. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0509315102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Narayan AD, Chase JL, Lewis RL, Tian X, Kaufman DS, Thomson JA, Zanjani ED. Human embryonic stem cell-derived hematopoietic cells are capable of engrafting primary as well as secondary fetal sheep recipients. Blood. 2006;107:2180–2183. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-05-1922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Pixley JS, Tavassoli M, Zanjani ED, Shaft DM, Futamachi KJ, Sauter T, Tavassoli A, MacKintosh FR. Transplantation in utero of fetal human hematopoietic stem cells into mice results in hematopoietic chimerism. Pathobiology. 1994;62:238–244. doi: 10.1159/000163916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Porada GA, Porada C, Zanjani ED. The fetal sheep: a unique model system for assessing the full differentiative potential of human stem cells. Yonsei Med J. 2004;45 Suppl:7–14. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2004.45.Suppl.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Qian H, Wang J, Wang S, Gong Z, Chen M, Ren Z, Huang S. In utero transplantation of human hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells partially repairs injured liver in mice. Int J Mol Med. 2006;18:633–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sun Y, Xiao D, Pan XH, Zhang RS, Cui GH, Chen XG. Generation of human/rat xenograft animal model for the study of human donor stem cell behaviors in vivo. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13:2707–2716. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i19.2707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sun Y, Xiao D, Zhang RS, Cui GH, Wang XH, Chen XG. Formation of human hepatocyte-like cells with different cellular phenotypes by human umbilical cord blood-derived cells in the human-rat chimeras. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;357:1160–1165. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.04.087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Troeger C, Surbek D, Schoberlein A, Schatt S, Dudler L, Hahn S, Holzgreve W. In utero haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Experiences in mice, sheep and humans. Swiss Med Wkly. 2006;136:498–503. doi: 10.4414/smw.2006.11380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Turrini P, Monego G, Gonzalez J, Cicuzza S, Bonanno G, Zelano G, Rosenthal N, Paonessa G, Laufer R, Padron J. Human hepatocytes in mice receiving pre-immune injection with human cord blood cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;326:66–73. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.10.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wang ML, Yan JB, Xiao YP, Huang SZ. Construction of an allogenic chimeric mouse model for the study of the behaviors of donor stem cells in vivo. Chin Med J (Engl) 2005;118:1444–1450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zeng F, Chen MJ, Baldwin DA, Gong ZJ, Yan JB, Qian H, Wang J, Jiang X, Ren ZR, Sun D, et al. Multiorgan engraftment and differentiation of human cord blood CD34+ Lin- cells in goats assessed by gene expression profiling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:7801–7806. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0602646103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Katoh M, Tateno C, Yoshizato K, Yokoi T. Chimeric mice with humanized liver. Toxicology. 2008;246:9–17. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2007.11.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Azuma H, Paulk N, Ranade A, Dorrell C, Al-Dhalimy M, Ellis E, Strom S, Kay MA, Finegold M, Grompe M. Robust expansion of human hepatocytes in Fah-/-/Rag2-/-/Il2rg-/- mice. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:903–910. doi: 10.1038/nbt1326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bissig KD, Le TT, Woods NB, Verma IM. Repopulation of adult and neonatal mice with human hepatocytes: a chimeric animal model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:20507–20511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0710528105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Shafritz DA. A human hepatocyte factory. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:871–872. doi: 10.1038/nbt0807-871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Nonome K, Li XK, Takahara T, Kitazawa Y, Funeshima N, Yata Y, Xue F, Kanayama M, Shinno E, Kuwae C, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived cells differentiate into hepatocyte-like cells in the Fas-mediated liver injury model. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2005;289:G1091–G1099. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00049.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sharma AD, Cantz T, Richter R, Eckert K, Henschler R, Wilkens L, Jochheim-Richter A, Arseniev L, Ott M. Human cord blood stem cells generate human cytokeratin 18-negative hepatocyte-like cells in injured mouse liver. Am J Pathol. 2005;167:555–564. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)62997-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Marshak DR, Gardner RL, Gottlieb D. Stem cell biology. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York; 2001. pp. 455–497. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Meuleman P, Libbrecht L, De Vos R, de Hemptinne B, Gevaert K, Vandekerckhove J, Roskams T, Leroux-Roels G. Morphological and biochemical characterization of a human liver in a uPA-SCID mouse chimera. Hepatology. 2005;41:847–856. doi: 10.1002/hep.20657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Tateno C, Yoshizane Y, Saito N, Kataoka M, Utoh R, Yamasaki C, Tachibana A, Soeno Y, Asahina K, Hino H, et al. Near completely humanized liver in mice shows human-type metabolic responses to drugs. Am J Pathol. 2004;165:901–912. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63352-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Tam PP, Rossant J. Mouse embryonic chimeras: tools for studying mammalian development. Development. 2003;130:6155–6163. doi: 10.1242/dev.00893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Palmes D, Spiegel HU. Animal models of liver regeneration. Biomaterials. 2004;25:1601–1611. doi: 10.1016/s0142-9612(03)00508-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yin L, Sun M, Ilic Z, Leffert HL, Sell S. Derivation, characterization, and phenotypic variation of hepatic progenitor cell lines isolated from adult rats. Hepatology. 2002;35:315–324. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.31355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Shultz LD, Ishikawa F, Greiner DL. Humanized mice in translational biomedical research. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:118–130. doi: 10.1038/nri2017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]