Abstract
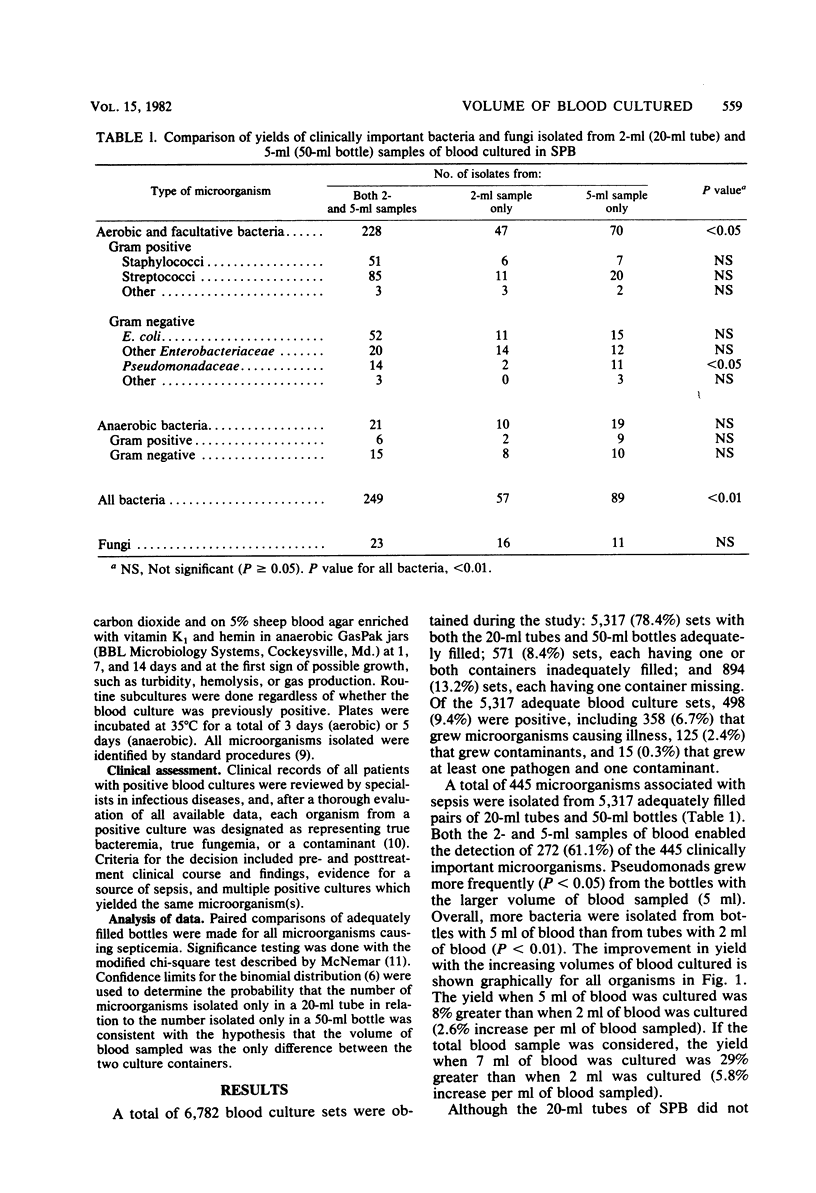
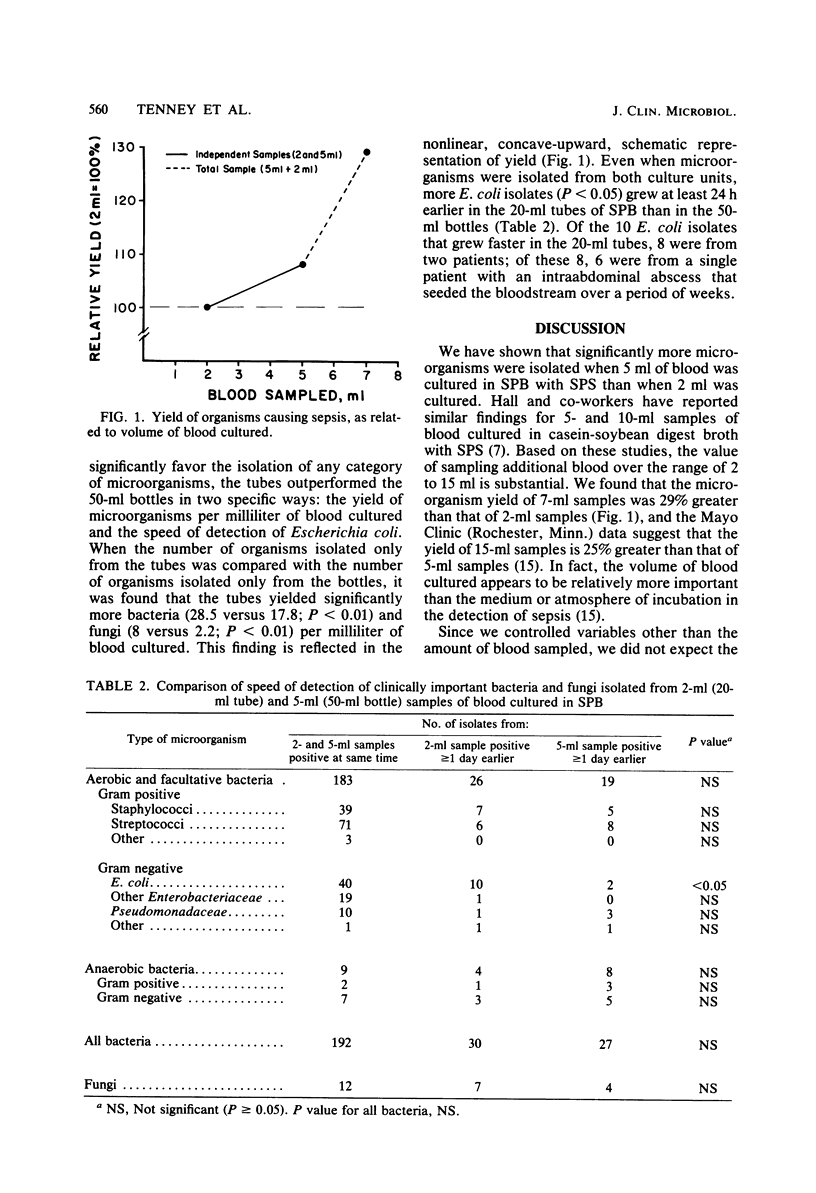
To evaluate the role of the volume of blood cultured in the detection of clinically important bacteremia and fungemia in adults, we evaluated the yield and speed of detection of microorganisms from 5,317 paired 2- and 5-ml samples of blood. The same kind of medium (supplemented peptone broth with 0.03% sodium polyanetholsulfonate) and atmosphere of incubation (open venting units) were used for all blood cultures. Only adequately filled (less than or equal to 80% of stated volume) sets (20-ml tube and 50-ml bottle) were compared statistically. Significantly more bacteria (p less than 0.01), Pseudomonas spp. In particular (P less than 0.05), were isolated from the 5-ml samples of blood. We conclude that the volume of blood cultured is a critical factor in the detection of septicemia. Consequently, valid evaluation of other factors influencing the detection of septicemia must be based on comparisons in which equal volumes of blood are cultured.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dietzman D. E., Fischer G. W., Schoenknecht F. D. Neonatal Escherichia coli septicemia--bacterial counts in blood. J Pediatr. 1974 Jul;85(1):128–130. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80308-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durbin W. A., Szymczak E. G., Goldmann D. A. Quantitative blood cultures in childhood bacteremia. J Pediatr. 1978 May;92(5):778–780. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80151-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyster E., Bernene J. Nosocomial anemia. JAMA. 1973 Jan 1;223(1):73–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franciosi R. A., Favara B. E. A single blood culture for confirmation of the diagnosis of neonatal septicemia. Am J Clin Pathol. 1972 Feb;57(2):215–219. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/57.2.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. M., Ilstrup D. M., Washington J. A., 2nd Effect of volume of blood cultured on detection of bacteremia. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jun;3(6):643–645. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.6.643-645.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M., Warren E., Washington J. A., 2nd Detection of bacteremia with liquid media containing sodium polyanetholsulfonate. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):187–191. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.187-191.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor R. R., Beaty H. N. Evaluation of positive blood cultures. Guidelines for early differentiation of contaminated from valid positive cultures. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Jul;130(1):84–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renner E. D., Gatheridge L. A., Washington J. A., 2nd Evaluation of radiometric system for detecting bacteremia. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Sep;26(3):368–372. doi: 10.1128/am.26.3.368-372.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. D., Horstmeier C., Hall M., Washington J. A., 2nd Recovery of yeast from vented blood culture bottles. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jul;2(1):18–20. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.1.18-20.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szymczak E. G., Barr J. T., Durbin W. A., Goldmann D. A. Evaluation of blood culture procedures in a pediatric hospital. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):88–92. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.88-92.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


