Abstract
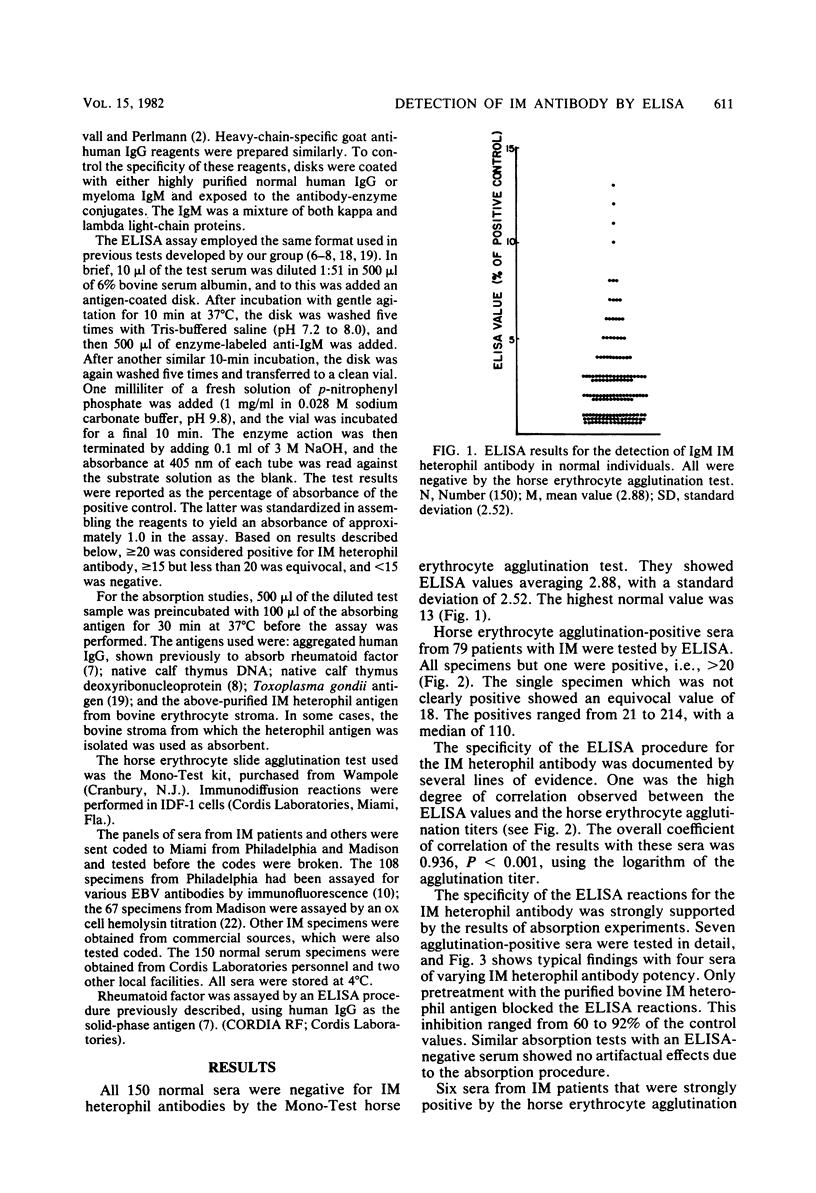
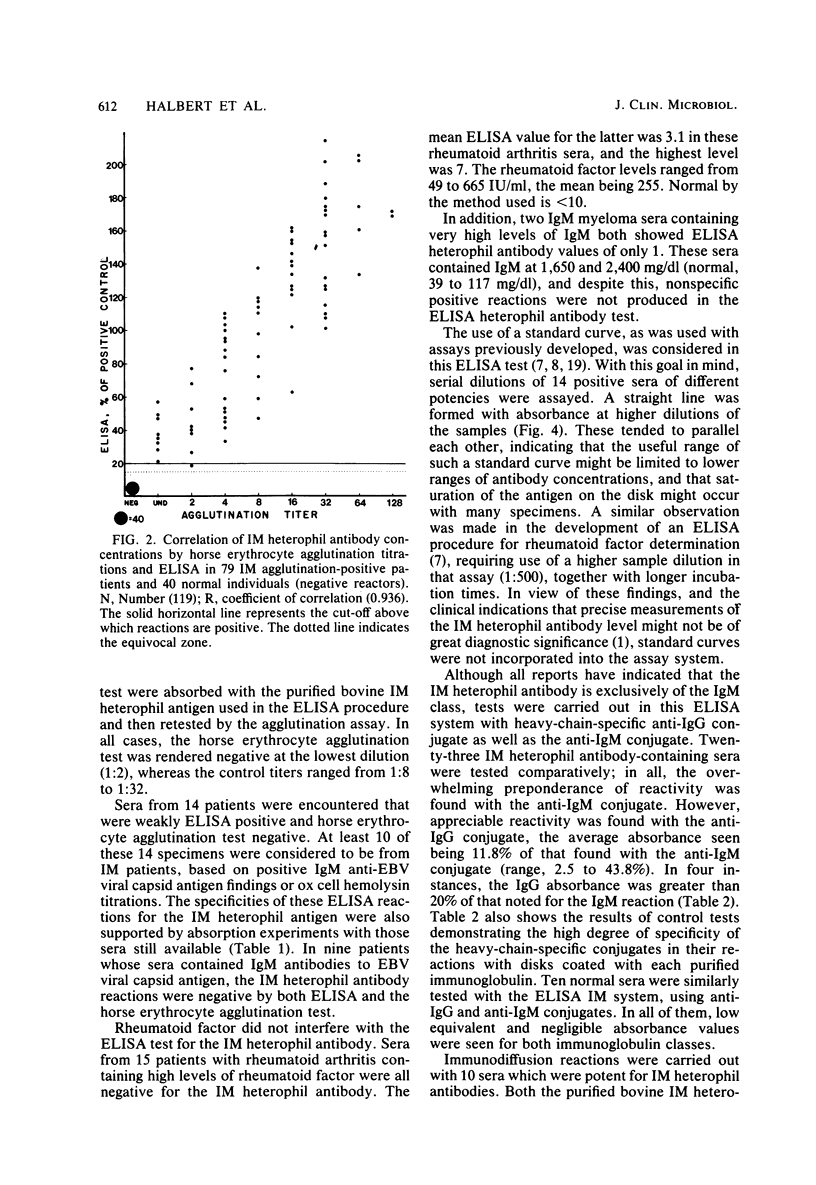
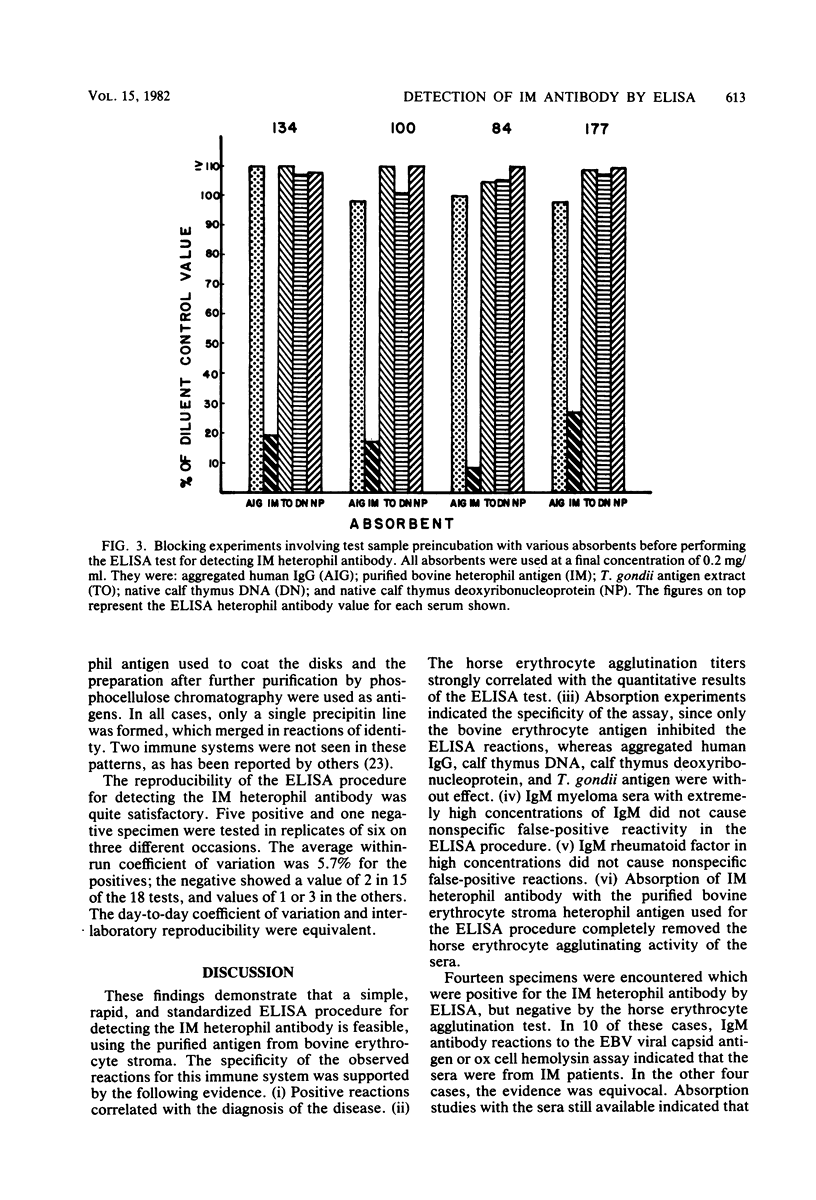
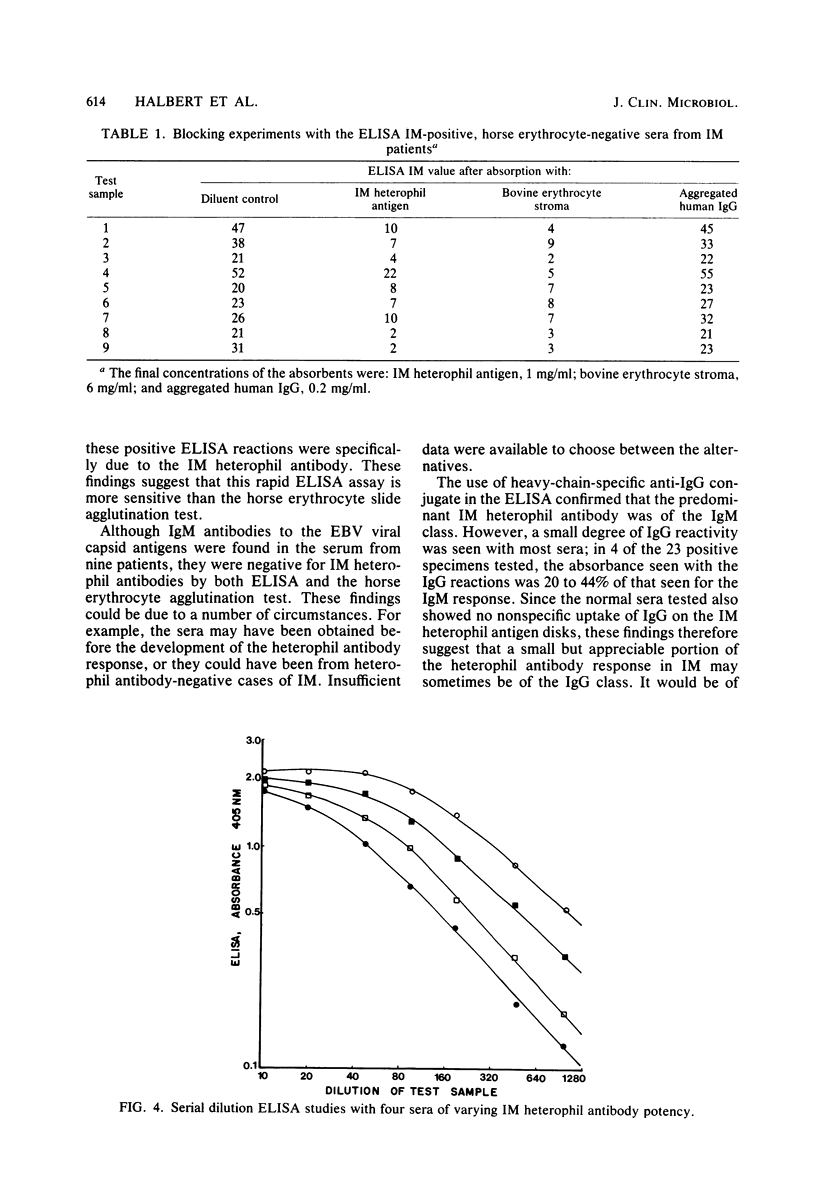
A rapid, specific, sensitive, standardized, a reproducible enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) procedure has been developed for detecting the heterophil antibody associated with infectious mononucleosis (IM). The IM heterophil antibody used for the solid phase was purified from bovine erythrocyte stroma. The test uses heavy-chain-specific anti-immunoglobulin M (IgM) labeled with alkaline phosphatase and three 10-min incubations. The quantitative results correlated well with horse erythrocyte agglutination titers. Absorption tests confirmed the specificity of the ELISA reactions for IM heterophil antibodies. Neither very high levels of IgM in myeloma sera nor high levels of rheumatoid factor caused false-positive reactions. A number of probable IM cases were encountered which positive by ELISA but negative by the horse erythrocyte slide agglutination test. Absorption studies indicated that these were true-positives for the IM heterophil antibody. The IM heterophil antibodies were confirmed to be predominantly of the IgM class, but moderate proportions of the IgM class were sometimes encountered.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chretien J. H., Esswein J. G., Holland W. G., McCauley C. E. Predictors of the duration of infectious mononucleosis. South Med J. 1977 Apr;70(4):437–439. doi: 10.1097/00007611-197704000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clamp J. R., Hughes K. W., McPherson J. C. Glycoproteins from human spleen cell surfaces. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):874–879. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90455-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher M. A., Lo T. M., Levey B. A., Graves W. R. Immunochemical studies of infectious mononucleosis. VI. a radioimmunoassay for the detection of infectious mononucleosis heterophile antibody and antigen. J Immunol Methods. 1977;14(1):51–58. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(97)90021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher M. A., Woolfolk B. J. Immunochemical studies on infectious mononucleosis. I. Isolation and characterization of heterophile antigens from hemoglobin-free stroma. J Immunol. 1971 Sep;107(3):842–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golubjatnikov R., Koehler J. E., Inhorn S. L. Absorbed heterophile and ox-cell hemolysin test in serodiagnosis of infectious mononucleosis. Health Lab Sci. 1975 Jul;12(3):201–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert S. P., Anken M. Detection of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBS Ag) with use of alkaline phosphatase-labeled antibody to HBS Ag. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136 (Suppl):S318–S323. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement_2.s318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert S. P., Karsh J., Anken M. A quantitative enzyme immunoassay for IgM rheumatoid factor using human immunoglobulin G as substrate. Am J Clin Pathol. 1980 Dec;74(6):776–784. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/74.6.776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert S. P., Karsh J., Anken M. Studies on autoantibodies to deoxyribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleoprotein with enzyme-immunoassay (ELISA). J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Jan;97(1):97–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G. Epstein-Barr virus and infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Feb 1;288(5):263–264. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197302012880512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert J. T., Feorino P., Caldwell G. G. False-positive epidemic infectious mononucleosis. Am Fam Physician. 1977 Feb;15(2):119–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoagland R. J. Infectious mononucleosis. Prim Care. 1975 Jun;2(2):295–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz C. A., Henle W., Henle G., Penn G., Hoffman N., Ward P. C. Persistent falsely positive rapid tests for infectious mononucleosis. Report of five cases with four--six-year follow-up data. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979 Nov;72(5):807–811. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/72.5.807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz C. A. Practical approach to diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis. Postgrad Med. 1979 Jun;65(6):179–184. doi: 10.1080/00325481.1979.11715183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano K., Milgrom F. Heterophile antigens and antibodies in medicine. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1977;77:43–69. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66740-4_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. L., Davidsohn I., Slaby R. Horse agglutinins in infectious mononucleosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1968 Jan;49(1):3–11. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/49.1.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennette E. T., Henle G., Henle W., Horwitz C. A. Heterophil antigen in bovine sera detectable by immune adherence hemagglutination with infectious mononucleosis sera. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):923–927. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.923-927.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levey B. A., Lo T. M., Caldwell K. E., Fletcher M. A. Latex test for serodiagnosis of infectious mononucleosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Mar;11(3):256–262. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.3.256-262.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. M., Halbert S. P., Chiu C. T., Zarco R. Simple standardized enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for human antibodies to Entamoeba histolytica. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Apr;13(4):646–651. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.4.646-651.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. M., Halbert S. P., O'Connor G. R. Standardized quantitative enzyme-linked immunoassay for antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jun;11(6):675–681. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.6.675-681.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIKKELSEN W., TUPPER C. J., MURRAY J. The ox cell hemolysin test as a diagnostic procedure in infectious mononucleosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 Oct;52(4):648–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick J. M., Schifferle R., Zadarlik K., Kano K., Milgrom F. Isolation and partial characterization of the heterophile antigen of infectious mononucleosis from bovine erythrocytes. J Supramol Struct. 1977;6(2):275–290. doi: 10.1002/jss.400060212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miale T. D., Barbosa J. L., Dellinger C. T., Wolfson S. L. Positive monospot tests preceding the diagnosis of acute monocytic leukemia in two adolescents. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1978;4(2):111–114. doi: 10.1002/mpo.2950040205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milgrom F., Loza U., Kano K. Double diffusion in gel tests with Paul-Bunnell antibodies of infectious mononucleosis sera. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1975;48(1):82–93. doi: 10.1159/000231294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher H. R., Austin R. M., Stass S. A. False-positive serology in infectious monoucleosis. Lancet. 1979 Mar 31;1(8118):722–722. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91171-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. H. Fatal adenovirus infection with misleading positive serology for infectious mononucleosis. Lancet. 1979 Feb 10;1(8111):299–302. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90708-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


