Abstract
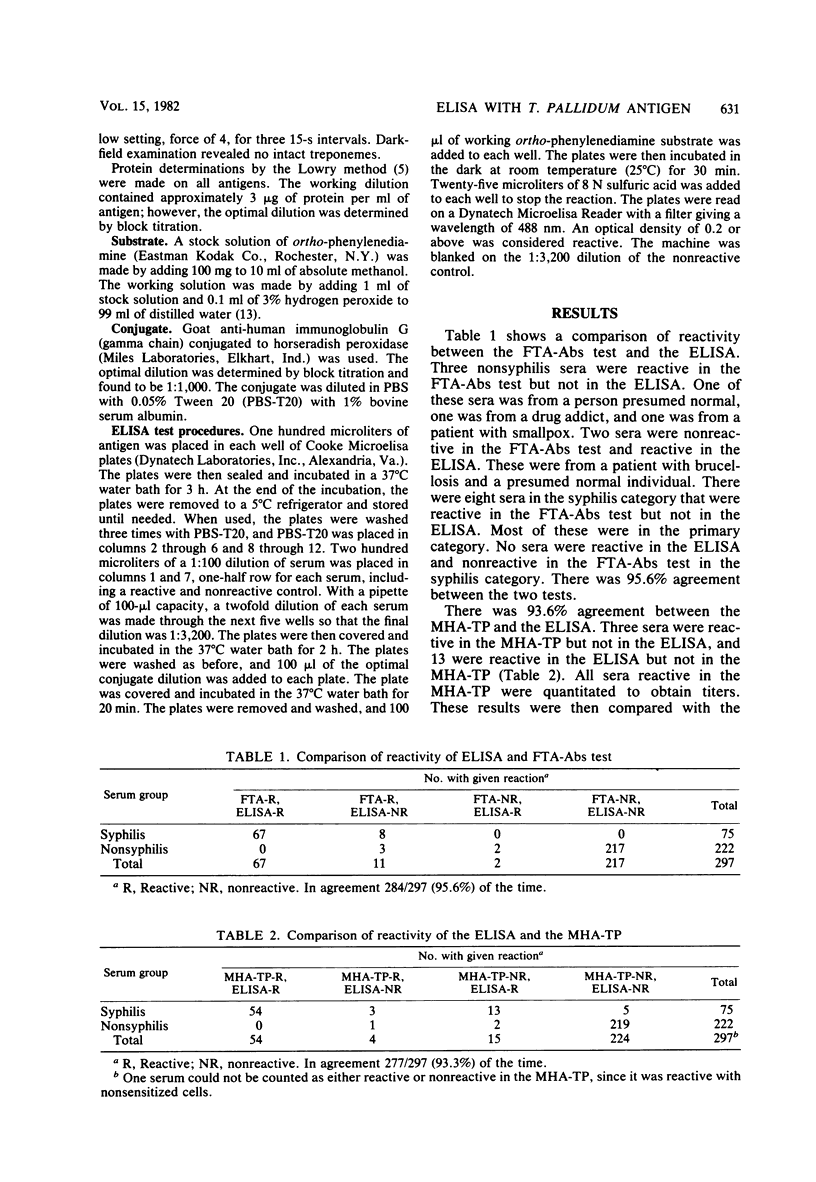
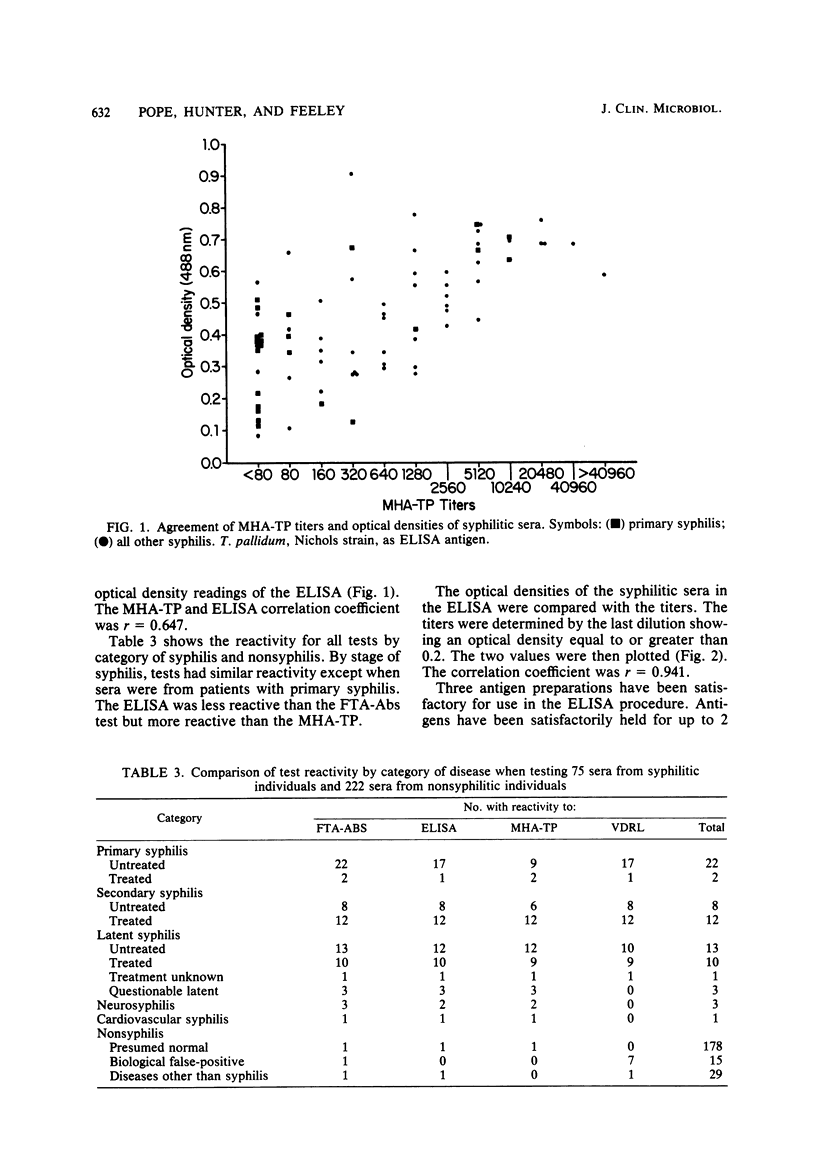
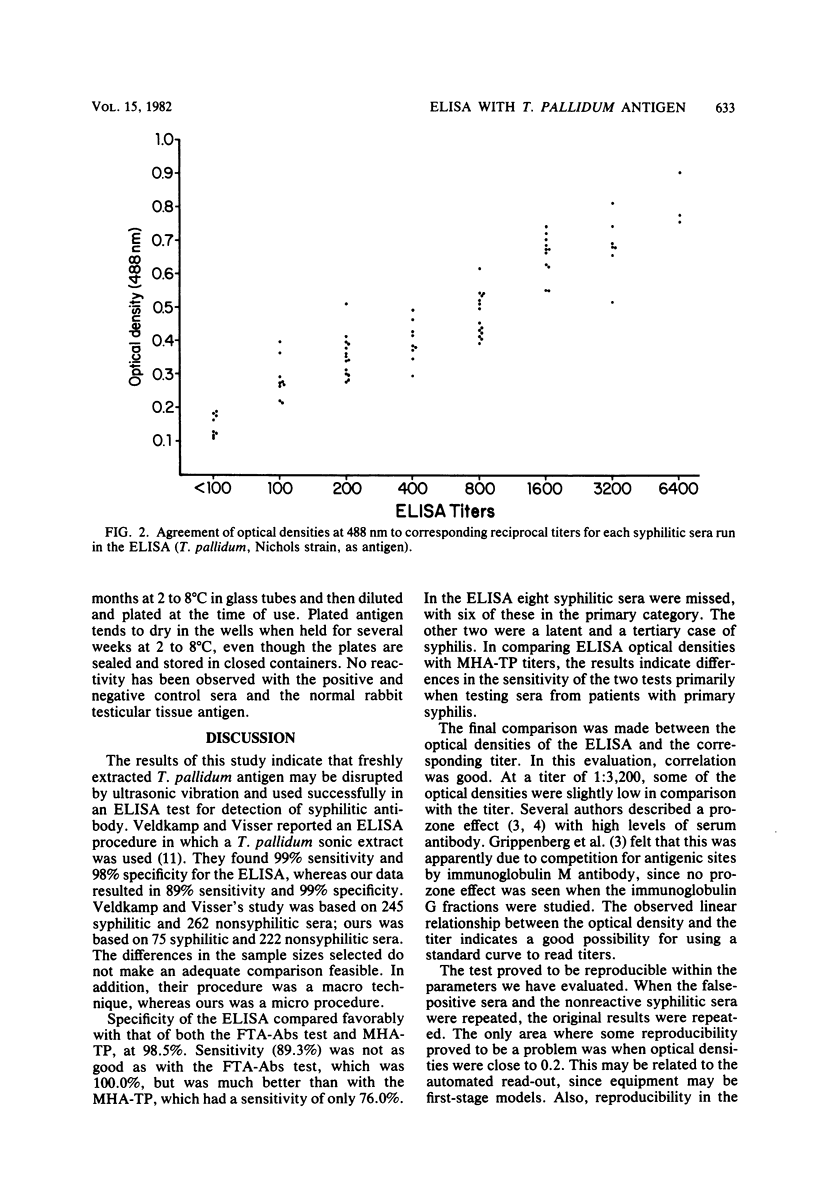
Whole-cell sonicates of Treponema pallidum, Nichols strain, were evaluated in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (Elisa) for syphilis, and results were read in a Dynatek Microelisa Reader. The antigen was evaluated with sera from patients with syphilis, persons presumed normal, and biological false-positives. Two hundred and ninety-seven sera were tested by the ELISA with T. pallidum antigens, the Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) slide test, the fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption (FTA-Abs) test, and the microhemagglutination assay for T. pallidum antibodies (MHA-TP). The results of all of the tests were compared. The ELISA, with 89.3% sensitivity, was less sensitive than the VDRL (93.3%) and FTA-Abs (100.0%) tests but more sensitive than the MHA-TP (76.0%). THe ELISA was considerably more sensitive in primary syphilis than the MHA-TP. Specificity was as follows: ELISA, 98.5%; FTA-Abs test, 97.8%; MHA-TP, 98.2%; and VDRL test, 92.7%. The ELISA has good potential as a confirmatory test in the serodiagnosis of syphilis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gripenberg M., Nissinen A., Väisänen E., Linder E. Demonstration of antibodies against Yersinia enterocolitica lipopolysaccharide in human sera by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Sep;10(3):279–284. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.3.279-284.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. N., Fulford K. M., Przybyszewski A., Pope V. Center for disease control diagnostic immunology proficiency testing program results for 1976. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Sep;6(3):224–232. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.3.224-232.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Weemen B. K., Schuurs A. H.W.M. Immunoassay using antigen-enzyme conjugates. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 24;15(3):232–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80319-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldkamp J., Visser A. M. Application of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in the serodiagnosis of syphilis. Br J Vener Dis. 1975 Aug;51(4):227–231. doi: 10.1136/sti.51.4.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Draper C., Bidwell D. E., Bartlett A. Microplate enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for chagas' disease. Lancet. 1975 Feb 22;1(7904):426–428. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91492-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walls K. W., Bullock S. L., English D. K. Use of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and its microadaptation for the serodiagnosis of toxoplasmosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Mar;5(3):273–277. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.3.273-277.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


