Abstract
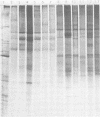
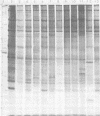
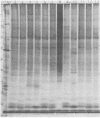
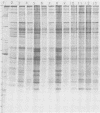
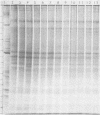
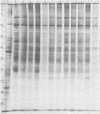
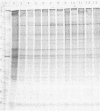
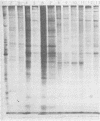
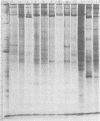
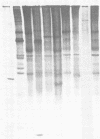
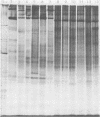
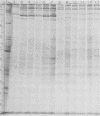
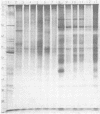
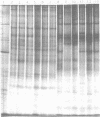
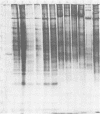
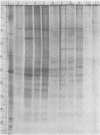
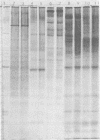
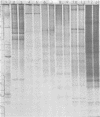
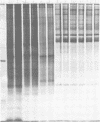
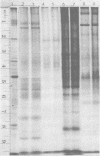
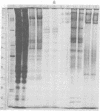
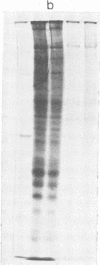
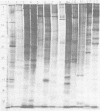
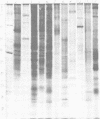
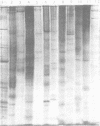
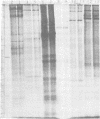
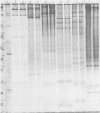
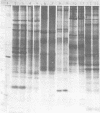
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic analysis of soluble cellular proteins (without sodium dodecyl sulfate) of 70 Clostridium species indicated that the procedure was readily applicable to the differentiation of species in the genus. The protein patterns correlated well with the available DNA homology data and with most accepted differential tests. Results indicated that several earlier names for species were synonyms of those of accepted species and that two accepted species may be synonymous.
Full text
PDF



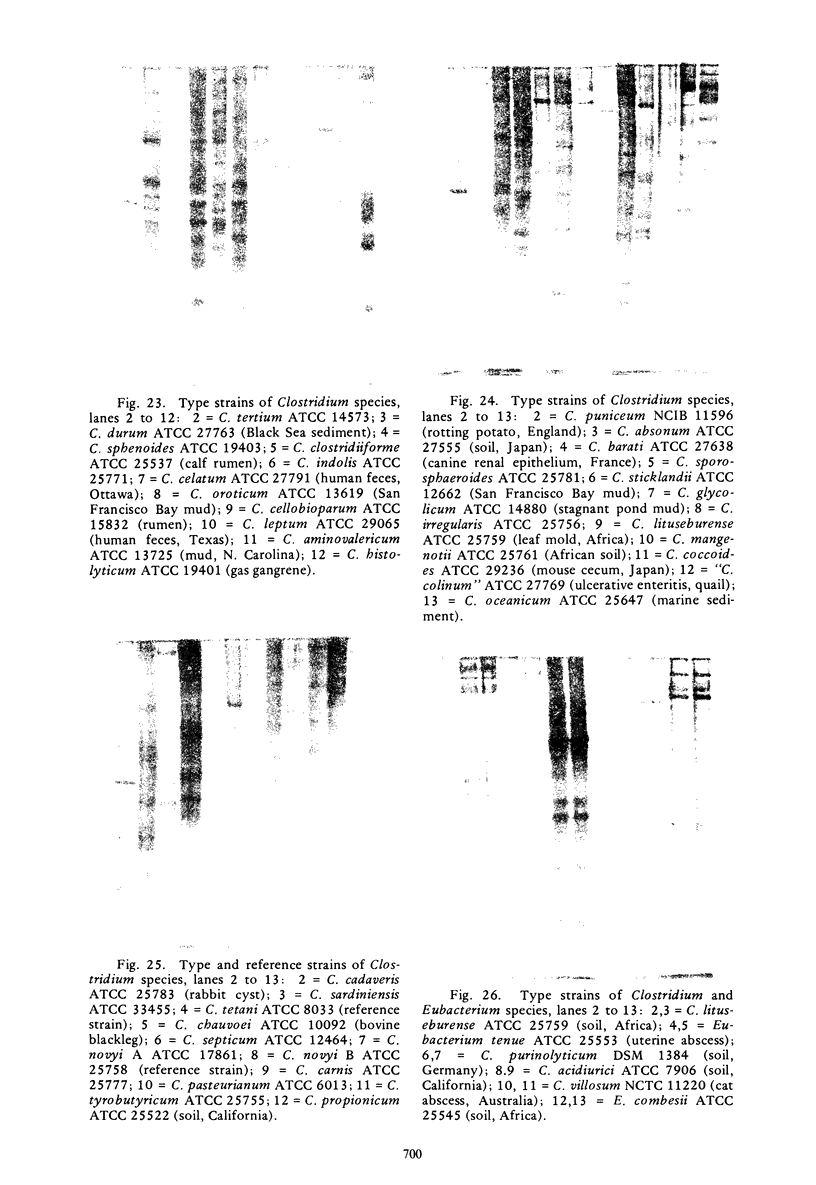


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker H. A., Beck J. V. Clostridium acidi-uridi and Clostridium cylindrosporum, Organisms Fermenting Uric Acid and Some Other Purines. J Bacteriol. 1942 Mar;43(3):291–304. doi: 10.1128/jb.43.3.291-304.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhoff G. A., Campbell S. G., Naylor H. B., Smith L. D. Etiology and pathogenesis of ulcerative enteritis ("quail disease"). Characterization of the causative anaerobe. Avian Dis. 1974 Apr-Jun;18(2):195–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calhoon D. A., Mayberry W. R., Slots J. Cellular fatty acid and soluble protein composition of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and related organisms. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Oct;14(4):376–382. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.4.376-382.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund M. W., Poysky F. T., Meyers J. A., Pelroy G. A. Interspecies conversion of Clostridium botulinum type C to Clostridium novyi type A by bacteriophage. Science. 1974 Nov 1;186(4162):456–458. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4162.456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farshy D. C., Moss C. W. Characterization of clostridia by gas chromatography differentiation of species by trimethylsilyl derivatives of whole-cell hydrolysates. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jul;20(1):78–84. doi: 10.1128/am.20.1.78-84.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis A. W., Wolff J. M. Grouping of lactic streptococci by gel electrophoresis of soluble cell extracts. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):391–398. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.391-398.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kersters K., De Ley J. Identification and grouping of bacteria by numerical analysis of their electrophoretic protein patterns. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Apr;87(2):333–342. doi: 10.1099/00221287-87-2-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Riemann H. Correlation of toxic and non-toxic strains of Clostridium botulinum by DNA composition and homology. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Jan;60(1):117–123. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-1-117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Hash D. E., Holdeman L. V., Cato E. P. Polyacrylamide slab gel electrophoresis of soluble proteins for studies of bacterial floras. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Apr;39(4):900–907. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.4.900-907.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Shimamura T., Hayashi H., Nishida S. Reinvestigation of the taxonomy of Clostridium bifermentans and Clostridium sordellii. J Med Microbiol. 1975 May;8(2):299–309. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-2-299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Shimamura T., Nishida S. Urease-negative strains of Clostridium sordellii. Can J Microbiol. 1976 May;22(5):673–676. doi: 10.1139/m76-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strom A., Dyer J. K., Marsh C., Tribble J. L. Identification and characterization of species of the family Bacteriodaceae by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Dent Res. 1976 Mar-Apr;55(2):252–256. doi: 10.1177/00220345760550021501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. I., Riemann H., Lee W. H. Thermal stability of the deoxyribonucleic acid hybrids between the proteolytic strains of Clostridium botulinum and Clostridium sporogenes. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Jan;18(1):97–99. doi: 10.1139/m72-016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]